Increasing prosperity linked to unhealthy eating patterns in Kenyan youth
2023-05-09
Philadelphia, May 9, 2023 – The increase in obesity in lower-middle-income countries (LMIC) is largely thought to be affected by lifestyle transition away from traditional diets toward unhealthy Western dietary patterns that follow economic development. This study in the Journal of Nutrition Education and Behavior, published by Elsevier, collected data on eating and physical activity behaviors from families in two socioeconomically-different communities in Nairobi, Kenya. Researchers found that increasing prosperity is linked to unhealthy eating patterns in Kenyan preadolescents.
"Dietary ...
Systematic racism in healthcare boosted COVID-19 vaccine mistrust in Black communities: Study
2023-05-09
The University of Ottawa’s Interdisciplinary Centre for Black Health survey reveals scope of coronavirus vaccine hesitancy in Black communities in relation to healthcare.
The health care system must play a significant role in combatting COVID-19 mistrust among Black individuals in Canada according to a new University of Ottawa study that found distrust in the healthcare network was so profound that educated individuals were hesitant to receive the vaccine.
Professor Jude Mary Cénat, Associate Professor in the School of Psychology at the Faculty of Social Sciences, is the Chair of the Interdisciplinary Centre ...
Hey Siri, can you hear me? #ASA184
2023-05-09
CHICAGO, May 9, 2023 – Millions of people now regularly communicate with AI-based devices, such as smartphones, speakers, and cars. Studying these interactions can improve AI’s ability to understand human speech and determine how talking with technology impacts language.
In their talk, “Clear speech in the new digital era: Speaking and listening clearly to voice-AI systems,” Georgia Zellou and Michelle Cohn of the University of California, Davis will describe experiments to investigate how speech and comprehension change when humans communicate ...
Lack of belief in body’s ability to function through pain linked to daily pre-surgery prescribed opioid use among candidates for elective spine surgery
2023-05-09
According to a new Johns Hopkins Medicine study, low pain self-efficacy can predict daily pre-surgery prescribed opioid use among patients seeking elective spine surgery. The study defined pain self-efficacy as the “beliefs held by people with chronic pain that they can carry out certain activities, even when experiencing pain.” Previous studies showed that lower pain self-efficacy is associated with higher pain intensity and greater pain interference in day-to-day life. However, the Johns Hopkins research team believes its study is among the first to investigate ...
Reduced cancer mortality with daily vitamin D intake
2023-05-09
Vitamin D intake could reduce cancer mortality in the population by twelve percent - provided the vitamin is taken daily. This was the result of an evaluation of 14 studies of the highest quality conducted at the German Cancer Research Center with a total of almost 105,000 participants.
Vitamin D deficiency is widespread worldwide and is particularly common among cancer patients. Averaged over the year, the vitamin D blood levels of about 15 percent of German adults are below the threshold for a pronounced vitamin D deficiency*. In contrast, in a study of colorectal ...
Scientists develop AI tool to predict Parkinson’s disease onset
2023-05-09
Scientists from UNSW Sydney with collaborators at Boston University have developed a tool that shows early promise in detecting Parkinson’s disease years before the first symptoms start appearing.
In research published today in the journal ACS Central Science, the researchers described how they used neural networks to analyse biomarkers in patients’ bodily fluids.
The researchers from UNSW School of Chemistry examined blood samples taken from healthy individuals gathered by the Spanish European ...
SwRI selected for Phase A study to develop next-generation NOAA coronagraph
2023-05-09
SAN ANTONIO — May 9, 2023 —NASA has selected Southwest Research Institute for a Phase A study to develop SwRI’s Space Weather Solar Coronagraph (SwSCOR) on behalf of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA’s Space Weather Next Program is charged with providing critical data for its space weather prediction center. SwRI is one of five organizations developing a definition-phase study to produce the next-generation NOAA L1 Series COR instrument to detect and characterize Earth-directed coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
CMEs are huge bursts of coronal plasma threaded with intense magnetic fields ...
Long molecule of RNA essential to our GI tract’s ability to contract and move food along
2023-05-09
AUGUSTA, Ga. (May 9, 2023) – A long molecule of RNA found in abundance in the healthy smooth muscle cells that give our blood vessels strength and flexibility is also essential to the continuous contraction that moves food through our gastrointestinal tract.
Without CARMN, a long, noncoding RNA, which means it doesn’t produce proteins but does help regulate cell activity, the 30-foot-long GI tract doesn’t contract as it should.
That can result in a painful even lethal situation where partially undigested food gets ...
