Comparison between ChatGPT and Google search as sources of postoperative patient instructions
2023-04-27
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that ChatGPT provides postoperative instructions that are helpful for patients with a fifth-grade reading level or different health literacy levels. However, ChatGPT generated instructions scored lower in understandability, actionability, and procedure-specific content than Google Search– and institution-specific instructions.
Authors: Noel Ayoub, M.D., M.B.A., of the Stanford University School of Medicine in Stanford, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2023.0704)
Editor’s ...
Arthropods in high-diversity forests contribute to improved productivity
2023-04-27
An international team of researchers led by Prof. MA Keping from the Institute of Botany of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IBCAS) has shown that forests with higher tree species richness tend to have greater arthropod diversity.
The researchers showed that higher tree diversity promotes productivity through the suppression of herbivores by enemy arthropods.
These findings, published recently in Nature Ecology & Evolution, underscore the importance of arthropod diversity as a mediator of the effects of tree diversity ...
Molecular autopsy sheds light on cause of sudden death of a child with COVID-19
2023-04-27
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) utilize an advanced DNA sequencing technique to reveal the factors that contributed to the death of a 5-year-old child with COVID-19
Tokyo, Japan – Sudden, unexplained child mortality is a tragedy; determining the cause of death is important for improving healthcare and providing loved ones with closure. Now, researchers from Japan have reported the use of an advanced DNA sequencing technique, whole-exome sequencing (WES), to determine why a young child died after a relatively mild infection.
In a study published ...
Bioinformatics specialists in Saarbrücken explore the molecular mechanisms of ageing
2023-04-27
A team led by bioinformatics experts Andreas Keller and Fabian Kern from Saarland University together with researchers at Stanford University have gained new insights into manifestations of ageing at the molecular level. They found that the process of reading genetic information does not run as smoothly in older individuals as it does in younger ones. These changes in the transcription process are due to particular RNA molecules that influence the activity of individual genes and thus determine which proteins the body produces – physiological ...
University of Cincinnati research examines the role of genetics in opioid use disorder
2023-04-27
New research out of the University of Cincinnati examines the association between genetics and the presence of opioid use disorder (OUD). The study identified six single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) or genetic variants that are linked to OUD.
The study was published in the journal Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics.
“We are trying to identify some of the genetic variants that might play into OUD,” says Caroline Freiermuth, MD, associate professor in the Department of Emergency ...
Light-based computing scheme reduces power needed to mine cryptocurrencies
2023-04-27
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new light-based computing scheme that uses a photonic integrated circuit to reduce the energy necessary for cryptocurrency and blockchain applications. Mining cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin—a process of verifying transactions and adding new cryptocurrency to the blockchain—consumes up to 1% of the world’s energy. This energy expenditure is expected to grow as cryptocurrency and blockchain applications become increasingly mainstream.
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies created using encryption algorithms. These alternative currencies require ...
CityU establishes the first UNESCO Regional Training and Research Centre on coastal contaminant monitoring in Hong Kong for the Western Pacific region
2023-04-27
The State Key Laboratory of Marine Pollution (SKLMP) of City University of Hong Kong (CityU) received approval from the UNESCO Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) Sub-Commission for the Western Pacific (WESTPAC) to establish the first UNESCO regional training and research Centre (the Coastal-COMMIT Centre, also known as the “Centre”) on coastal contaminant monitoring and marine innovative technologies in Hong Kong for the Western Pacific region.
The Centre aims to strengthen the monitoring capacity for marine pollution in the Western Pacific region, promote the development of marine innovation ...
James Fast selected as Jefferson Lab EIC project manager
2023-04-27
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility and DOE’s Brookhaven National Laboratory partnered early on to take on the design and construction of the Electron-Ion Collider. To keep the project moving forward, Jefferson Lab tapped members of its experienced leadership team to ensure project success. Now, Jefferson Lab is proud to announce it has appointed a dedicated EIC project manager: James Fast will lead the lab’s EIC project team and honor the lab’s project commitments going forward.
“The EIC project is central to the future of ...
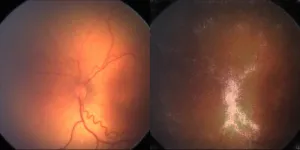
AI breakthrough in detecting leading cause of childhood blindness
2023-04-27
The team developed a deep learning AI model that can identify which at-risk infants have ROP that may lead to blindness if left untreated, and they hope their technique could improve access to screening in the many areas with limited neonatal services and few trained ophthalmologists.
