Putting hydrogen on solid ground: Simulations with a machine learning model predict a new phase of solid hydrogen
2023-04-21
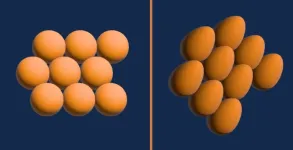
Hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, is found everywhere from the dust filling most of outer space to the cores of stars to many substances here on Earth. This would be reason enough to study hydrogen, but its individual atoms are also the simplest of any element with just one proton and one electron. For David Ceperley, a professor of physics at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, this makes hydrogen the natural starting point for formulating and testing theories of matter.
Ceperley, also a member of the Illinois Quantum ...
Researchers develop safety monitoring system for construction sites
2023-04-21
University of Houston computer scientists have developed a new system to keep construction workers safe at job sites. Their findings and process are laid out in a study published in the research journal Applied Sciences.
According to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, 4,764 workers died on the job in 2020. Employees in construction and extraction occupations accounted for 20% of those deaths. Many were struck by a vehicle or mobile machinery on construction sites. Although the construction industry has enlisted the help of safety experts, a great number of fatalities and injuries still occur.
“The point of our research project was to enhance safety of workers ...
Study finds alcohol-related liver disease soared in nearly all states during the pandemic, with one race particularly affected
2023-04-21
BOSTON – Alcohol consumption increased substantially across the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic, but the impact was greatest among American Indian and Alaska Native (AIAN) populations, where deaths from alcohol-associated liver disease were six times those of white people, according to a study by Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB). The disproportionately high mortality rate reflects not just the pandemic, but a systemic failure of supportive health care and lack of critical resources for AIAN populations ...
World’s largest grammar database reveals accelerating loss of language diversity
2023-04-21
There’s a crisis unfolding in the field of linguistics: Global language experts estimate that, without intervention, about one language will be lost every month for the next 40 years.
A study published in Science Advances debuts a grammatical database that documents the enormous diversity of current languages on the planet, highlighting just how much humanity stands to lose and why it's worth saving.
Known as Grambank, it is now the world’s largest publicly available comparative grammatical database. Initiated by scholars in the Department of Linguistic and Cultural Evolution at the ...
Study points to new approach to treat chronic transplant rejection
2023-04-21
University of Pittsburgh researchers have identified a type of immune cell that drives chronic organ transplant failure in a mouse model of kidney transplantation and uncovered pathways that could be therapeutically targeted to improve patient outcomes. The findings are published in a new Science Immunology paper.
“In solid organ transplantation, such as kidney transplants, one-year outcomes are excellent because we have immunosuppressant drugs that manage the problem of acute rejection,” ...
Cheaper method for making woven displays and smart fabrics – of any size or shape
2023-04-21
Researchers have developed next-generation smart textiles – incorporating LEDs, sensors, energy harvesting, and storage – that can be produced inexpensively, in any shape or size, using the same machines used to make the clothing we wear every day.
The international team, led by the University of Cambridge, have previously demonstrated that woven displays can be made at large sizes, but these earlier examples were made using specialised manual laboratory equipment. Other smart textiles can be manufactured in specialised microelectronic fabrication facilities, but these are highly expensive and produce large volumes of waste.
However, the team found that flexible ...
Researchers devise cascaded microfluidic circuits for pulsatile filtration of extracellular vesicles directly from whole blood samples
2023-04-21
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are cell-secreted lipid bilayer bioparticles with a diameter of 30 to 250 nm. They are a promising source of biomarkers for liquid biopsies for early cancer diagnosis and real-time monitoring of tumor development. However, analysis of nanosized EVs in blood samples has been hampered by the lack of effective, rapid, and standardized methods to isolate and purify EVs.
In a study published in Science Advances, SUN Jiashu’s group from the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology (NCNST) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) and collaborators from the Fifth Medical Center of the Chinese PLA General ...
Nanowire networks learn and remember like a human brain
2023-04-21
An international team led by scientists at the University of Sydney has demonstrated nanowire networks can exhibit both short- and long-term memory like the human brain.
The research has been published today in the journal Science Advances, led by Dr Alon Loeffler, who received his PhD in the School of Physics, with collaborators in Japan.
“In this research we found higher-order cognitive function, which we normally associate with the human brain, can be emulated in non-biological hardware,” Dr Loeffler said.
“This work builds on our previous research in which we showed how nanotechnology could be used to build a brain-inspired electrical device with neural ...
Long distance voyaging among the Pacific Islands
2023-04-21
Polynesian peoples are renowned for their advanced sailing technology and for reaching the most remote islands on the planet centuries before the Europeans reached the Americas. Through swift eastward migrations that are now well covered by archaeological research, Polynesian societies settled virtually every island from Samoa and Tonga to Rapa Nui/Easter Island in the east, Hawai’i in the north, and Aotearoa/New Zealand in the south. But little is known about Polynesian migrations west of the 180th meridian.
