Exposure to cannabinoids in pregnancy increases newborn mortality and respiratory problems
2023-04-25
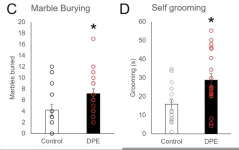
Consumption of cannabis (marijuana) or derivatives during pregnancy can cause respiratory problems for the baby, such as impaired control of breathing and diminished sensitivity to carbon dioxide, both of which favor sudden infant death syndrome. These are the main findings of a study conducted in Brazil and reported in an article published in the British Journal of Pharmacology.
The authors are researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) and the University of São Paulo (USP). They gave pregnant rats a synthetic compound (WIN 55) that acts on the brain in a similar manner to natural cannabinoids. Harmful effects occurred mainly in male pups.
“Cannabis ...
Matching form and function of brain cell types
2023-04-25
Investigators at Cedars-Sinai have created computer-generated models to bridge the gap between “test tube” data about neurons and the function of those cells in the living brain. Their study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications, could help in the development of treatments for neurological diseases and disorders that target specific neuron types based on their roles.
“This work allows us to start looking at the brain like the complex machine that it is, rather than ...
Small steps can yield big energy savings and cut emissions from MRIs
2023-04-25
Medical centers around the world could significantly reduce their carbon footprint and expenses by turning off MRIs and putting them in the lowest power mode instead of idling them when not in use, a new study in Radiology found.
Health care is responsible for up to 4.4% of global carbon emissions, and imaging contributes an outsized share due to its energy-intensive devices, especially MRI. A 2020 study found that three CTs and four MRIs used the same amount of energy per year as a town of 852 people, for example.
Though turning a machine off is better than idling, a substantial amount of MRI energy consumption occurs in “off” ...
Study links nutrients, brain structure, cognition in healthy aging
2023-04-25
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — In a new study, scientists explored the links between three measures known to independently predict healthy aging: nutrient intake, brain structure and cognitive function. Their analysis adds to the evidence that these factors jointly contribute to brain health in older adults.
Reported in the Journal of Nutrition, the study found that blood markers of two saturated fatty acids, along with certain omega-6, -7 and -9 fatty acids, correlated with better scores on tests of memory and with larger brain structures in the frontal, ...
UNC Charlotte faculty member receives NASA Exobiology grant
2023-04-25
For the first time in the University of North Carolina at Charlotte’s nearly 80-year history, a faculty member has won a NASA Exobiology grant. Assistant Professor of Bioinformatics and Genomics Richard Allen White III will use the ultra-competitive grant in his research on microbialites, a kind of “living rock” that could hold the key to how life formed on Earth.
Microbialites form when microbial mats, living colonies of mostly bacteria, transform into stronger hard structures. White explores how viruses may have helped to kickstart the transformation (i.e., lithification) of modern microbialites, which ...
Study: Treatment for opioid addiction lags despite policies designed to increase it
2023-04-25
Treating opioid addiction should be much easier now than it was a few years ago, thanks to pandemic-era rule changes that aim to improve access to buprenorphine, a medicine proven to help in recovery.
But a new study shows the rate of people starting on buprenorphine remained flat from 2019 through 2022, while the percentage of patients who stayed on buprenorphine for at least six months hovered at just over 20% from 2016 through 2022.
Until more health care providers start offering buprenorphine treatment -- and to take advantage of opportunities like emergency visits and hospitalizations ...
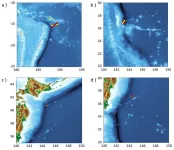
Creating a tsunami early warning system using artificial intelligence
2023-04-25
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – Tsunamis are incredibly destructive waves that can destroy coastal infrastructure and cause loss of life. Early warnings for such natural disasters are difficult because the risk of a tsunami is highly dependent on the features of the underwater earthquake that triggers it.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of California, Los Angeles and Cardiff University in the U.K. developed an early warning system that combines state-of-the-art acoustic technology with artificial intelligence to immediately classify earthquakes and determine potential tsunami ...
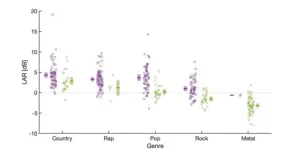
Lead vocal tracks in popular music go quiet
2023-04-25
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – A general rule of music production involves mixing various soundtracks so the lead singer’s voice is in the foreground. But it is unclear how such track mixing – and closely related lyric intelligibility – has changed over the years.
Scientists from the University of Oldenburg in Germany carried out an analysis of hundreds of popular song recordings from 1946 to 2020 to determine the lead vocal to accompaniment ratio, or LAR. Their results appear in JASA Express Letters, published on behalf of the ...
