High-throughput experiments might ensure a better diagnosis of hereditary diseases
2023-05-03
Researchers at the Department of Biology, University of Copenhagen, have now contributed to solving this problem for a specific gene called GCK. The study has just been published in Genome Biology.
Figure: GCK gene
Rasmus Hartmann-Petersen, Professor at the Department of Biology, explains:
- “The GCK gene, which codes for the enzyme glucokinase, regulates the secretion of insulin in the pancreas. GCK gene variants can therefore cause a form of hereditary diabetes. ...
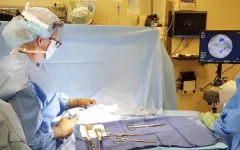
Study finds fluorescent guide can help detect tumor left behind after breast cancer surgery
2023-05-03
A new technique designed to allow surgeons to identify and remove residual tumor tissue during breast-conserving surgery showed promising results in a multi-center trial led by investigators from the Mass General Cancer Center, a member of Mass General Brigham. The clinical trial, which was funded in part by Lumicell, Inc., evaluated Lumicell’s investigational optical imaging agent pegulicianine in fluorescence-guided surgery (pFGS). In pFGS, pegulicianine is activated to a fluorescent form at sites of residual tumor, allowing surgeons to identify tumor remaining in the surgical site during breast cancer surgery. Investigators found that ...
Eric and Wendy Schmidt announce the 2023 Schmidt Science Fellows
2023-05-03
New York, NY, 3 May 2023 - Today, Eric and Wendy Schmidt announced the members of the 2023 cohort of Schmidt Science Fellows. The 32 exceptional early career scientists will receive support to develop research projects and the leadership skills necessary to harness interdisciplinary science to tackle some of the world’s most intractable problems.
Schmidt Science Fellows is the inaugural program of Schmidt Futures, the philanthropic initiative of Eric and Wendy Schmidt with a mission to find and connect talented people to solve our world’s hardest ...
How to protect consumers from deceptive comparison pricing
2023-05-03
Researchers from Duke University, University of Notre Dame, and Microsoft published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines using “true normal prices” during a sale as a way to reduce deceptive pricing tricks.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Competition and the Regulation of Fictitious Pricing” and is authored by Richard Staelin, Joel E. Urbany, and Donald Ngwe.
Does competition make firms more honest? Over 50 years ago, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) assumed the answer was yes when it stopped enforcing ...
Astronomers find distant gas clouds with leftovers of the first stars
2023-05-03
Using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), researchers have found for the first time the fingerprints left by the explosion of the first stars in the Universe. They detected three distant gas clouds whose chemical composition matches what we expect from the first stellar explosions. These findings bring us one step closer to understanding the nature of the first stars that formed after the Big Bang.
“For the first time ever, we were able to identify the chemical traces of the explosions of the first stars in very distant ...
Sleep phase can reduce anxiety in people with PTSD
2023-05-03
A new study shows that sleep spindles, brief bursts of brain activity occurring during one phase of sleep and captured by EEG, may regulate anxiety in people with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
The study shines a light on the role of spindles in alleviating anxiety in PTSD as well as confirms their established role in the transfer of new information to longer-term memory storage. The findings challenge recent work by other researchers that has indicated spindles may heighten intrusive and violent thoughts in people with PTSD.
The final draft of the preprint publishes in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging on ...
New investigators join Stowers Institute for Medical Research
2023-05-03
KANSAS CITY, MO—May 3, 2023—The Stowers Institute for Medical Research announced the hiring of three principal investigators to further expand its team of scientists who seek to answer life’s biggest mysteries through foundational research. Siva Sankari, Ph.D., from Massachusetts Institute for Technology, Neşet Özel, Ph.D., from New York University, and Ameya Mashruwala, Ph.D., from Princeton University, will join the Institute’s current team of 17 principal investigators and staff of 500. The addition of these scientists ...
The biophysicist names Padmini Rangamani as new Editor-in-Chief
2023-05-03
ROCKVILLE, MD – The Biophysical Society is pleased to announce that Padmini Rangamani of the University of California, San Diego has been named as the new Editor-in-Chief of the The Biophysicsist, the Society’s open access education journal. The journal was developed under the leadership and vision of founding and current Editor-in-Chief, Sam Safran of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel, to highlight and nurture biophysics education and its scholarship and development.
“Now, more than ever, is the time for an education journal such as The Biophysicist to steer the ...
Gender gap found in research grant award amounts, re-applications
2023-05-03
VANCOUVER, Wash. – Women researchers received substantially less funding in grant awards than men—an average of about $342,000 compared to men’s $659,000, according to a large meta-analysis of studies on the topic.
Women were also less likely to receive second grants to continue their research. In first-time grant applications, proportional numbers of women and men scientists were approved for funding, but for re-applications, 9% fewer women who applied were approved than their male ...
