Early crop plants were more easily ‘tamed’
2023-04-10
The story of how ancient wolves came to claim a place near the campfire as humanity’s best friend is a familiar tale (even if scientists are still working out some of the specifics). In order to be domesticated, a wild animal must be tamable — capable of living in close proximity to people without exhibiting dangerous aggression or debilitating fear. Taming was the necessary first step in animal domestication, and it is widely known that some animals are easier to tame than others.
But did humans also favor certain wild plants for domestication because they were more easily “tamed”? Research from Washington University in St. ...
Table tennis brain teaser: Playing against robots makes our brains work harder
2023-04-10
Captain of her high school tennis team and a four-year veteran of varsity tennis in college, Amanda Studnicki had been training for this moment for years.
All she had to do now was think small. Like ping pong small.
For weeks, Studnicki, a graduate student at the University of Florida, served and rallied against dozens of players on a table tennis court. Her opponents sported a science-fiction visage, a cap of electrodes streaming off their heads into a backpack as they played against either Studnicki or a ball-serving machine. That cyborg look was vital ...
For chatbots and beyond: Improving lives with data starts with improving machine learning
2023-04-10
You’d be hard pressed to find an industry today that doesn’t use data in some capacity. Whether it's health care workers using data to report the rate of flu infections in a certain state, manufacturers using data to better understand average production times, or even a small coffee shop owner flipping through sales data to learn about the previous month’s bestselling latte, data can reveal patterns and offer insights into our everyday behavior.
All of this data plays a critical role in artificial intelligence ...
Mild COVID during pregnancy does not slow brain development in babies, study finds
2023-04-10
NEW YORK, NY (April 10, 2023)--Columbia researchers have found that babies born to moms who had mild or asymptomatic COVID during pregnancy are normal, based on results from a comprehensive assessment of brain development.
The findings expand on a smaller study that used maternal reports to assess the development of babies born in New York City during the first wave of the pandemic. That study found no differences in brain development between babies who were exposed to COVID in utero and those who were not exposed.
For the new study, the researchers developed a method of observing infants remotely, ...
Kids judge Alexa smarter than Roomba, but say both deserve kindness
2023-04-10
DURHAM, N.C. –- Most kids know it’s wrong to yell or hit someone, even if they don’t always keep their hands to themselves. But what about if that someone’s name is Alexa?
A new study from Duke developmental psychologists asked kids just that, as well as how smart and sensitive they thought the smart speaker Alexa was compared to its floor-dwelling cousin Roomba, an autonomous vacuum.
Four- to eleven-year-olds judged Alexa to have more human-like thoughts and emotions than Roomba. But despite the perceived difference in intelligence, kids felt neither the Roomba nor the Alexa deserve to be yelled at or harmed. That feeling dwindled as kids advanced ...
Hooper creating public database of slaving voyages across the Indian Ocean and Asia
2023-04-10
Jane Hooper, Associate Professor, History, received funding for the project: "Global Passages: Creating a Public Database of Slaving Voyages across the Indian Ocean and Asia."
Hooper, along with three other scholars, has received a three-year digital production grant from the National Endowment for the Humanities to support a major expansion of the open access SlaveVoyages website, available online at https://www.slavevoyages.org. The primary investigators will create an Indian Ocean and Asia (IOA) database of voyages that ...
A new technique opens the door to safer gene editing by reducing the mutation problem in gene therapy
2023-04-10
CRISPR-Cas9 is widely used to edit the genome by studying genes of interest and modifying disease-associated genes. However, this process is associated with side effects including unwanted mutations and toxicity. Therefore, a new technology that reduces these side effects is needed to improve its usefulness in industry and medicine. Now, researchers at Kyushu University in southern Japan and Nagoya University School of Medicine in central Japan have developed an optimized genome-editing method that vastly reduces mutations, opening the door to more effective treatment of genetic diseases with fewer unwanted mutations. Their findings were published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
Genome-editing ...
Medicaid ‘cliff’ adds to racial and ethnic disparities in care for near-poor seniors
2023-04-10
PITTSBURGH, April 10, 2023 – Black and Hispanic older adults whose annual income is slightly above the federal poverty level are more likely than their white peers to face cost-related barriers to accessing health care and filling medications for chronic conditions, according to new research led by a University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health scientist.
Published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, the analysis links these disparities to a Medicaid “cliff” – an abrupt end ...
Potential drug treats fatty liver disease in animal models, brings hope for first human treatment
2023-04-10
A recently developed amino acid compound successfully treats nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in non-human primates — bringing scientists one step closer to the first human treatment for the condition that is rapidly increasing around the world, a study suggests.
Researchers at Michigan Medicine developed DT-109, a glycine-based tripeptide, to treat the severe form of fatty liver disease called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. More commonly known as NASH, the disease causes scarring and inflammation in the liver and is estimated to affect up to 6.5% of the global population.