The study, by an international team of scientists and clinicians in the UK, Brazil, Egypt and the US, supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at Moorfields Eye Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and UCL Institute of Ophthalmology, is published in The Lancet Digital Health.
Lead author Dr Konstantinos Balaskas ...
Why people include themselves in photos
2023-04-27
Embargoed until 9 AM ET on Thursday, April 27, 2023
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new study may help explain why people choose to include themselves in some photos – and it is not vanity.
Researchers found that first-person photos (capturing the scene as it looks from one’s own eyes) best represent the physical experience of an event for people.
But third-person photos like selfies (documenting a moment with themselves in it) better depict the deeper meaning of the event in their lives.
“We found that people have a natural intuition about which perspective to take to capture what they want out ...
Selfies and other third-person photos help us capture the meaning of moments
2023-04-27
Imagine you are eating your dream meal and want to commemorate the moment: Should you snap a picture of the food by itself or take a selfie with your partner while you eat? New research suggests that people use first-person photography, taking a photo of the scene from one’s own perspective, when they want to document a physical experience, but opt for third-person photos, depicting themselves in the scene (like selfies), to capture the deeper meaning of events.
Previous research has focused how the photo-taker wants to present themselves to others. The current research, published today in Social Psychological and Personality Science, ...
How can we fight blood cancer more effectively?
2023-04-27
Multiple myeloma is a rare blood cancer caused by the uncontrolled multiplication of abnormal plasma cells. These plasma cells are a special type of white blood cells that play an important role in the immune system by producing essential antibodies in the bone marrow and lymph nodes.
Despite an increasing number of approved drugs and treatment approaches such as immunotherapy becoming available, the disease is still not curable. The average life expectancy of patients after diagnosis is only five years.
One of the main challenges is the cancer’s tendency to return even after treatment. This is because treatment makes the cancer cells ...
Researchers call for national governments to mandate real-time indoor air quality monitoring
2023-04-27
In a response to the COVID-19 pandemic, a team of researchers has published an editorial calling for national governments to consider mandating real-time indoor air quality monitoring in at least all public buildings.
Their editorial is published in the journal Building Simulation on 25 April 2023.
The three-year-long COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has revealed that there is a global indoor-air crisis. Vaccination alone has not completely controlled the COVID-19 pandemic and the virus continues to threaten human health and life. Scientists now know most if not nearly all ...
Routine antibiotics don't improve outcomes of post-mastectomy breast reconstruction
2023-04-27
April 27, 2023 – For breast cancer patients undergoing breast reconstruction after mastectomy, avoiding postoperative oral antibiotics does not reduce the risk of infections, reports a study in the May issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"Our experience suggests that discontinuing routine oral antibiotic treatment after implant-based breast reconstruction ...
MD Anderson and Generate:Biomedicines enter co-development and commercialization agreement to accelerate novel protein therapeutics for oncology using generative AI
2023-04-27
HOUSTON and SOMERVILLE, Mass. ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Generate:Biomedicines today announced a strategic collaboration to jointly discover and co-develop protein therapeutics for up to five oncology targets in advanced cancers, including small-cell and non-small-cell lung cancer.
Under the co-development and commercialization agreement, MD Anderson and Generate:Biomedicines will each contribute toward creating optimized, potentially best-in-class therapeutics that can rapidly advance into proof-of-concept clinical trials. The agreement combines Generate:Biomedicines’ integrated machine-learning capabilities and experimental/wet lab capabilities – ...
Sounds from nature: A soothing remedy for gambling addiction
2023-04-27
Gambling addiction, also called “pathological gambling” and “gambling disorder (GD),” is known to have severe economic, social, mental, and physical consequences on those affected. One of the major factors contributing to the development and relapse of this disorder is stress. However, studies show that replacing gambling with alternative leisure activities may reduce the likelihood of developing the disorder. In recent years, forest bathing, or “shinrin-yoku,” a form of nature therapy, has emerged ...
Estimating the impact of new high seas activities on the environment: The effects of ocean-surface macroplastic removal on sea surface ecosystems
2023-04-27
“The surface is the skin through which our ocean breathes. It is a critical nursery ground for hundreds, possibly thousands, of species, and it is also one of the most vulnerable regions to human impacts. This is why we must treat the surface with exceptional care. It is an extremely unique and fragile environment, and small impacts at the surface could ripple into large impacts above and below the waves.” - Dr. Rebecca Helm, Assistant Professor of Environmental Science at Georgetown University
New research ...
AI in the ICU
2023-04-27
Clinicians in an intensive care unit need to make complex decisions quickly and precisely, monitoring critically ill or unstable patients around the clock.
