Newfound link between Alzheimer’s and iron could lead to new medical interventions
2023-04-19
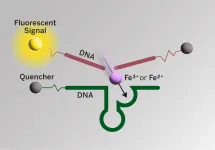
There is a growing body of evidence that iron in the brain may play a role in Alzheimer’s disease. Lending weight to that idea, a new imaging probe has for the first time shown that in the same regions of the brain where the amyloid beta plaques associated with Alzheimer’s occur, there is also an increase in iron redox, meaning the iron in these regions is more reactive in the presence of oxygen. Their imaging probe could yield even more details about the causes of Alzheimer’s and help in the search for new drugs to treat it.
A ...
Scientists identify 2022 sea urchin killer
2023-04-19
TAMPA, Fla. (APRIL 19, 2023) – The search for the 2022 killer that decimated the long-spined sea urchin population in the Caribbean and along Florida’s east coast is over. A team of researchers organized by Mya Breitbart, Distinguished University Professor at the University of South Florida’s College of Marine Science, identified a single-celled organism called a ciliate as the cause of a massive die-off event to a marine animal vital to coral reef health.
Their findings were reported in Science Advances.
“We’re beyond ...
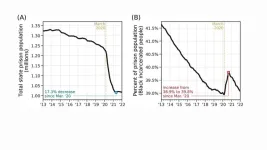
How the pandemic exacerbated racial inequalities in the US criminal legal system
2023-04-19
APRIL 19, 2023
As Covid roared through prisons in 2020, the U.S. prison population fell by as much as 30 percent, creating the largest, fastest reduction in prison population in American history. But this decarceration disproportionately benefited white incarcerated people, sharply increasing the fraction of incarcerated Black and Latino people. A new study in Nature shows that this increased racial disparity in U.S. prisons stems in large part from a long-standing problem with the justice system: Non-white people tend ...
MD Anderson Research Highlights for April 19, 2023
2023-04-19
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include effective combination therapies for patients with BRAFV600E mutations, an approach to identify cancer biomarkers in extracellular vesicles, therapeutic strategies for improving ...
A once-stable glacier in Greenland is now rapidly disappearing
2023-04-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio – As climate change causes ocean temperatures to rise, one of Greenland’s previously most stable glaciers is now retreating at an unprecedented rate, according to a new study.
Led by researchers at The Ohio State University, a team found that between 2018 and 2021, Steenstrup Glacier in Greenland has retreated about 5 miles, thinned about 20%, doubled in the amount of ice it discharges into the ocean, and quadrupled in velocity. According to the study, such a rapid change is so extraordinary ...
The Container Store offers $10,000 in scholarships for Charisma Virtual Social Coaching
2023-04-19
The Container Store, the nation’s leading retailer of storage and organization solutions, custom spaces, and in-home organizing services, will fund $10,000 in scholarships for Charisma™ Virtual Social Coaching, a strengths-based social skills training developed by Center for BrainHealth.
Charisma is a personalized, avatar-driven program that provides real-time, unscripted social coaching in a safe, non-threatening virtual environment. Drawing on extensive cognitive neuroscience research, this program is demonstrated to help people with social challenges to ...
Study seeks to define quantum compression
2023-04-19
A study led by Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers identifies a new potential application in quantum computing that could be part of the next computational revolution.
The study surveys techniques for compressing data generated by sensors in edge computing — which processes data at or near sensors — and compares classical techniques with quantum approaches, which are mostly in development. Compressing data saves storage space and network bandwidth.
Classical computing stores information in bits equal to 0 or 1. Quantum computing stores information in qubits, which can exist ...
Antibody combination provided strong protection against severe COVID-19 in large international trial
2023-04-19
A treatment combining two antibodies against the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 strongly protected high-risk people with early COVID-19 symptoms from hospitalization and death in an international Phase 2/3 clinical trial conducted in the first half of 2021 and co-led by researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian.
The trial, described in a paper appearing online Apr. 18 in Annals of Internal Medicine, enrolled more than 800 non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19 at high-risk of progression of the disease in the United States and ...
Accredited geriatric emergency departments continue to grow within VA hospitals
2023-04-19
WASHINGTON, D.C.—April 19, 2023—The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), the largest integrated healthcare system in the nation, today announced that 60 of its 111 emergency departments have earned Geriatric Emergency Department Accreditation (GEDA) from the American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP). Another 11 departments are on track to earn the designation in coming months and the VA has plans to expand the program to the majority of its hospitals over the next three years.
