Previous cancer linked to long term heightened risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-04-19
Cancer survivors may be at long term heightened risk of subsequent cardiovascular disease, irrespective of traditional underlying risk factors, suggest the findings of a large UK Biobank study, published online in the journal Heart.
Those with previous breast or blood cancers may be at greatest risk, the findings indicate.
Shared vascular risk factors as well as the treatments and biological processes related to the cancer itself are all associated with a heightened risk of incident cardiovascular ...
Menu calorie labels estimated to save U.S. billions on cancer care
2023-04-19
The 2018 implementation of menu calorie labels is already helping American adults make healthier choices at restaurants and fast-food operations, with analyses showing a net decrease in caloric intake by 20 to 60 calories per meal out. While this may sound minor, a modelling study led by Tufts University researchers, published April 18 in the journal BMJ Open, estimates this is enough to prevent at least 28,000 obesity-associated cancer cases and 16,700 cancer deaths over a lifetime, saving a combined $2.8 billion in net healthcare and societal costs.
Based on available national nutritional survey data gathered from U.S. adults aged 20+, in the years 2015-2016, and integrated ...
Menu calorie counts likely linked to lower obesity-related cancer rates and healthcare costs
2023-04-19
Specifying the number of calories for each item on restaurant menus is likely linked to lower rates of cancers associated with obesity and attendant healthcare costs in the US, suggests a modelling study, published in the open access journal BMJ Open.
Thousands of cancer cases and deaths could potentially be averted and billions of dollars saved as a result of the policy, the figures indicate, prompting the researchers to suggest that additional food industry product reformulation could substantially boost its impact.
One in three Americans is obese, and obesity is ...
Research shows why some children may be slower to learn words
2023-04-19
New research from University of East Anglia reveals why some children may be slower to learn words than others.
A study published today investigates where toddlers look when they learn new words. It finds that children with larger vocabularies looked quickly towards objects when learning new words.
Meanwhile, children who knew fewer words looked back and forth between objects and took more time.
The research team say that their findings could help identify children with delays in language development at an ...
Talking therapies linked with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-04-19
Sophia Antipolis, 19 April 2023: Effective management of depression through psychological therapy is associated with a lower likelihood of heart disease and stroke, according to research published today in European Heart Journal, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“Our study suggests that improving mental health could also help physical health, especially in those aged under 60,” said study author Ms. Céline El Baou, a PhD student at University ...
Talking therapies could reduce future risk of cardiovascular disease
2023-04-19
Using talking therapies to effectively treat depression in adults over the age of 45 may be linked with reduced rates of future cardiovascular disease, finds a new analysis of health data led by UCL researchers.
In the first-of-its-kind study, published in the European Health Journal, researchers assessed whether evidence-based psychological therapies, such as cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), used to treat depression could play a role in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease later in life.
Cardiovascular diseases, such as stroke and heart disease, are the leading cause of death worldwide. They represent 32% of ...
Investigating the growth of snow algal blooms on Mount Gassan, Japan
2023-04-19
Rising temperatures have led to the growth of algal blooms in water bodies, mountainous areas, and coastal regions as far as the Arctic. Recently, pigmented snow algae have been spotted on Japan’s Mount Gassan after the winter season. The presence of such algal blooms is concerning because they reduce the reflectivity of snow-covered surfaces, resulting in faster snow melting. Additionally, the algal blooms can have unforeseen impacts on the surrounding wildlife and vegetation. The growth and color of snow algae in mountainous areas appear to differ depending on the season, elevation, ...
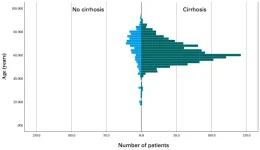
Vesicles produced by intestinal bacteria cause a malignant cycle in patients with cirrhosis
2023-04-19
Niigata, Japan - Researchers from Niigata University and Kyoto Prefectural University have revealed that small vesicles, around 100 nm in size, released by intestinal bacteria induce immune activation and progression of liver cirrhosis, as well as reduction of serum albumin level, subsequently leading to edema and ascites.
The global prevalence of cirrhosis is high and it can be fatal upon progressing to end-stages. The progression of cirrhosis results in various symptoms including jaundice, ascites, rupture of varices, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Often, even if root causes, such as hepatitis virus, alcohol, and lifestyle factors, ...
77% of Americans have used addictive behaviors or unhealthy coping mechanisms to manage their mental health, according to Myriad Genetics nationwide survey
2023-04-19
From restricted or binge eating to excessive gambling to extreme social media use, 77% of Americans surveyed say they have used at least one addictive behavior and/or unhealthy coping mechanism to manage their mental health issues, according to the GeneSight® Mental Health Monitor, a nationwide survey from Myriad Genetics, Inc. (NASDAQ: MYGN).