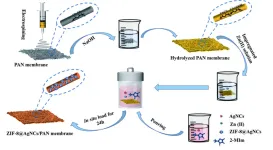
Treating polluted water with nanofiber membranes
2023-04-25
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – When oil contaminates water, it creates a film that reduces oxygen levels and introduces toxic substances. This can lead to the death of aquatic plants and animals, contaminate soil, and ultimately threaten human health.
Separating oil from polluted water is therefore of great importance. Current methods can be expensive and challenging, and some may introduce further pollutants into the system. For example, membrane materials can act as a barrier to intercept ...
Trends in buprenorphine initiation and retention
2023-04-25
About The Study: During January 2016 through October 2022, the monthly buprenorphine initiation rate in the U.S. increased, then flattened. This flattening occurred prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, suggesting that factors other than the pandemic were involved.
Authors: Kao-Ping Chua, M.D., Ph.D., of the University of Michigan Medical School in Ann Arbor, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2023.1207)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
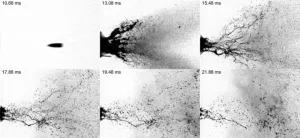
Improving bloodstain pattern analysis with fluid dynamics
2023-04-25
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – Often left on the surfaces of a crime scene or on the clothes of an accused criminal, blood back spatter can be used as evidence for forensic scientists to reconstruct what occurred. However, the fluid dynamics at play are complicated, and neglecting the interaction between the blood and the muzzle gases from the firearm could skew the results.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago and Iowa State University modeled the behavior of blood drops during secondary atomization to examine how the phenomenon affects a crime scene.
“Primary atomization of blood is caused by ...
Self-awareness of memory function and clinical progression in cognitively normal older adults
2023-04-25
About The Study: In this study of 436 cognitively normal older adults, unawareness, rather than heightened awareness, of memory decline was strongly associated with future clinical progression, providing further support that discordant self- and informant-reported cognitive decline may provide important information to practitioners.
Authors: Patrizia Vannini, Ph.D., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.9964)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
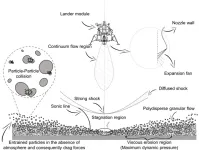
How to land on a planet safely
2023-04-25
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – When a lander descends toward the moon – or a rocky planet, asteroid, or comet – the exhaust plume of the rocket interacts with the surface, causing erosion and kicking up regolith particles. The resulting blanket of dusty debris can create a dangerous brownout effect, limiting visibility and potentially damaging the spacecraft or nearby equipment.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Chungnam National University, the University of Edinburgh, Gyeongsang National University, and the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information ...
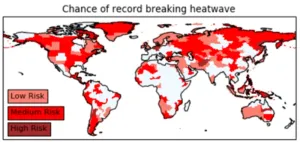
Global research reveals countries where record-breaking heatwaves are likely to cause most harm
2023-04-25
A new study has highlighted under-prepared regions across the world most at risk of the devastating effects of scorching temperatures.
The University of Bristol-led research, published today in Nature Communications, shows that unprecedented heat extremes combined with socioeconomic vulnerability puts certain regions, such as Afghanistan, Papua New Guinea, and Central America, most in peril.
Countries yet to experience the most intense heatwaves are often especially susceptible, as adaptation measures are often only introduced after the event. A high chance of record-breaking ...
Using artificial intelligence to create a tsunami early warning system
2023-04-25
Cardiff University media release/Datganiad i’r wasg gan Brifysgol Caerdydd
Under embargo until 16:00 BST/11:00 EST on Tuesday 25 April 2023/O dan embargo tan 16:00 BST/11:00 EST ddydd Mawrth 25 Ebrill 2023
Using artificial intelligence to create a tsunami early warning system
Real-time classification of underwater earthquakes enables earlier and more reliable tsunami alerts
An early warning system that quickly classifies submarine earthquakes and determines the risk of tsunami events has been developed by scientists at Cardiff ...
Researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine discover how long-lasting memories form in the brain
2023-04-25
April 25, 2023—(BRONX NY)—Helping your mother make pancakes when you were three…riding your bike without training wheels…your first romantic kiss: How do we retain vivid memories of long-ago events? As described in a paper published online on April 25 in Neuron, researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine have found the explanation.
“The ability to learn new information and store it for long periods is one of the brain’s most remarkable features,” said Robert H. Singer, Ph.D., ...
Researchers find rhythmic brain activity helps to maintain temporary memories
2023-04-25
New research shows that rhythmic brain activity is key to temporarily maintaining important information in memory. Researchers at the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester published these findings today in Current Biology that found brain rhythms—or patterns of neuronal activity—organize the bursts of activity in the brain that maintain short-term connections.
“The thought has been that the temporary storage of important information is linked to neurons in the brain that just fire away, retaining that information until it is no longer needed. Recent research has shown that it might not be such persistent ...