Results ...
Scientists show how we can anticipate rather than react to extinction in mammals
2023-04-10
Most conservation efforts are reactive. Typically, a species must reach threatened status before action is taken to prevent extinction, such as establishing protected areas. A new study published in the journal Current Biology on April 10 shows that we can use existing conservation data to predict which currently unthreatened species could become threatened and take proactive action to prevent their decline before it is too late.
“Conservation funding is really limited,” says lead author Marcel Cardillo (@MarcelCardillo) of Australian National University. “Ideally, what we need is some way of anticipating species that may not be threatened ...
This elephant’s self-taught banana peeling offers glimpse of elephants’ broader abilities
2023-04-10
Elephants like to eat bananas, but they don’t usually peel them first in the way humans do. A new report in the journal Current Biology on April 10, however, shows that one very special Asian elephant named Pang Pha picked up banana peeling all on her own while living at the Berlin Zoo. She reserves it for yellow-brown bananas, first breaking the banana before shaking out and collecting the pulp, leaving the thick peel behind.
The female elephant most likely learned the unusual peeling behavior ...
Health care access, affordability among adults with self-reported post–COVID-19 condition
2023-04-10
About The Study: In this survey study of 9,400 adults ages 18 to 64, a higher rate of respondents with self-reported post–COVID-19 condition (PCC; also known as long COVID) did not obtain needed health care in the past year because of cost compared with adults without PCC. Adults with PCC were also more likely to have unmet needs because of difficulties getting timely appointments or health plan authorization, among other challenges with health care institutions or health insurance. These findings suggest that improved health care access for adults with PCC may require developing clinical protocols and addressing insurance-related barriers.
Authors: Michael ...
Changes in children’s screen time during pandemic
2023-04-10
About The Study: The largest increase in children’s recreational screen time during the pandemic was on weekdays, especially at the outset of the pandemic when schools were closed; this increase was greater than expected for age-related growth. Change in weekend screen time during the pandemic was not significant compared with weekday screen time. Once in-person school resumed, weekday screen time decreased versus that during the COVID-1 wave (spring 2020), although it remained consistently higher than pre-pandemic estimates and age-related expectations.
Authors: Sheri Madigan, Ph.D., of the University of Calgary in Calgary, Canada, is the corresponding ...
Study: Shutting down nuclear power could increase air pollution
2023-04-10
Nearly 20 percent of today’s electricity in the United States comes from nuclear power. The U.S. has the largest nuclear fleet in the world, with 92 reactors scattered around the country. Many of these power plants have run for more than half a century and are approaching the end of their expected lifetimes.
Policymakers are debating whether to retire the aging reactors or reinforce their structures to continue producing nuclear energy, which many consider a low-carbon alternative to climate-warming coal, oil, and natural gas.
Now, MIT researchers say there’s another factor to consider in weighing the future of nuclear power: ...
Study shows involuntary displacement of people experiencing homelessness may cause significant spikes in mortality, overdoses and hospitalizations
2023-04-10
AURORA, Colo. (April 10, 2023) – Involuntary displacement of people experiencing homelessness will likely lead to a substantial increase in morbidity and mortality over a 10-year period.
In a study, published today in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), researchers say practices such as encampment sweeps, bans, move-along-orders and cleanups that forcibly relocate individuals away from essential services will lead to substantial increases in overdose deaths, life threatening infections and hospitalizations.
In coordination with the National Healthcare for Homeless Council, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Foundation ...
Protein Beclin-1 is a major player in uterine remodeling and the establishment of pregnancy
2023-04-10
Throughout a woman's reproductive life, the endometrium, the mucous membrane lining the uterus, goes through cyclical remodeling. It thickens during the menstrual cycle in preparation for embryo implantation, and it is shed during menstruation when there is no fertilization.
Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine and collaborating institutions are investigating little-known factors directing uterine remodeling to advance the understanding of this process and provide new insights into fertility-associated gynecological conditions. They report today in the journal Developmental ...
Scientists map gusty winds in a far-off neutron star system
2023-04-10
An accretion disk is a colossal whirlpool of gas and dust that gathers around a black hole or a neutron star like cotton candy as it pulls in material from a nearby star. As the disk spins, it whips up powerful winds that push and pull on the sprawling, rotating plasma. These massive outflows can affect the surroundings of black holes by heating and blowing away the gas and dust around them.
At immense scales, “disk winds” can offer clues to how supermassive black holes shape entire galaxies. Astronomers have observed signs of disk winds in many systems, ...
