Narrative risk messaging and vaccine hesitancy
2023-04-18
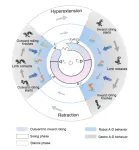
Public health messages that focus on protecting others are more effective at increasing vaccination rates than messages focused on protecting oneself, according to a study. Vaccine hesitancy is a challenge for public health workers and others concerned with reducing the deleterious effects of infectious diseases. Elizabeth Shanahan and colleagues tested three visual policy narrative messages promoting COVID-19 vaccination that emphasized protecting oneself, one’s circle of friends and family, or one’s community. A non-narrative control message simply urged participants to “get the vaccine” with an accompanying image of a syringe. ...
A neural coordination strategy for attachment and detachment of a climbing robot inspired by gecko locomotion
2023-04-18
A research article by scientists at the Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics developed a neural control algorithm to coordinate the adhesive toes and limbs of the climbing robot. The new research article, published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, provided a novel hybrid-driven climbing robot and introduced a neural control method based on CPG (Central Pattern Generator) for coordinating between adhesion and motion.
“Currently, the movement speed and stability of climbing robots have not yet reached the level of biological organisms. Animals have flexible climbing abilities on various slopes and roughness, ...
Children with COVID-19 treated safely at home, helping to take burden off hospitals
2023-04-18
Children with COVID-19 can be treated safely at home, helping to take the burden off the hospital system, according to a new study.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and published in Archives of Disease in Childhood, found COVID-positive children with moderate symptoms or pre-existing high-risk conditions could be treated effectively via a Hospital-in-the-Home (HITH) program. Additionally, many more sick children without COVID-19 were treated at home during the pandemic.
Murdoch Children’s Dr Laila Ibrahim said the program took pressure off paediatric emergency departments ...
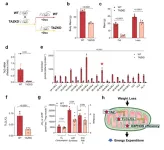
Increasing skeletal muscle mitochondrial efficiency after weight loss as a novel mechanism for lower energy expenditure
2023-04-18
Weight regains is a common problem for weight loss individuals. A number of studies have shown that weight loss in overweight people results in a reduction in whole-body energy expenditure. This reduction in energy expenditure is disproportionate across tissues, known as energetic mismatch which primarily originates from lean tissue, thus increasing weight regain risk. Although this phenomenon has long been identified and has been suggested that weight loss may alter skeletal muscle mitochondrial respiration, the mechanisms ...
Nuclear test ban treaty hydrophones help monitor ocean temperatures
2023-04-18
Ocean-based hydrophones in the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO)’s seismic-acoustic monitoring network could provide a better look at how ocean temperatures are changing over time, according to a presentation at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)’s 2023 Annual Meeting.
Finding new ways to monitor ocean temperatures is important for determining rates of warming, sea level rise and climate-related ocean circulation patterns as average global temperatures continue to rise, the researchers said.
Sound ...
Surveys, focus groups reveal what Puerto Rico residents want to know after 2020-21 earthquakes
2023-04-18
In the wake of the 2020-2021 Southwest Puerto Rico earthquake sequence, researchers asked emergency responders and residents in affected communities about the information they needed to prepare for the next earthquake.
Residents surveyed door to door and in focus groups said they wanted to know more about and have easier access to an aftershock forecast, along with information on potential tsunami risk, according to a presentation at the SSA 2023 Annual Meeting.
Residents also wanted more information tailored specifically to their local area, said Jenniffer M. Santos-Hernández ...
Severe COVID-19 linked with 16-fold risk of life-threatening heart rhythm within 6 months
2023-04-18
Barcelona, Spain – 18 April 2023: Patients with severe COVID-19 requiring mechanical ventilation are 16 times more likely to develop ventricular tachycardia within six months compared to their peers without severe infection, according to research presented at EHRA 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 Risks of other heart rhythm disorders were also elevated.
“The actual likelihood of developing ventricular tachycardia or other arrhythmias after severe COVID-19 is low for the individual ...
Stereotactic radiosurgery is effective for treatment of vestibular schwannomas in neurofibromatosis type 2
2023-04-18
April 18, 2023 –Vestibular schwannomas related to neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) are difficult to manage and are sometimes treated with a noninvasive option, stereotactic radiosurgery. A retrospective study conducted by an international, multicenter team found that stereotactic radiosurgery is effective for patients with these tumors while preserving serviceable hearing and not causing radiation-related tumor development or malignant transformation. These results are reported in the May issue of the Congress of ...
Global study first to compare COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy among college students
2023-04-18
As the world enters a post-pandemic phase, an international study is providing unique perspectives on COVID-19 vaccine hesitancies among college students.
Researchers from Florida Atlantic University, Ariel University in Israel, and the University of West Bohemia in Pilsen, Czech Republic, are the first to perform a cross-cultural comparison to investigate factors that influenced the decision to get the COVID-19 vaccine in an international sample of college students from the United States, Israel and the Czech Republic.
The study explored associations between vaccine hesitancy and ...
