New paper advances understanding of geographic health disparities
2023-04-21
By looking at where people were born instead of where they ultimately move to and die, geographic disparities in mortality look different than previously assumed, according to a new study published on April 1, 2023, in the journal Demography.
interstate migration may mitigate regional inequalities in mortality according to “Understanding Geographic Disparities in Mortality,” a paper led by Jason Fletcher, professor in the La Follette School of Public Affairs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and director of the Center for Demography of Health and Aging with an appointment in Population Health Sciences.
“At a time when nearly ...
Newly funded Morris Animal Foundation study assesses CBD use for postsurgical pain in dogs
2023-04-21
DENVER/April 21, 2023 – A new study is testing whether the addition of CBD can improve pain management in dogs following orthopedic surgery. The study, funded by Morris Animal Foundation, will be conducted by a veterinary research team at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada.
CBD use in pets has gained in popularity in the last decade, but there are few controlled studies closely examining its efficacy as a pain management tool. This study hopes to help partially close this knowledge gap.
The research team, led by Dr. Alan Chicoine, Assistant Professor, Department ...
Endocrine Society endorses bipartisan bill to address insulin affordability
2023-04-21
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society today endorsed the Improving Needed Safeguards for Users of Lifesaving Insulin Now (INSULIN) Act of 2023, a bipartisan insulin affordability bill introduced by Sens. Jeanne Shaheen (D-NH) and Susan Collins (R-ME). This legislation would cap out-of-pocket insulin costs for those with private insurance, ensure patients can share in insulin rebates and discounts, and promote competition in the insulin market.
These measures would protect access to life-saving insulin for more than 7 million people nationwide who rely on the medication to manage their diabetes. According to the U.S. Center for Disease Control ...
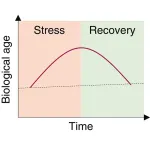
Biological age is increased by stress and restored upon recovery
2023-04-21
The biological age of humans and mice undergoes a rapid increase in response to diverse forms of stress, which is reversed following recovery from stress, according to a study publishing on April 21 in the journal Cell Metabolism. These changes occur over relatively short time periods of days or months, according to multiple independent epigenetic aging clocks.
“This finding of fluid, fluctuating, malleable age challenges the longstanding conception of a unidirectional upward trajectory of biological age over the life course,” says co-senior study author James White of Duke University School of Medicine. “Previous reports ...
Most people feel “psychologically close” to climate change
2023-04-21
When spurring action against climate change, NGOs and governmental agencies frequently operate on the assumption that people are unmotivated to act because they view climate change as a problem that affects distant regions far in the future. While this concept, known as psychological distance, seems intuitive, researchers report in the journal One Earth on April 21 that most people see climate change as an important and timely issue even if its impacts are not immediately noticeable.
“There is no consistent evidence ...
The Mathematics of Cell Boundary 'Ruggedness'
2023-04-21
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers have uncovered both the mathematical and biological mechanism behind the rugged structures at cell boundaries found in tissues such as the kidneys and nasal glands. The team hopes that their new insights can help develop new ways of treating associated pathologies and build better biological models for future study.
Our cells come in all sorts of shapes and sizes. From the neurons that extend across the central nervous system, to the spherical white blood cells that protect us from infection, a cell's form and ...
Effect of COVID-19 pandemic on food insecurity and inability to pay rent hit immigrant families hardest, Drexel study finds
2023-04-21
Under embargo until April 21, 2023
Although families with immigrant mothers experienced higher rates of food insecurity and inability to pay rent during the pandemic than other groups, they reported less participation in economic impact payments (EIP) in the form of stimulus checks and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) – two programs designed to provide stopgap financial support, according to a new study in JAMA Health Forum from researchers at the Dornsife School of Public Health and Children’s HealthWatch.
The team surveyed 1,396 caregivers in Boston, ...
Firearms injure or kill up to a quarter of juvenile justice youth after detention
2023-04-21
CHICAGO – A new study by Northwestern University found that among youth who had entered juvenile detention, one-quarter of Black and Hispanic males were later injured or killed by firearms within 16 years.
While the nation’s youth and young adults are disproportionately affected by the daily occurrence of 100 firearm deaths and 234 non-fatal firearm injuries, youth who have been previously involved with the juvenile justice system had up to 23 times the rate of firearm mortality than the general population.
The study is the first to focus on the incidence rate of firearm injuries and death within the juvenile justice population.
“Who ...
