Sugary drink tax improves health, lowers health care costs
2023-04-18
Oakland residents have bought fewer sugary beverages since a local “soda tax” went into effect, and that is likely improving their health and saving the city money, a new UC San Francisco study found.
According to the study publishing April 18 in PLOS Medicine, purchases of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) dropped 26.8% – compared to similar cities not subject to a tax – between July 2017, when the one-cent-per-ounce tax went into effect, and Dec. 31, 2019.
The research comes a little ...
WVU transportation center will bring mobility to rural areas, opening access to country roads
2023-04-18
The upcoming launch of the SMARTER center in the West Virginia University Benjamin M. Statler College of Engineering and Mineral Resources will direct $1.5 million in federal funding toward the development of mobility solutions for transportation challenges faced by rural residents.
Beginning this summer, West Virginia’s SMARTER center — standing for Sustainable Mobility and Accessibility Regional Transportation Equity Research — will position the state to begin taking advantage of cutting-edge technologies like self-driving cars within the next decade, according to lead researcher and assistant ...
Do prescription opioids impact cognitive function in older adults?
2023-04-18
ROCHESTER, Minn. — Prescription opioid use could have a negative effect on cognitive function in older adults, according to a recent Mayo Clinic study published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. The population-based observational study used data from the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging, a research initiative examining the cognitive decline in older people for nearly 20 years.
Findings
The study found that 70% of participants received at least one opioid prescription over an ...
Physics professor receives best paper award
2023-04-18
Wei Chen, professor of physics at The University of Texas at Arlington, is co-author of an article that has received a prestigious best paper award from Bioactive Materials, an international, peer-reviewed research publication.
His study, titled “Nitrogen-doped fluorescence carbon dots as multi-mechanism detection for iodide and curcumin in biological and food samples,” is about the development of nitrogen-doped fluorescent carbon dots as a detection mechanism for iodine and curcumin in food.
The Bioactive Materials best paper award is fully merit-based and is given to researchers who publish articles that make significant ...
New passive device continuously generates electricity during the day or night
2023-04-18
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new thermoelectric generator (TEG) that can continuously generate electricity using heat from the sun and a radiative element that releases heat into the air. Because it works during the day or night and in cloudy conditions, the new self-powered TEG could provide a reliable power source for small electronic devices such as outdoor sensors.
“Traditional power sources like batteries are limited in capacity and require regular replacement or recharging, which can be inconvenient and unsustainable,” said research team leader Jing Liu from Jimei University in China. “Our new TEG design could offer a ...
Casino Guru calls on City, University of London expertise to research and recommend best-practice for self-exclusion standards
2023-04-18
Casino Guru, a global gambling authority with the most extensive database of online casinos, is partnering with City, University of London, to identify best practice in online gambling self-exclusion and to recommend a set of standards for adoption across different jurisdictions.
The origins of the project can be traced back to Casino Guru's Global Self-Exclusion Initiative, launched back in 2020, whose aim is to establish an online self-exclusion scheme on a global scale that would ...
Next decade decisive for PV growth on the path to 2050
2023-04-18
Global experts on solar power strongly urge a commitment to the continued growth of photovoltaic (PV) manufacturing and deployment to power the planet, arguing that lowballing projections for PV growth while waiting for a consensus on other energy pathways or the emergence of technological last-minute miracles “is no longer an option.”
The consensus reached by participants in the 3rd Terawatt Workshop last year follows increasingly large projections from multiple groups around the world on the need for large-scale PV to drive electrification and greenhouse gas reduction. The increasing acceptance of PV ...
AACR: Early trial results show benefits of FGFR inhibitors and PARP/ATR inhibitor combinations in multiple tumor types
2023-04-18
ABSTRACTS: CT016, CT018
ORLANDO, Fla. ― Researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center presented promising findings from multiple clinical trials today at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023. The studies, which describe results from a novel FGFR inhibitor and from new PARP/ATR inhibitor combinations, were featured in a plenary session highlighting novel biomarker-driven molecularly targeted therapy trials. Information on all MD Anderson AACR Annual Meeting content can be found at MDAnderson.org/AACR.
Basket trial results suggest wider population may benefit from FGFR inhibitor pemigatinib ...
Tiny biobattery with 100-year shelf life runs on bacteria
2023-04-18
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- A tiny biobattery that could still work after 100 years has been developed by researchers at Binghamton University, State University of New York.
Last fall, Binghamton University Professor Seokheun “Sean” Choi and his Bioelectronics and Microsystems Laboratory published their research into an ingestible biobattery activated by the Ph factor of the human intestine.