Geriatric emergency departments provide specialized care to older veterans and their families during and after a ...
NASA selects NAU researcher for international mission to Martian moons
2023-04-19
A planetary scientist at NAU is part of a Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) mission to travel to Mars and survey the planet’s two moons, including collecting a sample from one and returning it to Earth.
Christopher Edwards, an associate professor in the Department of Astronomy and Planetary Science, received a six-year, $650,000 grant for the Martian Moons eXploration (MMX) mission awarded by NASA. This goal is to send an uncrewed spacecraft to Mars’ two moons, Phobos and Deimos, to gather information about them. It also will collect surface material from Phobos, a first-of-its-kind attempt.
Edwards, ...
Warm-up time corrects creativity power imbalance
2023-04-19
ITHACA, N.Y. – Power often boosts an employee’s creativity because being powerful liberates the individual from constraints, such as worrying that their ideas will be rejected. However, new research shows that employees who are not in positions of power can become more creative when given time to “warm up” to a task by engaging in the creative task more than once.
“This is important because when people with more power are able to express their creative ideas more than those with less power, ...
Study finds extreme mortality rate in Central African Republic
2023-04-19
A new study by public health researchers presents stark evidence that the Central African Republic (CAR) is experiencing a severe health and humanitarian emergency, with what is likely the highest measured nationwide mortality rate in the world, a rate four times higher than a 2010 United Nations estimate. The present crisis is linked to the arrival of COVID and its associated disruptions, as well as human rights abuses by the Wagner Group, a Russian paramilitary organization, which seeks to regain national territory after a decades-long hold by rebel groups.
The findings are based on a nationwide mortality survey and appear in the peer-reviewed journal Conflict ...
Georgetown psychologists map the psyche of extreme altruists
2023-04-19
Although many people admire the actions of people who engage in acts of extraordinary altruism, like altruistic organ donors, bone marrow donors, and heroes who rescue people from fires or accidents, they are also often mystified at what motivates these altruists to act.
A new paper from a team of Georgetown researchers aims to answer this question by mapping out the psychological profiles of a range of extreme real-world altruists, like heroic rescuers, humanitarian aid workers, and people who donate organs or bone marrow to strangers at no benefit to themselves.
“After evaluating more than 300 extreme ...
STEMM opportunity alliance announces more than 100 partners
2023-04-19
Washington, D.C. – The STEMM Opportunity Alliance (SOA), a national effort galvanizing stakeholders to achieve equity and excellence in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, and medicine (STEMM) by 2050, announced a milestone of more than 100 partners since its launch at the White House Summit on STEMM Equity and Excellence in December 2022.
Some highlights from SOA’s newest partners and their commitments include:
Johnson & Johnson will continue growing multiple projects ...
Model that uses machine learning methods and patient data at hospital arrival predicts strokes more accurately than current system
2023-04-19
Stroke is among the most dangerous and commonly misdiagnosed medical conditions. Black and Hispanic people, women, older people on Medicare, and people in rural areas are less likely to be diagnosed in time for treatment to be effective. In a new study, researchers used machine learning methods and data available when patients enter the hospital to develop a model that predicts strokes with more accuracy than current models.
The study, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU), Florida International University (FIU), and Santa Clara University (SCU), appears in the Journal of Medical Internet ...
Organic beekeeping rivals conventional methods for bee health, productivity
2023-04-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Honey bee colonies managed using organic methods were as healthy and productive as those managed in conventional systems, while avoiding the use of synthetic pesticides to control pests and pathogens inside the hive, according to newly published research led by Penn State entomologists.
The researchers said they believe that their study, which compared the performance of honey bees under three types of management systems, is the first to show that organic beekeeping management is sustainable and supports high honey-bee survival and honey production.
The methods beekeepers use to manage honey ...
Tribal water rights underutilized in U.S. West
2023-04-19
A new North Carolina State University study shows that Indigenous groups in the western United States are – for various reasons – having difficulty turning water they have a legal right to, under water rights settlements, into actual water that can generate revenue through leases to other groups or through direct uses such as agriculture.
Western tribal water rights are a longstanding, yet underpublicized, component of a large and seemingly intractable problem: how to satisfy all water-rights holders when available ...