Steep 66% drop in party registration with Automatic Voter Registration
2023-05-03
In 2016, Oregon became the first state to adopt and implement an Automatic Voter Registration (AVR) system. Now, twenty-two states, plus Washington D.C., have such systems in place. Early research on the impacts of this innovation has shown an increase in the number of people registered, and greater diversity among the registrants.
Now, a researcher using Oregon voter data has identified an unintended consequence of Automatic Voter Registration: a steep drop in party registration. These results have been published in the journal Electoral Studies ...
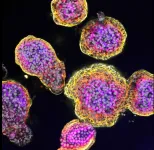
New insights into liver cancer using organoids
2023-05-03
PRESS RELEASE: PRINCESS MÁXIMA CENTER FOR PEDIATRIC ONCOLOGY
EMBARGO: WEDNESDAY 3 MAY 2023 AT 10:00AM BST (11:00AM CEST)
Scientists of the Princess Máxima Center for pediatric oncology and Hubrecht Institute in the Netherlands have revealed new scientific insights into the features of fibrolamellar carcinoma (FLC), a rare type of childhood liver cancer. Their findings, published today in Nature Communications, may help in developing new drug therapies in the future. Mini organs and the ‘molecular scissor’ system CRISPR-Cas9, allowed the researchers to better understand tumor biology and biological ...
Can low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets prolong life in middle-aged and older adults?
2023-05-03
Short-terms clinical trials have demonstrated the health benefits of low-carbohydrate diets (LCDs) and low-fat diets (LFDs) for weight loss and heart protection. Now a study published in the Journal of Internal Medicine looks at the effects of these diets on mortality in middle-aged and older adults.
In the study of 371,159 individuals aged 50 to 71 years, 165,698 deaths occurred over a median follow-up of 23.5 years.
A healthy LFD—characterized by low intake of saturated fat and high intakes of plant protein and high-quality carbohydrates—was related to fewer deaths from all causes, from cardiovascular diseases, and from cancers. In ...
Research reveals an increase in the range of invasive American mink in Europe
2023-05-03
The American mink Neogale vison is an invasive species in Europe introduced for fur farming in the 1920s and later established in the wild after escapes and illegal releases. As a feral species, it threatens native species and biodiversity, and poses a risk for boosting disease circulation, including mink-related strains of COVID-19. New research published in Mammal Review provides information on the presence of the species in Europe over the past 15 years.
The study, which was conducted by an international team of scientists, compiled a diverse set of data resources covering 32 nations. The work uncovers a progressive spread of the American mink in most ...
Can internet usage help protect against dementia?
2023-05-03
New research published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society found a link between regular use of the internet and a lower risk of dementia.
For the study, investigators followed 18,154 dementia-free adults aged 50 to 64.9 years for a median of 7.9 years and a maximum of 17.1 years. During follow-up, 4.68% of participants were diagnosed with dementia.
Regular internet usage was associated with approximately half the risk of dementia compared with non-regular usage. This link was found regardless of educational attainment, race-ethnicity, sex, and generation.
“Online engagement may help to develop and maintain cognitive reserve, which ...
How well do face masks worn by children block the release of exhaled particles?
2023-05-03
New research published in Pediatric Investigation provides evidence that face masks reduce the release of exhaled particles when used by school-aged children.
For the study, 23 healthy children were asked to perform activities that ranged in intensity (breathe quietly, speak, sing, cough, and sneeze) while wearing no mask, a cloth mask, or a surgical mask.
The production of exhaled particles that were 5 μm or smaller, which is the dominant mode of transmission of many respiratory viruses, increased with coughing and sneezing. Face masks—especially surgical face masks—effectively reduced the release of ...
How does glucocorticoid therapy affect the developing cardiovascular system during pregnancy?
2023-05-03
Glucocorticoid therapy is widely used during pregnancies at risk of premature delivery to promote fetal lung maturation. While it is an effective treatment, it can also trigger heart and blood vessel problems. New research published in The FASEB Journal uncovers the mechanisms behind the cardiovascular-related effects of the most commonly used glucocorticoids, Dexamethasone (Dex) and Betamethasone (Beta).
When investigators treated chicken embryos with these different glucocorticoids, they found that both caused growth restriction, with Beta being more severe. At the level ...
Cigarette butts leak deadly toxins into the environment
2023-05-03
Cigarette filters are the world’s most common form of litter. Researchers from the University of Gothenburg can now show that the filters leak thousands of toxins and plastic fibres that are toxic to aquatic larvae. The researchers are therefore calling for these filters to be completely banned.
On the footpath, at the bus stop, in the park and on the beach. You can hardly avoid seeing cigarette butts in the streetscape. And these butts aren’t just butt-ugly to behold – they’re also really bad for the environment. A research ...