A CRISPR-edited calf shows virus resistance
2023-05-09
A gene-edited calf shows resistance to a common bovine virus. Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) causes gastrointestinal and respiratory symptoms as well as reproductive failure in cattle around the world. Vaccines against the virus exist but the virus evolves quickly and vaccines are not always fully protective. Aspen Workman and colleagues used the CRISPR/Cas9 system to swap out just six amino acids in the bovine CD46 receptor in one calf. The calf showed a dramatic reduction in susceptibility to the virus and ...
Potential found to counter depression by restoring key brain rhythm
2023-05-09
Led by researchers from NYU Grossman School of Medicine and University of Szeged in Hungary, a new study in mice and rats found that restoring certain signals in a brain region that processes smells countered depression.
Publishing in the journal Neuron online May 9, the study results revolve around nerve cells (neurons), which “fire” – or emit electrical signals – to transmit information. Researchers in recent years discovered that effective communication between brain regions ...
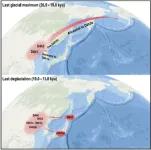
Evidence of Ice Age human migrations from China to the Americas and Japan
2023-05-09
Scientists have used mitochondrial DNA to trace a female lineage from northern coastal China to the Americas. By integrating contemporary and ancient mitochondrial DNA, the team found evidence of at least two migrations: one during the last ice age, and one during the subsequent melting period. Around the same time as the second migration, another branch of the same lineage migrated to Japan, which could explain Paleolithic archeological similarities between the Americas, China, and Japan. The study appears May 9 in the journal Cell Reports.
“The Asian ...
Trends in deaths from falls among adults age 65 or older
2023-05-09
About The Study: Between 1999 and 2020, deaths coded as being caused by falls among adults age 65 or older in the U.S. increased in number and rates for the overall population and for every population subgroup, although the magnitude of the increase varied. However, the relative ranking of the different groups has not changed over time.
Authors: Alexis R. Santos-Lozada, Ph.D., of Pennsylvania State University in University Park, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.3054)
Editor’s ...
Extracting the best flavor from coffee
2023-05-09
WASHINGTON, May 9, 2023 – Espresso coffee is brewed by first grinding roasted coffee beans into grains. Hot water then forces its way through a bed of coffee grains at high pressure, and the soluble content of the coffee grains dissolves into the water (extraction) to produce espresso.
In 2020, researchers found that more finely ground coffee beans brew a weaker espresso. This counterintuitive experimental result makes sense if, for some reason, regions exist within the coffee bed where less or even no coffee is extracted. This uneven extraction becomes more pronounced when coffee is ground more finely.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, ...
Preserving pine forests by understanding beetle flight
2023-05-09
WASHINGTON, May 9, 2023 – The mountain pine beetle is one of the main causes of tree mortality in the pine forests of North America. For example, the insect has killed thousands of acres of pine forest in British Columbia and Alberta, and as a result, the areas are more vulnerable to wildfire. Increased tree mortality has turned Canada’s forests into a large net source of atmospheric carbon dioxide – emitted from the burned or decaying wood of dead trees – rather than a sink.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Alberta studied the flight performance of the mountain pine beetle from a fluid mechanics and an entomological perspective. ...
US gun violence: half of people from Chicago witness a shooting by age 40, study suggests
2023-05-09
Study following Chicagoans over a 25-year period suggests over half of the city’s Black and Hispanic population, and a quarter of its White population, have seen a shooting by age 40.
Researchers followed over two thousand people, with 50% of all the study’s participants witnessing a shooting.
Average age when first witnessing a shooting was just 14 years old.
Women only slightly less likely than men to witness shootings, despite men being far more likely to get shot.
Such levels of violence exposure may cause chronic stress and knock-on health implications for populations in Chicago and elsewhere.
A ...
Assessment of medical cannabis and health-related quality of life
2023-05-09
About The Study: In this study, patients using medical cannabis reported improvements in health-related quality of life, which were mostly sustained over time. Adverse events were rarely serious but common, highlighting the need for caution with prescribing medical cannabis.
Authors: Thomas R. Arkell, Ph.D., of the Swinburne University of Technology in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
Making vaccines longer lasting
2023-05-09
The SARS-Cov-2 pandemic illustrates how variable vaccines can be in their length of efficacy, with regular boosters needed to keep people protected. In comparison, the immunity generated by a single vaccination against the measles virus can last decades.
It has always remained a scientific mystery as to why only some vaccines lead to life-long protection. Now a paper published in the journal, Immunity, led by Prof. David Tarlinton and Dr Marcus Robinson, both from Monash University’s Central Clinical School in Melbourne, Australia, has found that the clue likely lies in the body producing a unique subtype of an immune cell in response to some ...
