How drugs get into the blood
2023-04-14
There is a need for new drugs. For example, many of the antibiotics that we have been using for a long time are becoming less effective. Chemists and pharmaceutical scientists are frantically searching for new active substances, especially those that can penetrate cell membranes, as these are the only ones that patients can take orally in the form of a tablet or syrup. Only these active ingredients pass through the intestinal wall in the small intestine and enter the bloodstream to reach the affected area in the body. For active ingredients that cannot penetrate the cell membrane, physicians have no choice but to inject them directly into ...
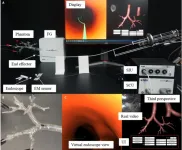
A novel robotic bronchoscope system for navigation and biopsy of pulmonary lesions
2023-04-14
Cancers are notoriously known for their high mortality rate and increasing incidence worldwide. Among them, lung cancer is arguably one of the most devastating ones. According to the World Cancer Research Fund International, lung cancer was the second most common cancer around the world in 2020, with more than 2.2 million new cases and 1.8 million deaths.
However, lung cancer, like other cancers, is easier to treat if caught earlier. “The reported 1-year survival rate for stage V is just 15% to 19% compared with 81% to 85% for stage I, which means that the early ...
Black cancer patients 71% more likely to experience heart damage following chemotherapy treatment
2023-04-14
Chemotherapy is associated with an increased risk of treatment-related heart damage, including heart failure and cerebrovascular disease, for many patients. But a new meta-analysis, presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient 2023 conference, finds that Black patients or patients of African ancestry have 71% higher odds of cardiotoxicity following cancer treatment compared to White patients.
Cardiotoxicity is any heart damage stemming from cancer treatment or drugs, including ...
Optica Publishing Group announces launch of Optica Quantum
2023-04-14
WASHINGTON—On World Quantum Day, Optica Publishing Group announced it will begin publishing a new journal in September 2023 dedicated to highly selective results in quantum information science and technology (QIST). The new journal, Optica Quantum, joins the Society’s portfolio of the most-cited journals in optics and photonics and will provide the community with articles of the same exceptional standards for quality, novelty, and significance as its parent journal, Optica.
The concept of quantum light serves as a foundation for many quantum technologies and ongoing ...
Farmer’ beetle finds suitable host trees by tracing scent of its fungus crop
2023-04-14
The alnus ambrosia beetle Xylosandrus germanus, also known as the black stem borer, was accidentally introduced by humans from its native east Asia to North America and Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. X. germanus is a so-called ambrosia beetle, which means that it farms its own food: a specialized fungal symbiont which it ‘sows’ and tends inside the galleries that it digs inside wood. It is a destructive invasive pest, known to attack more than 200 species from 51 families of broadleaf and conifer trees. While it prefers to colonize dead ...
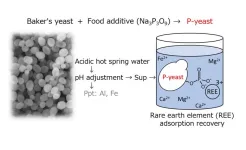
Treasure hunt in hot springs?
2023-04-14
The demand for precious metals and rare earths is expected to continue increasing in the future. Due to limited production areas, recycling from precision equipment and recovering from seawater and hot spring water are needed to ensure a stable supply.
A research group led by Professor Masayuki Azuma and Associate Professor Yoshihiro Ojima of the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Engineering has successfully developed an adsorbent material that can selectively recover rare earth elements (REEs) using environmentally friendly and inexpensive baker’s yeast and trimetaphosphate, which is used as a food additive.
The research group conducted experiments using ...
Why did the mpox (monkeypox) epidemic wane? Belgian researchers propose theory
2023-04-14
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Did the recent mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) outbreak end because of “network immunity”? That’s the theory being put forward by Belgian researchers at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
2022 saw a global outbreak of mpox, a viral ...
The Lancet Public Health: Hearing aids may protect against a higher risk of dementia associated with hearing loss, study suggests
2023-04-14
Peer-reviewed / Observational study / People
The Lancet Public Health: Hearing aids may protect against a higher risk of dementia associated with hearing loss, study suggests
Study of 437,704 people suggests those experiencing hearing loss and not using hearing aids may have a higher risk of dementia than people without hearing loss. Those using hearing aids did not appear to be at an increased risk of dementia.
After adjusting for other factors, study analysis suggests a 1.7% risk of dementia in people with hearing loss who are not using hearing aids, compared to 1.2% among those without hearing loss ...