Nearly all Americans (94%) surveyed agree that substance and behavioral addictions often mask underlying mental health issues. Though they may view these behaviors as addictive or as unhealthy coping mechanisms (or both), many ...
New open access journal series offers a fast and supported author experience
2023-04-19
Researchers looking to share their work openly and at pace have an exciting new publishing option that delivers on reach and impact. Launched by Taylor & Francis, the Elevate Series of broad-scope open access journals offers a fast, streamlined experience and full support in navigating the publication process.
Authors will experience the editorial excellence and high ethical standards of Taylor & Francis journals, along with personalized support at every step, allowing them to efficiently publish their work and comply ...
Time of day and a patient’s sex may alter the effectiveness of blood pressure medication
2023-04-19
New research from a team based at the University of Waterloo suggests that the time of day and a patient's sex may alter the effectiveness of certain blood pressure medications.
Biological sex and the body's circadian clock are critical factors in managing blood pressure. The circadian clock is a natural, internal process that regulates things like the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. Among its many other functions, the circadian clock also regulates kidney function. The kidneys play ...
Young adults with cancer at greater risk for HPV-related cancers
2023-04-19
A team of researchers at Huntsman Cancer Institute and the University of Utah (the U) found that human papillomavirus-related cancer diagnoses are more common in adolescent and young adults (AYAs) who have previously had cancer. The team is led by Anne Kirchhoff, PhD, MPH, investigator in the Cancer Control and Population Sciences Research Program and associate professor of pediatrics at the U.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common infection spread through sexual contact. ...
Could this copycat black hole be a new type of star?
2023-04-18
It looks like a black hole and bends light like a black hole, but it could actually be a new type of star.
Though the mysterious object is a hypothetical mathematical construction, new simulations by Johns Hopkins researchers suggest there could be other celestial bodies in space hiding from even the best telescopes on Earth. The findings are set to publish in Physical Review D.
“We were very surprised,” said Pierre Heidmann, a Johns Hopkins University physicist who led the study. “The object looks identical to a black hole, but there’s light coming out from its ...
Exercise boosts brain health with chemical signals
2023-04-18
Physical activity is frequently cited as a means of improving physical and mental health. Researchers at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology have shown that it may also improve brain health more directly. They studied how the chemical signals released by exercising muscles promote neuronal development in the brain.
Their work appears in the journal Neuroscience.
When muscles contract during exercise, like a bicep working to lift a heavy weight, they release a variety of compounds into the bloodstream. These compounds can travel to different parts of the body, including the brain. The researchers were particularly interested in how exercise could ...
Who goes to the ICU and why?
2023-04-18
More is not always better when it comes to hospital care. The same interventions that could save one patient’s life could lead to no benefit, higher hospital bills and even injury for another.
A University of Michigan led study published in the journal Intensive Care Medicine interviewed almost 90 clinicians and hospital staff and performed onsite observations across eight unaffiliated hospitals in Michigan to understand why different hospitals used the intensive care unit more than others.
“You would ...
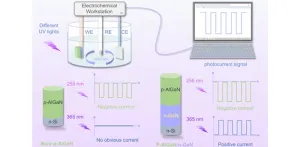
New self-powered ultraviolet photodetector
2023-04-18
Ultraviolet (UV) light detection can revolutionize industries such as civil engineering, military defense, aerospace exploration, and medical research. The future of electronics relies heavily on energy-efficient devices that can function independently, which makes the development of photoelectric UV detectors critical. These detectors come in two main types: photoconductive and photovoltaic, each with unique advantages and applications.
Photoconductive detectors rely on the changes in the conductivity ...
People with severe obesity and a genetic pathway variant have increased risk of hypertension, Mayo Clinic research finds
2023-04-18
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Obesity and its associated cardiometabolic issues are a major health concern in the U.S. and internationally. According to a study published in 2017, 12% of the world's adult population was affected by obesity in 2016, double the percentage from 30 years earlier.
With obesity comes an increasing risk of cardiovascular disease, including stroke, congestive heart failure and myocardial infarction. Fortunately, obesity is a multifactorial disease that results from an energy balance dysregulation and often is a modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease.
"Body ...
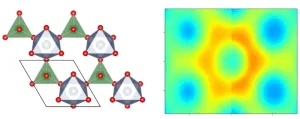
Physicists find unusual waves in nickel-based magnet
2023-04-18
HOUSTON – (April 18, 2023) – Perturbing electron spins in a magnet usually results in excitations called “spin waves” that ripple through the magnet like waves on a pond that’s been struck by a pebble. In a new study, Rice University physicists and their collaborators have discovered dramatically different excitations called “spin excitons” that can also “ripple” through a nickel-based magnet as a coherent wave.