Researchers from Carnegie Mellon University's Human-Computer Interaction Institute (HCII) collaborated with physicians and researchers from the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC to determine if artificial intelligence could help in this decision-making process and if clinicians would even trust such assistance.
The team gave 24 ICU physicians access to an AI-based ...
Record ammonia production achieved with inexpensive cobalt catalyst at low temperatures
2023-04-27
Ammonia (NH3) is one of the most widely produced chemicals in the world, with a production of over 187 million tons in 2020. About 85% of it is used to produce nitrogenous fertilizers, while the rest is used for refining petroleum, manufacturing a wide range of other chemicals, and creating synthetic fibers such as nylon. However, all this comes at a high energy cost. Currently, most of the ammonia is produced using the conventional Haber-Bosch process, which requires combining nitrogen and hydrogen at high temperatures (400-450°C) and pressures (200 atmospheres). As a result, scientists ...
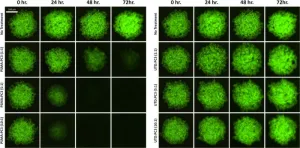
Analyzing CAR-T cells with image cytometry for potential solid tumor treatments
2023-04-27
Oak Brook, IL – The April 2023 issue of SLAS Discovery contains six full-length articles and one mini-review covering high-throughput screening (HTS) for protease-inhibiting drugs, high-content phenotypic screening and other life sciences research.
Featured in this month’s issue is the article “High-Throughput Method to Analyze the Cytotoxicity of CAR-T Cells in a 3D Tumor Spheroid Model Using Image Cytometry,” by Zurowski, et al, where the authors focus on the use of chimeric ...
10 popular diets scored for heart-healthy elements; some need improvement
2023-04-27
Statement Highlights:
A new American Heart Association scientific statement assesses and scores the heart healthiness of popular dietary patterns.
Several dietary patterns, including the DASH-style eating plan, Mediterranean, pescatarian and vegetarian eating patterns, received top ratings for aligning with the Association’s dietary guidance.
A few eating patterns, including Paleo and ketogenic diets, contradict the Association’s guidance and did not rank as heart-healthy eating patterns.
The statement suggests opportunities for dietary research and interventions to promote health equity, recognizing the importance of social determinants of health in shaping dietary ...
Twilight zone at risk from climate change
2023-04-27
Life in the ocean’s “twilight zone” could decline dramatically due to climate change, new research suggests.
The twilight zone (200m to 1,000m deep) gets very little light but is home to a wide variety of organisms and billions of tonnes of organic matter.
The new study warns that climate change could cause a 20-40% reduction in twilight zone life by the end of the century.
And in a high-emissions future, life in the twilight zone could be severely depleted within 150 years, with no recovery for ...
Researchers from ISGlobal and LSHTM call for incorporating heat stress indices into communication of dangerous heat waves
2023-04-27
In the summer of 2022, over 20,000 excess deaths across Spain, France, Germany and Great Britain were suggested to have been linked to extremely hot weather. In the context of global warming where climate models point to the fact that extreme heat waves are likely to increase both in frequency and magnitude, preventive measures and adequate communication of dangerous conditions take on special relevance. In a Brief Communication published in npj Climate and Atmospheric Science, researchers from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported ...
Discovery could improve survival of bladder cancer patients
2023-04-27
· Bladder cancer is the fourth-most diagnosed cancer in men, and survival for patients with advanced bladder is less than a year
· Doctors don’t know which bladder cancer patients will benefit from immunotherapy
·Treatment of patients with ineffective therapy causes unneeded harm and delays treatment with optimal therapies
Chicago --- In a discovery that could improve the survival of bladder cancer patients, Northwestern Medicine scientists have developed a biomarker signature test to predict which ...
Odyssey of a 90-Year-Old from Israel, the United Kingdom, Australia and Singapore
2023-04-27
Down Memory Lane: Peter Ellinger’s Memoirs details the life of Law Professor Peter Ellinger, which has taken him around the world from Israel, to the United Kingdom, Australasia and finally Singapore, where he has chosen to retire. From his escape from Austria during Hitler’s reign, to his growing-up years in Israel, academia and legal practice, and his eventual retirement, this book takes you on a journey in time alongside Professor Ellinger.
Professor Ellinger is a Professor Emeritus of the National University of Singapore ...
[1] ... [1966]
[1967]
[1968]
[1969]
[1970]
[1971]
[1972]
[1973]
1974
[1975]
[1976]
[1977]
[1978]
[1979]
[1980]
[1981]
[1982]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.