In order to better understand the relationship between these Polynesian societies of the western Pacific, Melanesia and Micronesia – often ...
Heart injury biomarker may help COVID-19 patients avoid hospitalization, new study shows
2023-04-21
A study led by the University of St Andrews suggests that a frequently used medical test for heart injury could one day be used to help COVID-19 patients avoid hospitalisation.
Cardiac troponins are proteins that form part of the heart’s contractile machinery and are released into the bloodstream when the heart is damaged. It can be measured in a blood test which is widely used in the assessment of heart attacks and other heart conditions.
Existing studies since 2020 have shown that COVID-19 patients who have elevated troponin levels are more likely to die or suffer adverse clinical outcomes compared with those who have normal ...
Study: Cells send maintenance crews to fix damaged protein factories
2023-04-21
JUPITER, Fla. — In a discovery fundamental to the inner workings of cells, scientists have discovered that if oxidative stress damages protein factories called ribosomes, repair crews may move in to help fix the damage so work can quickly resume.
The discovery, reported Friday in the journal Molecular Cell, could have implications for cancer, the aging process, and growth and development, said the study’s lead author, molecular biologist Katrin Karbstein, Ph.D., a professor at The Herbert ...
New stellar danger to planets identified by NASA'S Chandra program
2023-04-21
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — An exploded star can pose more risks to nearby planets than previously thought, according to a new study from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and other X-ray telescopes. This newly identified threat involves a phase of intense X-rays that can damage the atmospheres of planets up to 160 light-years away.
The results of the study, led by researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, Washburn University and the University of Kansas, are published in the Astrophysical Journal.
Earth is not in danger of such a threat today because there are no potential supernova progenitors within this distance, but it may have experienced ...
Why are COVID-19 vaccination rates among children so low? Parents’ worry about long-term risks, responsibility
2023-04-21
Despite efforts by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and pediatric clinicians to increase the COVID-19 vaccination rate among children, many remain unvaccinated due to parental concerns about the vaccine’s long-term effects and anticipated responsibility. Those are findings from a new study published in Pediatricsand conducted by the Center for Economic and Social Research(CESR) at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences.
The researchers sought to determine the causes of low child vaccination rates. Currently, only 39% of children 5 to 11 and 68% of those 12 to 17 have received ...
Insignum AgTech and Beck’s collaborate to help corn ‘talk’
2023-04-21
ATLANTA, Ind. – Insignum AgTech® and Beck’s have signed an agreement to test Insignum’s innovative corn traits in Beck’s elite varieties. The companies will collaborate to cross the trait into proprietary Beck’s genetics for field-testing in 2023 to evaluate commercial viability of the traits.
Insignum AgTech develops plant genetic traits that enable plants to “talk” and signal to farmers when specific plant stresses begin.
“With this trait, a corn plant generates purple pigment, indicating that a fungal infection has started ...
New study uncovers Colorado’s spicy ancient history of chili peppers
2023-04-21
Botanists and paleontologists, led by researchers from the University of Colorado Boulder, have identified a fossil chili pepper that may rewrite the geography and evolutionary timeline of the tomato plant family.
The team’s findings, published last month in the journal New Phytologist, show that the chili pepper tribe (Capsiceae) within the tomato, or nightshade (Solanaceae), family is much older and was much more widespread than previously thought. Scientists previously believed that chili peppers evolved in South America at most ...
360-million-year-old Irish fossil provides oldest evidence of plant self-defense in wood
2023-04-21
An international team of scientists, co-led by Dr Carla J. Harper, Assistant Professor in Botany in the School of Natural Sciences at Trinity, has discovered the oldest evidence of plant self-defence in wood in a 360-million-year-old fossil from south-eastern Ireland.
Plants can protect their wood from infection and water loss by forming special structures called “tyloses”. These prevent bacterial and fungal pathogens from getting into the heartwood of living trees and damaging it. However, it was not previously known how early in the evolution of plants woody species became capable of forming such defences.
Published ...
New paper advances understanding of geographic health disparities
2023-04-21
By looking at where people were born instead of where they ultimately move to and die, geographic disparities in mortality look different than previously assumed, according to a new study published on April 1, 2023, in the journal Demography.
interstate migration may mitigate regional inequalities in mortality according to “Understanding Geographic Disparities in Mortality,” a paper led by Jason Fletcher, professor in the La Follette School of Public Affairs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and director of the Center for Demography of Health and Aging with an appointment in Population Health Sciences.
“At a time when nearly ...
Newly funded Morris Animal Foundation study assesses CBD use for postsurgical pain in dogs
2023-04-21
DENVER/April 21, 2023 – A new study is testing whether the addition of CBD can improve pain management in dogs following orthopedic surgery. The study, funded by Morris Animal Foundation, will be conducted by a veterinary research team at the University of Saskatchewan, Canada.