Stronger paper bags, reused repeatedly then recycled for biofuel could be future
2023-04-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — As the world searches for ways to reduce the use of plastics such as single-use plastic bags, a novel study by Penn State researchers demonstrates a process to make paper bags stronger — especially when they get wet — to make them a more viable alternative.
The study suggests a process for creating paper bags durable enough to be used multiple times and then broken down chemically by an alkaline treatment to be used as a source for biofuel production, according to researcher Daniel Ciolkosz, associate ...
NSF grant to investigate the role of macrobiota in carbon cycling in estuaries
2023-04-19
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A Penn State-led interdisciplinary team of researchers across six institutions was awarded a $3.5 million grant from the National Science Foundation to investigate the role that macrobiota, such as clams, salt marshes and seagrasses, play in carbon cycling in estuaries.
“Estuaries are highly productive and diverse ecosystems and hence deserve study in their own right,” said Raymond Najjar, professor of oceanography and lead investigator on the project. “But estuaries ...
New blue light technique could enable advances in understanding nanoscale technologies
2023-04-19
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — With a new microscopy technique that uses blue light to measure electrons in semiconductors and other nanoscale materials, a team of Brown University researchers is opening a new realm of possibilities in the study of these critical components, which can help power devices like mobile phones and laptops.
The findings are a first in nanoscale imaging and provide a workaround to a longstanding problem that has greatly limited the study of key phenomena in a wide variety of materials that could one day lead to more energy-efficient semiconductors and electronics. ...
Study finds that child victims of violence face long-term psychological effects
2023-04-19
A study of young adults who were victims of violent injuries as children found significantly higher levels of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in this group than the general population.
The study – conducted by University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) researchers – surveyed 24 respondents who were victims of gunshot, stab, or assault wounds as children between the years of 2011 and 2020. Of the participants, 15 suffered a gunshot wound, eight suffered a stab wound, and one was assaulted. Respondents were primarily teenagers at the time of injury, with a median age of 16.6 years. An average of six years had passed from the initial injury to the time ...
Association for Chemoreception Sciences (AChemS) 45th Annual Meeting
2023-04-19
Bonita Springs, FL— Smell, taste, and chemesthesis are vital chemical senses that contribute to the multidimensional sensation of flavor. Together with other sensory inputs, they allow us to enjoy eating and drinking. Understanding the fundamental mechanisms underlying these sensations is a primary focus of the annual conference of the Association for the Chemoreception Sciences, AChemS XLV. Other key areas include factors that modulate these mechanisms and their impact on fundamental behavior in a wide array of species. Attendees and members of AChemS are leading scientific and biomedical researchers dedicated to better understanding the function ...
As pandemic prison populations fell, proportion of Black prisoners rose
2023-04-19
New Haven, Conn. — The U.S. prison population plummeted during the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic but the percentage of incarcerated Black people rose, according to a new analysis of prison data published April 19 in the journal Nature.
The higher percentage of incarcerated Black people by mid-2020 was found in almost all states, and temporarily reversed a decades-long decrease in the percentage of Black people in the national prison population, researchers from Yale and Northeastern Universities and the Santa Fe Institute found.
While several factors contributed to the increase in percentage of incarcerated Black people during the height of the pandemic, researchers ...
Cannabis exposures in suspected suicide attempts are on the rise
2023-04-19
VANCOUVER, Wash. – Suspected suicidal cannabis exposures have increased 17% annually, over a period of 12 years, according to a Washington State University-led analysis of U.S. poison center data.
The vast majority of the attempts, more than 92%, involved other substances in addition to cannabis, and the data cannot show a direct causal link between cannabis and suicide attempts. Still, the findings are cause for concern, the researchers said, especially since the increase was more pronounced among children and women ...
Mind-body connection is built into brain, study suggests
2023-04-19
Calm body, calm mind, say the practitioners of mindfulness. A new study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis indicates that the idea that the body and mind are inextricably intertwined is more than just an abstraction. The study shows that parts of the brain area that control movement are plugged into networks involved in thinking and planning, and in control of involuntary bodily functions such as blood pressure and heartbeat. The findings represent a literal linkage of body and mind ...
[1] ... [1983]
[1984]
[1985]
[1986]
[1987]
[1988]
[1989]
[1990]
1991
[1992]
[1993]
[1994]
[1995]
[1996]
[1997]
[1998]
[1999]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.