Study questions long term beta blocker use to curb further heart attack risk
2023-05-03
The accepted clinical practice of using beta blockers over the long term to curb the risk of further heart attacks or death doesn’t seem to be warranted in patients who don’t have heart failure, suggests a large study published in the journal Heart.
The researchers found no difference in these risks between patients taking beta blockers more than a year after their heart attack and those who weren’t on these drugs.
Beta blockers are a class of drugs that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, ...
Fresh hope for Australians living with chronic back pain
2023-05-03
Long-term sufferers of chronic back pain experienced dramatic reductions in pain and related disability that remained at their one-year follow-up after taking part in a new treatment tested by Curtin-Macquarie-Monash University research.
Published today in the leading medical journal The Lancet, the research found large clinically significant improvements in the intensity of pain and pain-related disability among almost 500 people who had been seeking help for their pain for an average of four years before trialling the new treatment.
The treatment, which delivered a healthcare and work productivity saving of more than $5000 per person, took a whole-person approach ...
Dogs may be at risk from high levels of lead from shotgun pellets in raw pheasant dog food, study finds
2023-05-03
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL: 01:00 BST / LONDON TIME WEDNESDAY 3 MAY 2023
Paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1GNT9-oVOFTREzjGTSGMK7nIUvlYR61PE?usp=sharing
Dogs may be at risk from high levels of lead from shotgun pellets in raw pheasant dog food, study finds
Researchers tested samples of raw pheasant dog food and discovered that the majority contained high levels of lead that could put dogs’ health at risk if they eat it frequently. ...
Why mosses are vital for the health of our soil and Earth
2023-05-03
Some people see moss growing in their gardens as a problem, but what they may not realise is this ancient ancestor of all plants is bringing lots of benefits to our green spaces, such as protecting against erosion.
Now a massive global study led by UNSW Sydney has found mosses are not just good for the garden, but are just as vital for the health of the entire planet when they grow on topsoil. Not only do they lay the foundations for plants to flourish in ecosystems around the world, they may play an important role mitigating against climate change by capturing ...
Hongkui Zeng elected to the National Academy of Sciences
2023-05-03
Hongkui Zeng, Ph.D., Executive Vice President and Director of the Allen Institute for Brain Science, a division of the Allen Institute, was today elected to the prestigious National Academy of Sciences for her work to understand the cells and connections in the mammalian brain, and leading the development of tools and openly available data resources that accelerate brain research worldwide.
“I am deeply honored to become a member of the National Academy of Sciences, joining more than 3,000 brilliant scientists around the country and the world,” said Zeng. “I feel incredibly fortunate to work at the Allen Institute alongside ...
Dementia and self-harm: why it's crucial to support patients in first year after diagnosis
2023-05-03
People diagnosed with dementia are more likely to self-harm within the first six to 12 months after initial diagnosis, highlighting the need for health services to offer more follow-up support in this crucial period.
In what is believed to be the largest study of its kind, researchers with expertise in medicine, psychiatry and psychology at UNSW Sydney looked at NSW hospital data captured for more than 180,000 people admitted to hospital between 2001 and 2015.
The researchers analysed statistics relating to two cohorts of patients admitted to hospital: 154,811 people recorded as having dementia, and ...
Boxing can take the fight to Parkinson’s Disease
2023-05-03
When we think of boxing, it’s understandable many of us wouldn’t associate it with being ‘good’ for our brains.
However, new Edith Cowan University (ECU) research undertaken in partnership with The Perron Institute and boxer Rai Fazio has shown the sport — without an opponent — could be a valuable way for people suffering Parkinson’s Disease (PD) to improve their quality of life.
Also collaborating with Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital and the University of Western Australia, ECU researchers had 10 people with early-stage PD perform three one-hour boxing sessions per week, over 15 weeks.
Rather ...
HKU’s innovative research novelties excel at 48th International Exhibition of Inventions of Geneva
2023-05-03
The University of Hong Kong (HKU) triumphed at the 48th International Exhibition of Inventions of Geneva, winning a total of 19 awards, including two special grand prizes Invention & Innovation CAI Award (China Delegation), and Prize of the Delegation of Malaysia. The results were announced yesterday (April 28).
Research teams from Faculty of Architecture, Faculty of Engineering, Faculty of Science, LKS Faculty of Medicine, and two HKU Inno Laboratories, established under the Hong Kong Government's InnoHK programme, garnered two special grand prizes, one Gold Medal with the Congratulations of the Jury, six Gold Medals, six Silver Medals ...
[1] ... [1954]
[1955]
[1956]
[1957]
[1958]
[1959]
[1960]
[1961]
1962
[1963]
[1964]
[1965]
[1966]
[1967]
[1968]
[1969]
[1970]
... [8835]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.