Health effects of involuntary displacement of homeless individuals who inject drugs
2023-04-10
About The Study: This simulation modeling study of 23 U.S. cities projects that involuntary displacement of people experiencing homelessness who inject drugs may yield substantial increases in morbidity and mortality over a 10-year period. Involuntary displacement is estimated to worsen overdose and hospitalizations, decrease initiations of medications for opioid use disorder, and contribute to deaths. These findings have implications for the practice of involuntary displacement, as well as policies such as access to housing and supportive services, that could mitigate these harms.
Authors: Joshua A. Barocas, M.D., ...
Bariatric surgery may reverse diabetes complications for people with obesity
2023-04-10
For more than 100 million Americans who are obese, bariatric surgery may reverse complications related to diabetes, including regenerating damaged nerves, a Michigan Medicine study shows.
A research team led by the University of Michigan Health Department of Neurology followed more than 120 patients who underwent bariatric surgery for obesity over two years after the procedure. They found that all metabolic risk factors for developing diabetes, such as high glucose and lipid levels, improved outside of blood pressure and total cholesterol, according to results published in Diabetologia.
Investigators ...
What is it good for? Absolutely one thing. Luna moths use their tails solely for bat evasion
2023-04-10
In a pair of complementary studies, researchers took a close look at Luna moth (Actias luna) tails through the eyes of birds and female moths to test the tails’ role in predation and sexual selection. Scientists have known for about a decade that Luna moths — and other related silkmoths — use their long, trailing tails to misdirect bat attacks.
“They have projections off the back of the hindwing that end in twisted, cupped paddles,” said Juliette Rubin, a doctoral student at the Florida Museum ...
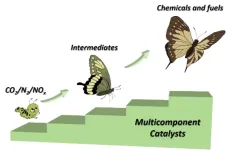
Breaking inert bonds: Multicomponent catalysts pave the way for green chemistry and green carbon science
2023-04-10
The chemical industry has played a significant role in the development of society, but its impact on the environment has become a growing concern. Green chemistry and chemical engineering have opened up possibilities for sustainability through the transformation of renewable feedstocks into environmentally friendly chemicals. However, the inert bonds in molecules such as CO2 and N2 present challenges to their activation and conversion.
Electrochemical conversion provides a promising carbon-neutral route to upgrading green chemical sources with inert bonds to chemicals and fuels under ambient conditions. Multicomponent electrocatalysts have advantages over monocomponent catalysts, ...
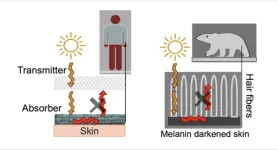
New textile unravels warmth-trapping secrets of polar bear fur
2023-04-10
AMHERST, Mass. – Three engineers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst have invented a fabric that concludes the 80-year quest to make a synthetic textile modeled on Polar bear fur. The results, published recently in the journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, are already being developed into commercially available products.
Polar bears live in some of the harshest conditions on earth, shrugging off Arctic temperatures as low as -50 Fahrenheit. While the bears have many adaptations that allow them to thrive when the temperature plummets, since the 1940s scientists have focused on one in particular: their fur. How, the scientific community ...
Navigating the cosmos with Georgia State’s CHARA Array
2023-04-10
ATLANTA—Plans are underway to add a seventh movable telescope to Georgia State University’s Center for High Angular Resolution Astronomy— known as the CHARA Array—that would increase the resolution, or the ability to see small objects, by a factor of three.
Located at Mount Wilson Observatory in Southern California and operated by Georgia State, the new telescope will be connected using fiber optics to transport the starlight, a technique that will serve as a pathfinder ...
BU doc honored by the Association of University Radiologists
2023-04-10
(Boston)— Priscilla J. Slanetz, MD, MPH, professor of radiology at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, was awarded the 2023 Association of Program Directors in Radiology (APDR) Achievement Award at the Association of University Radiologists’ annual meeting. The honor is given for outstanding service to APDR or to someone who has made significant contributions to the advancement of education in radiology.
Slanetz is a practicing breast radiologist at Boston Medical Center specializing in all aspects of breast imaging including screening, diagnostic evaluation and image-guided intervention, providing breast care to Boston’s most vulnerable ...
BU researcher awarded $1.5 million NIH grant
2023-04-10
Boston—Esther Bullitt, PhD, associate professor of pharmacology, physiology & biophysics at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, was awarded $1.5 million from the National Institutes of Health that will go toward the purchase of a cryogenic electron microscope. Additional funds have been pledged by University President Robert A. Brown and Professor and Chair of Pharmacology, Physiology & Biophysics Venetia Zachariou, PhD.
The FEI ThermoFisher Glacios-2 cryo-EM is capable of determining structures at near-atomic resolution. Researchers will use this new instrumentation to study cellular function and dysfunction, and to guide ...
[1] ... [1992]
[1993]
[1994]
[1995]
[1996]
[1997]
[1998]
[1999]
2000
[2001]
[2002]
[2003]
[2004]
[2005]
[2006]
[2007]
[2008]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.