Long-term study pinpoints who has been shot and witnessed shootings by race, sex, and birth year
2023-05-09
Exposure to gun violence is one of the great traumas of American life, but its harms are not equally distributed. In a first-of-its-kind study published Tuesday in JAMA Network Open, a Harvard sociology professor and his colleagues set out to examine exposure to shootings by race, sex, and birth year in a long-term study that followed respondents from childhood up to age 40.
“The idea here is to take a life-course perspective,” said Robert J. Sampson, the Woodford L. and Ann A. Flowers University Professor. ...
Not all statins are created equal
2023-05-09
We’ve all recently gotten a crash-course in drug repurposing, thanks to near-daily news reports about efforts to identify existing medicines that could help treat COVID-19 in the early phase of the pandemic. A team of scientists at the Wyss Institute at Harvard University jumped into the fray in the spring of 2020, applying novel computational drug repurposing approaches to confront the COVID-19 challenge. This early work led to the surprising prediction that a some, but not all, types of statins (drugs that are widely prescribed to lower cholesterol) might protect patients against SARS-CoV-2 infection. In the flurry of clinical studies being published by other scientists studying ...
Motion capture and 3D scans bring history to life for new Dambusters docudrama
2023-05-09
A new docudrama featuring the attack on the Sorpe Dam, using motion capture technology and 3D scans to create life-like digital representations of RAF 617 Squadron aircrew, is being premiered in Bristol on 13 May 2023 to coincide with the 80th anniversary of the Dambusters raid.
Bristol-based film maker Andrew Panton worked with University of Bath researchers at CAMERA, using the latest digital technology to recreate specific scenes for a film featuring the attack on the Sorpe Dam.
Andrew started working on the documentary in 2017 with the last surviving Dambuster George ...
Exploring the underground connections between trees
2023-05-09
Fungal networks interconnecting trees in a forest is a key factor that determines the nature of forests and their response to climate change. These networks have also been viewed as a means for trees to help their offspring and other tree-friends, according to the increasingly popular “mother-tree hypothesis”. An international group of researchers re-examined the evidence for and against this hypothesis in a new study.
Trees in a forest are interconnected through thread-like structures of symbiotic fungi, called hyphae, which together form an underground network called a mycorrhizal network. While it is well known that ...
New research sheds light on how human vision perceives scale
2023-05-09
Researchers from Aston University and the University of York have discovered new insights into how the human brain makes perceptual judgements of the external world.
The study, published on 8 May in the journal PLOS ONE, explored the computational mechanisms used by the human brain to perceive the size of objects in the world around us.
The research, led by Professor Tim Meese, in the School of Optometry at Aston University and Dr Daniel Baker in the Department of Psychology at University of York, tells us more about how our visual system can exploit ‘defocus blur’ to infer perceptual scale, but that it does ...
Chinese Medical Journal article reviews role of gene involved in brain functions and disorders
2023-05-09
Leucine-rich repeats containing 4 (LRRC4)—a gene abundantly found in the brain and located on human chromosome 7q31–32—plays a pivotal role in memory formation, autism, spinal cord injury, as well as in determining the malignant potential, development, and progression of glioblastoma (GB), an aggressive cancer involving the brain and/or spinal cord. In a review article published (in volume 136 issue 1 on 5 January 2023, and online on 10 February 2023) in the Chinese Medical Journal, researchers shed light on the ...
EuroPCR 2023 – The interventional cardiovascular community is gathering in Paris to learn, share, and shape the future of patient care worldwide
2023-05-09
EuroPCR, the annual world-leading Course in interventional cardiovascular medicine, has been taking place for over 30 years. It is tailored for all those dedicated to the sharing of knowledge and skills, and improvement of patient care worldwide: interventional cardiologists, cardiac surgeons, imaging specialists, radiologists, nurses, allied professionals and other practitioners, as well as researchers, innovators and industry representatives. The 4-day meeting addresses interventions for coronary and peripheral vessels, for the structural heart including valves, for hypertension, heart failure and stroke, while keeping the community up ...
Spanish courts hand down milder sentences for rapes if they are committed by the victim's partner or ex-partner
2023-05-09
Just four years ago, the Spanish Supreme Court pointed out in a ruling that there is no such thing as a 'conjugal debt'. In other words, a woman is not obliged to satisfy her husband's sexual needs. It may come as a surprise that this point still needs to be made, but the statistics speak for themselves. According to a national survey carried out in 2019, 7.5% of Spanish women over 16 years old have been raped by their partners or ex-partners.
These rapes are usually subject to less attention, and they tend to be "perceived as something less serious". So says Josep Maria Tamarit Sumalla, a full ...
[1] ... [1942]
[1943]
[1944]
[1945]
[1946]
[1947]
[1948]
[1949]
1950
[1951]
[1952]
[1953]
[1954]
[1955]
[1956]
[1957]
[1958]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.