CBD use in pets has gained in popularity in the last decade, but there are few controlled studies closely examining its efficacy as a pain management tool. This study hopes to help partially close this knowledge gap.
The research team, led by Dr. Alan Chicoine, Assistant Professor, Department ...
Endocrine Society endorses bipartisan bill to address insulin affordability
2023-04-21
WASHINGTON—The Endocrine Society today endorsed the Improving Needed Safeguards for Users of Lifesaving Insulin Now (INSULIN) Act of 2023, a bipartisan insulin affordability bill introduced by Sens. Jeanne Shaheen (D-NH) and Susan Collins (R-ME). This legislation would cap out-of-pocket insulin costs for those with private insurance, ensure patients can share in insulin rebates and discounts, and promote competition in the insulin market.
These measures would protect access to life-saving insulin for more than 7 million people nationwide who rely on the medication to manage their diabetes. According to the U.S. Center for Disease Control ...
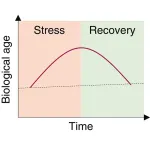
Biological age is increased by stress and restored upon recovery
2023-04-21
The biological age of humans and mice undergoes a rapid increase in response to diverse forms of stress, which is reversed following recovery from stress, according to a study publishing on April 21 in the journal Cell Metabolism. These changes occur over relatively short time periods of days or months, according to multiple independent epigenetic aging clocks.
“This finding of fluid, fluctuating, malleable age challenges the longstanding conception of a unidirectional upward trajectory of biological age over the life course,” says co-senior study author James White of Duke University School of Medicine. “Previous reports ...
Most people feel “psychologically close” to climate change
2023-04-21
When spurring action against climate change, NGOs and governmental agencies frequently operate on the assumption that people are unmotivated to act because they view climate change as a problem that affects distant regions far in the future. While this concept, known as psychological distance, seems intuitive, researchers report in the journal One Earth on April 21 that most people see climate change as an important and timely issue even if its impacts are not immediately noticeable.
“There is no consistent evidence ...
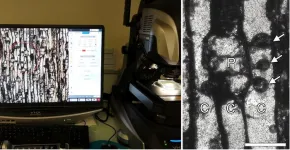
The Mathematics of Cell Boundary 'Ruggedness'
2023-04-21
Fukuoka, Japan—Researchers have uncovered both the mathematical and biological mechanism behind the rugged structures at cell boundaries found in tissues such as the kidneys and nasal glands. The team hopes that their new insights can help develop new ways of treating associated pathologies and build better biological models for future study.
Our cells come in all sorts of shapes and sizes. From the neurons that extend across the central nervous system, to the spherical white blood cells that protect us from infection, a cell's form and ...
Effect of COVID-19 pandemic on food insecurity and inability to pay rent hit immigrant families hardest, Drexel study finds
2023-04-21
Under embargo until April 21, 2023
Although families with immigrant mothers experienced higher rates of food insecurity and inability to pay rent during the pandemic than other groups, they reported less participation in economic impact payments (EIP) in the form of stimulus checks and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) – two programs designed to provide stopgap financial support, according to a new study in JAMA Health Forum from researchers at the Dornsife School of Public Health and Children’s HealthWatch.
The team surveyed 1,396 caregivers in Boston, ...
Firearms injure or kill up to a quarter of juvenile justice youth after detention
2023-04-21
CHICAGO – A new study by Northwestern University found that among youth who had entered juvenile detention, one-quarter of Black and Hispanic males were later injured or killed by firearms within 16 years.
While the nation’s youth and young adults are disproportionately affected by the daily occurrence of 100 firearm deaths and 234 non-fatal firearm injuries, youth who have been previously involved with the juvenile justice system had up to 23 times the rate of firearm mortality than the general population.
The study is the first to focus on the incidence rate of firearm injuries and death within the juvenile justice population.
“Who ...
Neighborhood disadvantage and breast cancer–specific survival
2023-04-21
About The Study: In this study of 5,000 patients with breast cancer, a shorter breast cancer–specific survival in women from disadvantaged neighborhoods compared with advantaged neighborhoods was identified, even after controlling for individual-level sociodemographic, comorbidity, breast cancer risk factor, access to care, tumor, and National Comprehensive Cancer Network guideline-concordant treatment characteristics. The findings suggest potential unaccounted mechanisms, including unmeasured social determinants of health and access to care measures.
Authors: Neha Goel, M.D., of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, is ...
[1] ... [1977]
[1978]
[1979]
[1980]
[1981]
[1982]
[1983]
[1984]
1985
[1986]
[1987]
[1988]
[1989]
[1990]
[1991]
[1992]
[1993]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.