One of first studies to assess new bivalent Covid-19 booster vaccine shows it is highly effective in reducing deaths and hospitalizations
2023-04-14
*Note: this is a joint press release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) and The Lancet Infectious Diseases. Please credit both the congress and the journal in your stories*
Since September, 2022, bivalent mRNA vaccines – which contain elements from both the original wild type COVID strain and an updated component from the omicron strain – have replaced older style monovalent boosters in the USA, Israel, and other countries. These vaccines were designed to help improve vaccine-induced immunity against the omicron variant and subsequent subvariants.
A new study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases and ...
A $1 million boost to UT’s venture culture
2023-04-14
Adding fuel to The University of Texas at Austin’s startup engine, alumnus William “Billy” Freed, BBA ’81, and his family have given $1 million to the Herb Kelleher Entrepreneurship Center in the McCombs School of Business.
The gift establishes the Freed Family Entrepreneurship Excellence Fund and endows the Freed Family Pitch Competition, previously called DisrupTexas. Freed’s wife Cheryl, BA ’82, JD ’84; sons Tyler, BS ’17, and Russell, BBA ’21; and daughter-in-law Leslie Lugrin Freed, BS ’17, ...
Data can now be processed at the speed of light!
2023-04-14
How can Marvel movie character Ant-Man produce such strong energy out of his small body? The secret lies in the “transistors” on his suit that amplify weak signals for processing. Transistors that amplify electrical signals in the conventional way lose heat energy and limit the speed of signal transfer, which degrades performance. What if it were possible to overcome such limitation and make a high-performance suit that is light and small but without loss of heat energy?
A POSTECH team of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Yeonjeong Koo from the Department of Physics and a team from ...
Disrupted rhythms of rest and wakefulness contribute to worse symptoms in schizophrenia patients
2023-04-14
PITTSBURGH, April 13, 2023 – In a paper published today in Molecular Psychiatry, a team of scientists from the University of Pittsburgh in collaboration with researchers in Italy described shared patterns of sleep disturbances and irregularities in daily rhythms of rest and activity across patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorder, or SSD.
By using wrist monitors that measured activity and rest as proxies of wakefulness and sleep, researchers found that individuals with SSD who resided in psychiatric hospitals and those who manage their condition in outpatient settings had erratic sleep patterns, dysregulated transitions between sleep ...
How AI and a mobile phone app could help you quit smoking
2023-04-14
A stop smoking mobile app that senses where and when you might be triggered to light up could help people quit – according to University of East Anglia research.
Quit Sense is the world’s first Artificial Intelligence (AI) stop smoking app which detects when people are entering a location they used to smoke in. It then provides support to help manage people’s specific smoking triggers in that location.
Funding for the Quit Sense app has come from the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) and the Medical Research Council.
A study published today shows how the new ...
Nurse sounds a warning on hearing loss for COVID-19 patients
2023-04-14
A University of South Australia nursing lecturer has used her own COVID-19 experience to inform research into a little-known side effect of the virus – sudden deafness.
Kim Gibson, a registered nurse with a clinical background in neonatal intensive care, has documented her experience with sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) five weeks after testing positive to COVID-19. She was fully vaccinated.
Her findings and recommendations are published in the latest edition of the British Medical Journal Case Reports.
Gibson developed acute hearing loss in one ear, along with ...
Scientists from Singapore and Sweden achieve promising results towards restoring vision in blindness caused by cellular degeneration in the eye
2023-04-14
SINGAPORE, 14 April 2023 – A preclinical study using stem cells to produce progenitor photoreceptor cells—light-detecting cells found in the eye—and then transplanting these into experimental models of damaged retinas has resulted in significant vision recovery. This finding, by scientists at Duke-NUS Medical School, the Singapore Eye Research Institute and the Karolinska Institute in Sweden, marks a first step towards potentially restoring vision in eye diseases characterised by photoreceptor loss.
“Our laboratory has developed a novel method that enables the production of photoreceptor ...
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards
2023-04-14
In celebration of World Quantum Day (14th April), IOP Publishing (IOPP) is launching a special collection of its most popular, cutting-edge quantum research published in the last two years.
The IOPP quantum collection is openly available for anyone to read and showcases world-class quantum research published in the academic journals Materials for Quantum Technology, Quantum Science and Technology, New Journal of Physics and Reports on Progress in Physics. The special collection will also include unique perspectives from women in quantum and their contributions to this popular field.
Quantum research and technology is evolving ...
Toppan and Hokkaido University launch Comprehensive Dementia Research Unit
2023-04-14
Tokyo – April 13, 2023 – Toppan (TYO: 7911), a global leader in communication, security, packaging, décor materials, and electronics solutions, and Hokkaido University have launched the “Comprehensive Dementia Research Unit,” an industry creation section that will collaborate with the Hokkaido University Collaborative Project Center’s Cognitive Science Research Center, which conducts comprehensive research on diagnosis technologies for dementia.