Neighborhood disadvantage and breast cancer–specific survival
2023-04-21
About The Study: In this study of 5,000 patients with breast cancer, a shorter breast cancer–specific survival in women from disadvantaged neighborhoods compared with advantaged neighborhoods was identified, even after controlling for individual-level sociodemographic, comorbidity, breast cancer risk factor, access to care, tumor, and National Comprehensive Cancer Network guideline-concordant treatment characteristics. The findings suggest potential unaccounted mechanisms, including unmeasured social determinants of health and access to care measures.
Authors: Neha Goel, M.D., of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, is ...
Firearm injury and mortality in high-risk youths and young adults 25 years after detention
2023-04-21
About The Study: This 25-year longitudinal cohort study (n = 1,829) found that youths involved with the juvenile justice system had up to 23 times the rate of firearm mortality as the general population; rates varied by sex, race and ethnicity, and age. Sixteen years after detention, more than one-quarter of Black and Hispanic males had been injured or killed by firearms.
Authors: Linda A. Teplin, Ph.D., of the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine in Chicago, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Association of hardship among families with young children with federal relief program participation
2023-04-21
About The Study: The results of this study suggest that the COVID-19 crisis exacerbated pre-existing inequities in food insecurity and difficulty paying rent according to race and ethnicity and maternal nativity and that equity-focused policy changes are needed to ensure that all children and their families in the U.S. can afford basic needs for optimal health.
Authors: Stephanie Ettinger de Cuba, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Boston University School of Public Health, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Social media data provides first glimpse at increased popularity of air conditioning worldwide
2023-04-21
With temperatures rising worldwide, more and more people globally consider air-conditioning an essential element of living with climate change. However, air-conditioning units are also rather power-hungry and are likely to increase energy consumption in areas where they are used often. To limit the impact of air-conditioners on our energy grids and our climate, we need data to better understand where they're sold globally. That's quite a struggle in regions where that data is not available. However, through social media advertising ...
Study shows most children recover from Lyme disease within six months of treatment
2023-04-21
WHAT:
A majority of parents of children diagnosed with Lyme disease reported that their kids recovered within six months of completing antibiotic treatment, according to a new joint study from Children’s National Research Institute and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, published in Pediatric Research. The findings, based on Lyme disease treatment outcome data from 102 children in the United States, also revealed that a notably small percentage of children took longer than six months to recover ...
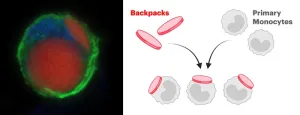
A backpack full of multiple sclerosis therapy
2023-04-21
A backpack full of multiple sclerosis therapy
A cell therapy using myeloid cells bound to drug delivery microparticles reduces disease burden in a preclinical multiple sclerosis model.
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a devastating autoimmune disease that destroys the protective myelin covering around nerves, disrupting communication between the brain and body, and causing patients’ ability to move and function to progressively decline. The MS atlas reported in 2020 that someone is diagnosed with MS every five minutes around the world, adding ...
USTC realizes light-driven programmable colloidal self-assembly
2023-04-21
Prof. PENG Chenhui's team from the School of Physics, University of Science and Technology of China (USTC), realized the collective transfer and reconfigurable self-assembly of colloidal particles by combining the light-driven molecular motors with liquid crystal (LC) molecules in the nematic phase whose orientations are programmed with topological patterns and disclination networks. The work was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America on April 11th. Through light irradiation, the cooperative reorganizations of nanomotors induce collective dynamics of the disclination networks. The morphology ...
Tiny plastic particles also find their way into the brain
2023-04-21
The study was carried out in an animal model with oral administration of MNPs, in this case polystyrene, a widely-used plastic which is also found in food packaging. Led by Lukas Kenner (Department of Pathology at MedUni Vienna and Department of Laboratory Animal Pathology at Vetmeduni) and Oldamur Hollóczki (Department of Physical Chemistry, University of Debrecen, Hungary) the research team was able to determine that tiny polystyrene particles could be detected in the brain just two hours after ingestion. The mechanism that enabled them to breach the blood-brain barrier ...
On-demand preparation of organosilicon reagents
2023-04-21
National University of Singapore (NUS) scientists have demonstrated that stepwise customised functionalisation of multihydrosilanes to access fully substituted silicon compounds can be realised using neutral eosin Y, an inexpensive dye molecule.
The development of a unified catalytic platform for stepwise and programmable functionalisation of multihydrosilanes is highly challenging. However, having this platform will facilitate the rational design of organosilanes with predictable functions, in which bespoke silane molecules are required. Three specific requirements ...
Green living environment in early childhood does not protect against eczema
2023-04-21
According to a new Finnish study, greenness around the home in early childhood does not seem to protect children from atopic eczema. Instead, the proximity of coniferous, mixed forests and agricultural areas was associated with elevated risk of eczema. The effect was seen especially in children who were born in the spring.