New research may hold key to better treatments for aggressive brain cancer
2023-04-18
Southfield, Mich., April 18, 2023 – For decades, researchers have marveled at the ability of glioblastoma, a particularly aggressive brain cancer, to turn off a patient’s cancer-fighting immune cells, thereby allowing tumors to grow freely. This remains a primary reason why there are very few effective therapies available for this mostly fatal disease.
In a new study using more than 100 patient-derived glioblastoma tumors, Prakash Chinnaiyan, M.D., a physician scientist in the Department of Radiation Oncology at Corewell Health in Southeast, Mich., along with colleague and lead author Pravin Kesarwani, Ph.D., ...
3D printing breakthroughs to accelerate ocular drug delivery, biodegradable contact lenses & pharma research
2023-04-18
WATERLOO, Ontario, April 18, 2023—Scientists from the Centre for Ocular Research & Education (CORE) are poised to unveil multiple advancements in 3D printing next week during the ARVO 2023 Annual Meeting in New Orleans. These innovations have widespread applications, with the potential to accelerate development of drug delivery systems, biodegradable contact lenses, and pharmaceuticals.
“Our multidisciplinary team has created one of the most sophisticated 3D printing environments for ocular research in the world,” said Alex Hui, OD, PhD, FAAO, head of Biosciences at CORE. “This ...
Nullarbor rocks reveal Australia’s transformation from lush to dust
2023-04-18
Curtin researchers have discovered how long ago the Australian Nullarbor plain dried out, with a new approach shedding light on how ancient climate change altered some of the driest regions of our planet.
Iron-rich layers formed in ancient sediments were used to narrow down when an area dried out in response to changes in climate, such as the dramatic decline of groundwater in southern Australia.
These ‘relics of drying’ suggest the Nullarbor drastically shifted to dry conditions between 2.4 and 2.7 million years ago, uncovering how these environmental changes were key in shaping Australia’s diverse ...
Recycled aluminum offers energy, emissions and electric vehicle battery range savings
2023-04-18
RICHLAND, Wash.—Scrap aluminum can now be collected and transformed directly into new vehicle parts using an innovative process being developed by the automotive industry, in particular for electric vehicles. Today, the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, in collaboration with leading mobility technology company Magna, unveils a new manufacturing process that reduces more than 50% of the embodied energy and more than 90% of the carbon dioxide emissions by eliminating the need to mine and refine the same amount of raw aluminum ore. ...
Keys to women’s resilience after 80: more education, less stress
2023-04-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Having a four-year college degree and a low level of stress are strongly linked to psychological resilience in American women aged 80 and older, a new study suggests.
Researchers analyzed data from the Women’s Health Initiative to identify factors that are associated with higher self-rated resilience – the ability to weather storms and rebound from setbacks – among almost 30,000 women with an average age of 84.
Other characteristics linked to higher resilience included stronger social support, higher self-rated health and a lower risk of depression than levels among women ...
Not such small things: Microplastics in our streams
2023-04-18
UC Riverside scientists are taking a modern approach to studying a murky subject — the quantity, quality, and sources of microplastics in Los Angeles County’s urban streams.
Microplastics are particles with a maximum diameter of 5 millimeters, roughly the size of a pencil eraser. The category can include nanoplastics, which are far smaller than the width of an average human hair.
Scientists have been aware that these particles have been filtering through the environment for decades, but concern about them has only started to ramp up more recently.
“There is mounting evidence that these materials are toxic,” said Andrew Gray, UCR assistant professor of ...
Researchers develop carbon-negative concrete
2023-04-18
PULLMAN, Wash. -- A viable formula for a carbon-negative, environmentally friendly concrete that is nearly as strong as regular concrete has been developed at Washington State University.
In a proof-of-concept work, the researchers infused regular cement with environmentally friendly biochar, a type of charcoal made from organic waste, that had been strengthened beforehand with concrete wastewater. The biochar was able to suck up to 23% of its weight in carbon dioxide from the air while still reaching a strength comparable to ordinary cement.
The research could significantly reduce carbon emissions of the concrete industry, which is one ...
Novel score predicts heart failure improvement after atrial fibrillation ablation
2023-04-18
Barcelona, Spain – 18 April 2023: A score based on four readily available clinical and imaging parameters identifies the heart failure patients who benefit most from atrial fibrillation ablation, according to late breaking science presented at EHRA 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
Atrial fibrillation and heart failure often coexist.2 It is estimated that approximately 30% of patients with heart failure will develop atrial fibrillation and patients with atrial fibrillation have a five-fold increased risk of developing heart failure.3 Each condition aggravates the prognosis of the other. Atrial fibrillation patients who develop ...
IOP Publishing expands its open access environmental portfolio with the launch of Environmental Research: Energy
2023-04-18
Responding to the increasing demand for sustainable energy research, IOP Publishing is launching a new open access (OA) environmental research journal. Environmental Research: Energy (EREN) will openly publish the latest findings around clean and sustainable energy for all. Aligned with a number of the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the journal launch comes at a time when research output around renewable energy and sustainability has seen a 600% increase compared to ten years ago.