Near-universal T cell immunity towards a broad range of bacteria
2023-04-25
Typically T cells of the immune system respond to a specific feature (antigen) of a microbe, thereby generating protective immunity. As reported in the journal Immunity, an international team of scientists have discovered an exception to this rule. Namely, a group of divergent bacterial pathogens, including pneumococci, all share a small highly conserved protein sequence, which is both presented and recognized by human T cells in a conserved population-wide manner.
The study set out to understand immune mechanisms that protect against pneumococcus, a bacterial pathobiont that can reside harmlessly in the upper respiratory mucosae but can also cause infectious ...
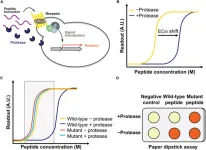
Novel living yeast-based dual biosensor for detecting peptide variants
2023-04-25
Biosensors—sensors that can detect biological samples—are powerful tools for understanding the function, composition, and structure of biochemical molecules. Biosensors are often applied for the detection of proteins and their subunits, called peptides, yielding a wide range of biomedical applications. In 2017, researchers from Columbia University in USA engineered a living yeast biosensor by rewiring pheromone-related signaling pathways used by yeast for mating. In the presence of the pheromone peptide, the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) could detect the peptide, triggering a cascade that would eventually activate a ...
Sizing them up! An algorithm to accurately quantify rapeseed silique morphology
2023-04-25
Rapeseed or oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) is an important crop cultivated worldwide for its oil-rich seeds. The rapeseed silique is an organ that plays a role in photosynthesis, sends developmental signals to maturing seeds, and provides a capsule that harbors the seeds. High-yield rapeseed varieties have both a high number and optimal morphology–the form and structure–of siliques. In this regard, rapeseed genotype and cultivation method directly influence the number of siliques that a plant produces. Thus, accurately quantifying silique development parameters is critical for predicting ...
Columbia University launches Center for Precision Psychiatry & Mental Health with $75 million grant from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation
2023-04-25
NEW YORK, April 24, 2023—Columbia University today announced the establishment of the Stavros Niarchos Foundation (SNF) Center for Precision Psychiatry & Mental Health at Columbia University. The center will catalyze the scientific innovation and clinical implementation of precision medicine to advance the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of mental illness. The center is being established with a $75 million grant from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation (SNF), an international philanthropic organization, as part of SNF’s Global Health Initiative (GHI).
The SNF Center is a joint effort of the Department of Psychiatry at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians ...
Research links common insecticide to neurodevelopmental disorders
2023-04-25
A new study from The University of Toledo suggests early exposure to a common class of insecticides called pyrethroids may increase the risk of autism and other developmental disorders, even at levels currently recognized as safe by federal regulators.
The findings, which come from a study of mice, were published today in the peer-reviewed journal PNAS Nexus.
Pyrethroids are some of the most widely used insecticides in the country, appearing in both consumer products and industrial preparations.
“If ...
New research sheds light on how to choose quality eHealth tools
2023-04-25
With so many eHealth tools available, it can be challenging to select the best one for a specific health need. A recent study published in JMIR Human Factors provides valuable insights on how to choose quality eHealth tools in an evolving landscape of digital health technology. This study titled “Assessing the Quality and Impact of eHealth Tools: Systematic Literature Review and Narrative Synthesis” comprehensively examined how the quality and impact of eHealth tools are currently assessed.
Led by Dr Christine Jacob, a health tech researcher at the University of Applied Sciences and Arts Northwestern ...
SwRI tests automated vehicles in virtual off-road environments
2023-04-25
SAN ANTONIO – April 25, 2023 – Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has created a 3D simulation tool to test automated vehicles in virtual off-road environments modeled after real-world conditions. The research expands SwRI’s investment into software-in-the-loop solutions to test connected and automated vehicles (CAVs) in scenarios ranging from congested roadways to off-road terrain. A simulated environment, or a 3D “software loop,” supports evaluations of an infinite number of scenarios that would be cost-prohibitive to test in the real world.
The technology meets U.S. Department of Defense demands ...
Pesticides and neurodevelopment disorders
2023-04-25
A study of 72 mice mothers and their litters suggests a popular pesticide may cause neurodevelopmental disorders in humans. Previous studies have shown that nearly half of the risk for neurodevelopment disorders, including autism, is environmental, but few specific environmental causes have been clearly identified. James Burkett and colleagues exposed mice to low doses of pyrethroid pesticide deltamethrin during pregnancy and lactation. Pups of exposed mothers vocalized less compared to pups of unexposed mothers. ...
[1] ... [1972]
[1973]
[1974]
[1975]
[1976]
[1977]
[1978]
[1979]
1980
[1981]
[1982]
[1983]
[1984]
[1985]
[1986]
[1987]
[1988]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.