“General greenness around the home did not protect children against eczema, which was contrary to our expectations and to the hypothesised allergy protective effect of nature contacts. Eczema is, however, only one of the allergic diseases in children, albeit generally the first to emerge,” says MD Minna Lukkarinen, a paediatric specialist from the ...
Finnish population-based study: Vulnerable groups were the least likely to uptake COVID-19 vaccination
2023-04-21
A large-scale registry study in Finland has identified several factors associated with uptake of the first dose of COVID-19 vaccination. In particular, persons with low or no labor income and persons with mental health or substance abuse issues were less likely to vaccinate.
The study, carried out in collaboration between the University of Helsinki and the Finnish Institute of Health and Welfare, tested the association of nearly 3000 health, demographic and socio-economic variables with the uptake of the first COVID-19 vaccination dose across the entire Finnish population.
This work, just published in the Nature Human Behavior, is the largest study ...
Best practices in new product development: what separates the Best from the Rest?
2023-04-21
No single one practice is sufficient for greater innovation performance, say the researchers, overviewing the results of the most recent PDMA's 2021 global survey. The Best companies, according to the results, are better at employing multiple types of innovation, but the spend more time on radical innovation, are oriented towards risk-taking, and employ long-term strategies. The results were drawn from responses from 651 companies in 37 countries, the most extensive PDMA survey so far.
“I believe, we should fundamentally look ...
New study: No evidence that shielding reduced COVID-19 infections in Wales
2023-04-21
A research team from Swansea University have been examining data from the year after the policy was introduced in March 2020, concluding that a “lack of clear impact on infection rates raises questions about the success of shielding.”
Shielding was introduced to protect those thought to be at highest risk of serious harm should they catch COVID-19, for example because of preconditions such as cancer or medications that they were taking. Key to protecting vulnerable people was to reduce their risk of contracting COVID-19.
The ...
The climate and biodiversity crises are not two separate things
2023-04-21
An unprecedented and continuing loss of biodiversity has been sparked by anthropogenic climate change together with the intensive use and destruction of natural ecosystems. However, since the public often views the climate crisis and the biodiversity crisis as two separate catastrophes, an international team of researchers including paleontologist Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Kiessling from Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU) calls for adopting a new perspective: In their review study just released in the journal “Science”, they recommend protecting and restoring at least 30 percent of all ...
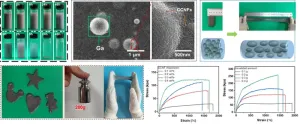
Highly sensitive and self-healing conductive hydrogels fabricated from cationic cellulose nanofiber-dispersed liquid metal for strain sensors
2023-04-21
This study is led by Dr. Wenxia Liu (State Key Laboratory of Biobased Materials and Green Papermaking, Qilu University of Technology, Shandong Academy of Science). To uniformly disperse LM into hydrogel, she conceived and designed using CCNFs rich in quaternary ammonium groups to encapsulate LM droplets through an approach of Pickering emulsion. “The strong electrostatic attraction and ion-dipole interaction between the quaternary ammonium groups of CCNFs and the hydroxyl groups on LM droplet surfaces were expected to prevent the LM droplets from aggregation and coalescence. The incorporation of CCNFs into hydrogel with the LM droplets was also expected to improve the mechanical ...
International team of physicists explore microscopic filament behavior
2023-04-21
Recently-published research from an international team of physicists reveals how the three-dimensional shape of rigid microscopic filaments determines their dynamics when suspended in water, and how control of that shape can be used to engineer solid-like behavior even when the suspension is more than 99% water.
The paper, “Bonded straight and helical flagellar filaments form ultra-low-density glasses,” was co-authored by Georgetown physics professors Peter Olmsted and Jeffrey Urbach and graduate student Matthew ...
Arctic ice algae heavily contaminated with microplastics
2023-04-21
The alga Melosira arctica, which grows under Arctic sea ice, contains ten times as many microplastic particles as the surrounding seawater. This concentration at the base of the food web poses a threat to creatures that feed on the algae at the sea surface. Clumps of dead algae also transport the plastic with its pollutants particularly quickly into the deep sea - and can thus explain the high microplastic concentrations in the sediment there. Researchers led by the Alfred Wegener Institute have now reported this in the journal Environmental Science and Technology.
It is a food lift for bottom-dwelling animals in the deep sea: the alga Melosira arctica grows ...
[1] ... [1965]
[1966]
[1967]
[1968]
[1969]
[1970]
[1971]
[1972]
1973
[1974]
[1975]
[1976]
[1977]
[1978]
[1979]
[1980]
[1981]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.