Environmental Research: Energy is the latest addition to IOP Publishing's expanding Environmental Research ...
Novel ablation strategy improves freedom from arrhythmias in atrial fibrillation patients
2023-04-18
Barcelona, Spain – 18 April 2023: An innovative three-step ablation approach including ethanol infusion of the vein of Marshall improves freedom from arrhythmias in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation compared to pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) alone, according to late breaking science presented at EHRA 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 Preliminary results at 10 months are presented, with follow up ongoing until 12 months.
The cornerstone of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation is complete isolation of the pulmonary veins.2 However, only 50–60% of patients remain in sinus rhythm at two years.3 Numerous ...
Patients with atrial fibrillation have an average of five additional medical conditions
2023-04-18
Barcelona, Spain – 18 April 2023: A novel software tool set to improve the management of elderly atrial fibrillation patients with multiple conditions is being designed by the EU-funded and ESC-coordinated EHRA-PATHS consortium. The latest updates on this clinical innovation will be presented at EHRA 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
Scientific coordinator Professor Hein Heidbuchel said: “EHRA-PATHS is developing a standardised approach to ensure that patients with atrial fibrillation receive evidenced-based therapies for the comorbidities that underlie or complicate their heart rhythm disorder.”
Atrial ...
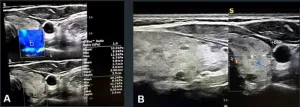
ARRS Annual Meeting: vascularity, elastography in suspicious TIRADS scores differentiate malignant thyroid nodules
2023-04-18
Honolulu, HI | April 18, 2023—Findings from an award-winning Scientific Online Poster presented during the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting on the island of Oahu determined that assessing the vascularity and elastography in suspect TIRADS categories can efficiently diagnose malignancy of thyroid nodules.
Acknowledging that sonographic TIRADS scoring remains the first method of imaging assessment for diagnosing malignant thyroid nodules, “we assessed the added value of shear-wave elastography (SWE) to classic TIRADS assessment,” said Leila Aghaghazvini, MD, from the department of radiology at Shariati Hospital and Iran’s University ...
American Roentgen Ray Society's Roentgen Fund presents 2023 Honorary Lecture, “Advanced High-Resolution CT,” in memory of W. Richard Webb
2023-04-18
Honolulu, HI | April 18, 2023—The American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is pleased to announce that The Roentgen Fund® 2023 Honorary Lecture, “Advanced High-Resolution CT (HRCT),” will be dedicated to W. Richard “Rick” Webb, MD—the late University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) radiologist who transformed the practice of thoracic imaging.
Exploring multiple conditions diagnosed via HRCT, as well as the radiologist’s role on today’s multidisciplinary teams, “Advanced HRCT” will take place on Tuesday, April 18, 2023, 1:00–2:20 PM local time, during the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting in Honolulu, HI.
A high-profile presentation ...
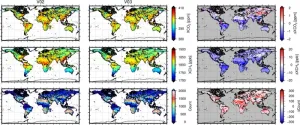
Update on the analysis method to estimate the greenhouse gas concentrations from GOSAT
2023-04-18
1. Background and objectives
The Greenhouse gases Observing SATellite (GOSAT) that is the joint mission of the Ministry of Environment, the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency has observed almost continuously since its launch and is currently in operation.
Thermal And Near-infrared Sensor for carbon Observation – Fourier Transform Spectrometer (TANSO-FTS) onboard GOSAT observes the shortwave infrared (SWIR) spectra(*1). The carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) concentrations can be estimated by ...
Healthcare epidemiologists and infectious diseases experts review changing context for masking in healthcare settings
2023-04-18
The time has come and gone for universal masking in healthcare settings, according to healthcare epidemiologists and infectious diseases experts from healthcare systems throughout Boston and beyond. In a commentary published in Annals of Internal Medicine and co-authored by experts from Mass General Brigham, Beth Israel Lahey Health, Tufts Medicine, the VA Healthcare System Boston, and other healthcare systems across the country, the authors describe the changing context and conditions of the pandemic and outline why universal masking should no longer be required in healthcare settings.
“While critically important in the earlier ...
Cardiac arrest in hospital: survival a matter of resources
2023-04-18
Hospital inpatients have better prospects of surviving a cardiac arrest in large hospitals and well-resourced wards, and daytime cardiac arrests are also associated with better chances of survival, a University of Gothenburg thesis shows.
Cardiac arrest means that the heart stops pumping blood. Within seconds, unconsciousness occurs; within minutes, brain cells start dying, causing irreparable damage.
The key to enhancing the patients’ chances of survival is restoring the circulation of oxygenated blood in the body. ...
[1] ... [1988]
[1989]
[1990]
[1991]
[1992]
[1993]
[1994]
[1995]
1996
[1997]
[1998]
[1999]
[2000]
[2001]
[2002]
[2003]
[2004]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.