Now, he and PhD student Maryam Rezaie have taken what they learned and incorporated it into new ideas for use outside the body.
A new study in the journal Small, which covers nanotechnology, shares the results from using spore-forming bacteria similar ...
Limited resources leave youth vulnerable to digital abuse
2023-04-18
ITHACA, N.Y. – Youth in the U.S. are targets of cross-platform digital abuse from peers, strangers, offline acquaintances and even relatives, with threats ranging from harassment and sexual violence to financial fraud, according to a new study from Cornell University and Google researchers.
Aided by firsthand accounts, researchers identified the need for more resources to educate youth and parents on digital abuse. They call for better communication and coordination among adult stakeholders in implementing sound protective practices.
“We really need to take a closer look at the types of things that young people are experiencing online, because these experiences ...
In some US schools, 1 in 4 students report misusing prescription stimulants
2023-04-18
U.S. middle and high schools with the most students taking prescription stimulants to treat ADHD also had, overall, the highest percentage of students who misused prescription stimulants within the past year.
The University of Michigan-led study highlights a significant association between ADHD stimulant therapy in schools and prescription stimulant misuse, said Sean Esteban McCabe, U-M professor of nursing and principal investigator on the study.
At some schools, 25% or more of kids reported misusing prescription stimulants in the past year—meaning they used ...
USPSTF statement on screening for skin cancer
2023-04-18
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of visual skin examination by a clinician to screen for skin cancer in adolescents and adults. Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the U.S. There are different types of skin cancer varying in disease incidence and severity. Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the most common types of skin cancer but infrequently lead to death or substantial morbidity. Melanomas represent about 1% of skin cancer and cause the most skin cancer deaths. The USPSTF routinely ...
Association of COVID-19 infection with incident diabetes
2023-04-18
About The Study: In this study of more than 600,000 individuals, SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with a higher risk of diabetes and may have contributed to a 3% to 5% excess burden of diabetes at a population level.
Authors: Naveed Z. Janjua M.B.B.S, Dr.P.H., of the British Columbia Centre for Disease Control in Vancouver, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.8866)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Factors associated with knowledge and experience of self-managed abortion among patients seeking care at abortion clinics
2023-04-18
About The Study: In this survey study of 19,000 patients attending 49 abortion clinics in 29 states, considering self-managed abortion was common before accessing in-clinic care, particularly among those on the margins of access or with a preference for at-home care. These findings suggest a need for expanded access to telemedicine and other decentralized abortion care models.
Authors: Abigail R. A. Aiken, Ph.D., of the University of Texas at Austin, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
School prevalence of stimulant therapy for ADHD associated with higher rates of prescription stimulant misuse among teens
2023-04-18
Researchers have identified a strong association between prevalence of prescription stimulant therapy for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and rates of prescription stimulant misuse (taken in a way other than as directed by a clinician) by students in middle and high schools. The study, which appeared today in JAMA Network Open, highlights the need for assessments and education in schools and communities to prevent medication-sharing among teens. This is especially important considering non-medical use of prescription stimulants among teens remains more prevalent than misuse ...
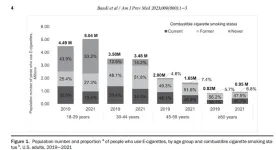
New research shows e-cigarette use up sharply among younger adults in U.S. during EVALI outbreak and COVID-19 pandemic
2023-04-18
ATLANTA, April 18, 2023 – A new study by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) shows almost three-quarters of a million more adults in the United States, ages 18-29 years, used e-cigarettes between 2019-2021 during the period that spanned the EVALI outbreak (E-cigarette or vaping product use–associated lung injury) and COVID-19 pandemic. Scientists report the year-on-year increase was primarily among adults who never smoked cigarettes. The study was published today in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine (AJPM).
“Unfortunately, these numbers show we’re moving in the wrong direction concerning e-cigarette use in this vulnerable ...
Over half of top selling Medicare drugs have low added therapeutic benefit
2023-04-18
Brand-name drugs cost two to three times more in the U.S. than in other countries, but many of the top-selling brand name drugs may provide little added therapeutic benefit. A new study led by researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of Mass General Brigham, used public Medicare data to identify the 50 highest-selling brand-name drugs in 2020. The researchers evaluated their therapeutic benefit compared to existing standards of care, based on ratings from the national health technology assessment (HTA) organizations of Canada, France, and Germany. The team found that 27 of the 50 drugs received ...