Fusing Toppan’s Digital ICA™1 technology for high-sensitivity ...
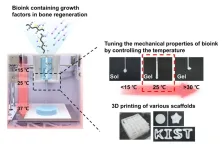
Safe bioink for artificial organ printing
2023-04-14
The development of biomaterials for artificial organs and tissues is active due to an increase in accidental injuries and chronic diseases, along with the entry into a super-aged society. 3D bioprinting technology, which uses cells and biomaterials to create three-dimensional artificial tissue structures, has recently gained popularity. However, commonly used hydrogel-based bioinks can cause cytotoxicity due to the chemical crosslinking agent and ultraviolet light that connect the molecular structure of photocuring 3D-printed bioink.
Dr. Song Soo-chang's research team at ...
Researchers turn to the power of native aquatic plants to clean coastal waters
2023-04-14
To find a fast, efficient way to clear harmful chemicals along the Gulf of Mexico coastline, researchers are turning to something already familiar with the task – several species of the aquatic grasses and rice that feel very much at home in murky coastal waters.
The research team led by University of Houston’s Venkatesh Balan, associate professor of biotechnology in the Cullen College of Engineering’s Division of Technology, studies the abilities of these water-loving flora to uptake concentrations ...
Rice U. engineering students’ brace puts patients first
2023-04-13
HOUSTON – (April 13, 2023) – Body image can have a significant impact on a person’s life, especially in their youth.
For those suffering from rib flaring associated with congenital deformations of the chest wall that cause it to jut out or cave in, a team of Rice University engineering students has come up with a potential solution.
Pectus carinatum and pectus excavatum are conditions in which a person is born with their breastbone protruding outward or sunken inward, respectively. There ...
PPPL hosts workshop on fusion energy and nonproliferation
2023-04-13
Public and private organizations around the world are developing fusion energy devices that could serve as models for fusion power plants. Scientists are striving to duplicate the fusion power that drives the sun and stars as a source of carbon-free energy to generate electricity without contributing to climate change.
While fusion plants could help meet global energy demands without emitting greenhouse gases and producing long-lived radioactive waste, they could also have risks — many of which were discussed at a two-day workshop hosted by the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory ...
Nurses trained via virtual reality performed better than those trained by inpatient clinical training
2023-04-13
In search of novel tactics to accommodate a larger student body and fulfill workforce demands, nursing schools are developing new approaches to optimize learning, engage learners, and provide methods to ensure competency in future nursing graduates.
A recent study by Bethany Cieslowski, associate professor of Nursing, and colleagues found that immersive virtual reality (VR) training has been shown to be as effective as inpatient training for students learning to provide care for acute care pediatric ...
Hallmarks to improving pancreatic cancer therapy identified by UC Irvine researchers
2023-04-13
Irvine, Calif., April 13, 2023 — Scientists from the University of California, Irvine, the University of Michigan and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center have made a significant contribution to the field of pancreatic cancer research. Their new study presents several crucial themes in the biology of pancreatic cancer that can serve as hallmarks for pancreatic cancer therapy. These themes include genomic alterations, metabolism, the tumor microenvironment, immunotherapy and innovative clinical trial design. The study appears in the journal Cell.
(Link to study: https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(23)00142-3)
Pancreatic ...
Four major Illinois research institutions form a collaboration to improve urban forest drought resilience
2023-04-13
Scientists at four leading Illinois research institutions, three in the Chicago region, are forming a new collaboration to study the effects of drought on urban trees and develop more effective drought response strategies nationwide through a grant from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The project is being led by researchers at The Morton Arboretum in conjunction with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, the University of Chicago and the Illinois State Water Survey at the Prairie Research ...
Good news! Only a modest reduction in added sugars consumption is needed to achieve the Healthy People 2030 target
2023-04-13
Ann Arbor, April 13, 2023 – Reducing caloric intake from added sugars is a Leading Health Indicator in Healthy People 2030, a national public health initiative led by the US Department of Health and Human Services that sets data-driven national objectives to improve health and wellbeing over the next decade. Although many Americans consume too much sugar, investigators found that only a modest reduction in added sugars intake is needed to reach a population mean of 11.5% of calories from added sugars by 2030. Prioritizing reducing added sugars intake among people not meeting recommendations could help those most at risk for chronic disease related to added sugars consumption. They report ...
[1] ... [1982]
[1983]
[1984]
[1985]
[1986]
[1987]
[1988]
[1989]
1990
[1991]
[1992]
[1993]
[1994]
[1995]
[1996]
[1997]
[1998]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.