In a study published in Nature Communications, ...
Sex after menopause doesn’t need to hurt
2023-04-18
Between 13% and 84% of postmenopausal women experience vaginal pain during sex
Causes of pain other than vaginal dryness are often undiagnosed and untreated
Pain during sex can harm relationships, self-esteem and contribute to depression, anxiety
Safe, effective therapies exist but condition is rarely evaluated or treated
CHICAGO --- Between 13% and 84% of postmenopausal women experience dyspareunia—vaginal pain during sex—but the condition is rarely evaluated or treated despite the availability of safe and effective therapies. With life expectancy increasing and the functional health of older adults improving, ...
Public lecture: My career in five equations, and the importance of mathematics education in the digital age
2023-04-18
Professor Stephen Garrett to discuss why the UK needs to up its game in maths education
He has a particular interest in the development of mathematical and computational solutions to real-world problems
Lecture will take place on Thursday 27 April at Aston University.
18 April 2023 | Birmingham, UK
The latest inaugural lecture at Aston University is to explore why the UK’s low level of mathematical skills don’t add up to a positive digital future.
Professor Stephen Garrett will discuss why school-level mathematics is so important in many areas of life and will discuss how ...
Mouse study hints at specific brain receptor behind PCOS symptoms
2023-04-18
Polycystic ovarian syndrome, or PCOS, can cause a range of symptoms, including disrupted menstrual cycles, abdominal obesity, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes. It’s also one of the biggest causes of infertility — in fact, many people don’t discover they have the condition until they try to become pregnant.
One of the hallmarks of PCOS are elevated levels of hormones produced by the ovaries called androgens. Androgens play important roles in puberty and reproduction in people with ovaries and people with testes.
Researchers are trying to understand why PCOS develops and how androgens lead to negative symptoms. A recent study led by Alexandra ...
Epic sepsis model’s ability to predict depends on hospital factors
2023-04-18
In the fight against sepsis, one of the leading causes of death in hospitalized patients, clinicians are increasingly reliant on prediction tools trained on massive amounts of data stored in electronic health records. One of the most popular tools comes from Epic Systems and is used in more than half of United States hospitals. However, research has shown that its performance varies depending on the hospital in which it’s being used.
In a recent research letter published in JAMA Internal Medicine, researchers from U-M, Oregon Health and Sciences University, and Washington University looked for a possible explanation for this variation. Using more than 800,000 ...
Could fixing a problem with the heart be good for your brain?
2023-04-18
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, TUESDAY, APRIL 18, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have an irregular heartbeat called atrial fibrillation that is treated with a procedure called catheter ablation may have a reduced risk of dementia compared to those who are treated with medication alone. The preliminary study released April 18, 2023, will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 75th Annual Meeting being held in person in Boston and live online from April 22-27, 2023.
Catheter ablation uses radiofrequency through a tube into the heart to destroy small areas of heart tissue that may be causing the abnormal heartbeat.
“Previous studies have ...
CA 19-9 and CEA in prognosis of duodenal adenocarcinoma: A retrospective study
2023-04-18
“To our knowledge, there are no studies evaluating the prognostic importance of CEA and Ca 19-9 in patients with DA [duodenal adenocarcinoma].”
BUFFALO, NY- April 18, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on April 15, 2023, entitled, “Importance of carbohydrate antigen (CA 19-9) and carcinoembrionic antigen (CEA) in the prognosis of patients with duodenal adenocarcinoma: a retrospective single-institution cohort study.”
Duodenal adenocarcinoma (DA) is a rare ...
UMD psychologist finds daily occurrences’ impact on suicide, self-harm ideation in LGBTQ+ teens
2023-04-18
Since the start of 2023, a record number of anti-LGBTQ+ bills have been introduced into state legislatures. According to University of Maryland Associate Professor Ethan Mereish, such current events add to the list of daily thoughts and experiences that lead LGBTQ+ teens to report having suicidal and non-suicidal self-harm thoughts.
Mereish recently led a first-of-its-kind study, published in the Journal of Psychopathology and Clinical Science, that asked 12-19 year-old LGBTQ+ teens to fill out a brief “daily dairy” survey for 28 days. The teens were asked to identify the unique kinds of stress they experience as a member of the LGBTQ+ community, ...
[1] ... [1947]
[1948]
[1949]
[1950]
[1951]
[1952]
[1953]
[1954]
1955
[1956]
[1957]
[1958]
[1959]
[1960]
[1961]
[1962]
[1963]
... [8797]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.