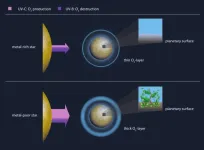
Metal-poor stars are more life-friendly
2023-04-18
Stars that contain comparatively large amounts of heavy elements provide less favourable conditions for the emergence of complex life than metal-poor stars, as scientists from the Max Planck Institutes for Solar System Research and for Chemistry as well as from the University of Göttingen have now found. The team showed how the metallicity of a star is connected to the ability of its planets to surround themselves with a protective ozone layer. Crucial to this is the intensity of the ultraviolet light that the star emits into space, in different wavelength ranges. The study provides scientists searching ...
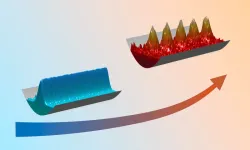
Quantum liquid becomes solid when heated
2023-04-18
Supersolids are a relatively new and exciting area of research. They exhibit both solid and superfluid properties simultaneously. In 2019, three research groups were able to demonstrate this state for the first time beyond doubt in ultracold quantum gases, among them the research group led by Francesca Ferlaino from the Department of Experimental Physics at the University of Innsbruck and the ÖAW Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) in Innsbruck.
In 2021, Francesca Ferlaino's team studied in detail the life cycle of supersolid states ...
Researchers ID gene that shapes heart attack, aneurysm risk
2023-04-18
University of School of Medicine researchers have identified a gene that plays a crucial role in determining our risk for heart attacks, deadly aneurysms, coronary artery disease and other dangerous vascular conditions.
The discovery advances our understanding of the underlying causes of a wide range of serious health conditions, including atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), and moves us closer to new treatments and preventive measures that could help people live longer, healthier lives.
“The first step towards translating the knowledge of population risk for vascular disease is disentangling the fundamental cellular ...
Extreme poverty a key driver for relapse in kids with ALL
2023-04-18
(WASHINGTON, DC, April 18, 2023) – Children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who live in extreme poverty and were undergoing maintenance therapy faced an almost two-fold greater risk of relapse compared with kids who weren’t as poor, according to a study published in today’s issue of Blood. Moreover, a higher proportion of these children had difficulty adhering to treatment, though researchers said this only partially explains the link between poverty and the risk of relapse.
“ALL is a curable disease, so while we observed relatively few relapses in total, children living in extreme poverty – those whose families were really stretched thin and not able ...
Study: vitamin D may play a role in prostate cancer disparities
2023-04-18
Vitamin D deficiency could be the reason African American men experience more aggressive prostate cancer at a younger age compared with European American men, new research from Cedars-Sinai Cancer suggests. The multi-institutional study, published today in Cancer Research Communications, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), could pave the way for revised nutritional guidelines.
While previous research has investigated vitamin D in the context of health disparities, this is the first study to look at its functions in a genome-wide manner in African American versus European American ...
Announcing inaugural Hevolution/AFAR New Investigator Awards in Aging Biology and Geroscience
2023-04-18
New York, New York — The American Federation for Aging Research (AFAR) and Hevolution Foundation are pleased to announce the inaugural Hevolution/AFAR New Investigator Awards in Aging Biology and Geroscience Research recipients. Eighteen three-year awards of US $375,000 each have been granted to support research projects in basic biology of aging or geroscience — a research paradigm based on addressing the biology of ...
Teasing strange matter from the ordinary
2023-04-18
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – In a unique analysis of experimental data, nuclear physicists have made the first-ever observations of how lambda particles, so-called “strange matter,” are produced by a specific process called semi-inclusive deep inelastic scattering (SIDIS). What’s more, these data hint that the building blocks of protons, quarks and gluons, are capable of marching through the atomic nucleus in pairs called diquarks, at least part of the time. These results come from an experiment conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility.
It’s a result that has been ...
Study provides evidence that peer-support groups can be beneficial in reducing healthcare worker stress and burnout
2023-04-18
INDIANAPOLIS – Serving on the front lines in the arduous battle against the coronavirus, emergency department (ED) physicians are among the true heroes of the pandemic, working long, stressful hours at great personal risk, especially in the many months before vaccines became available. A pilot study examining the feasibility, receptivity and preliminary effectiveness of peer-support groups for ED doctors during COVID-19 found this support provided potential benefit in terms of reduction of mental health stresses involved in emergency care during this time.
The researchers assessed change in symptoms of distress, depression and burnout before and after participating ...
[1] ... [1987]
[1988]
[1989]
[1990]
[1991]
[1992]
[1993]
[1994]
1995
[1996]
[1997]
[1998]
[1999]
[2000]
[2001]
[2002]
[2003]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.