One brain, multiple and simultaneous alternative decision strategies
2023-04-13
Choosing a checkout line in a supermarket might seem like a no-brainer, but it can actually involve a complex series of cerebral computations. Maybe you count the number of shoppers in each line and pick the shortest, or estimate the number of items on each conveyor belt. Perhaps you quickly weigh up both shoppers and items and maybe even the apparent speed of the cashier... In fact, there are a multiplicity of strategies for solving this problem.
So how does the brain know how to make decisions ...
Researchers warn of tick-borne disease babesiosis
2023-04-13
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- 'Tis the season for hiking now that spring has arrived and temperatures are on the upswing. But with hikes come insect bites and on the increase in North America is babesiosis, a malaria-like disease spread especially between May and October by a tick.
Indeed, recent research suggests an increase in the incidence of diseases transmitted by ticks around the world, not just the United States and Canada, due likely to climate change and other environmental factors. Among the tick-borne pathogens, Babesia parasites, which infect and destroy red blood cells, are considered a serious ...
Where did the first sugars come from?
2023-04-13
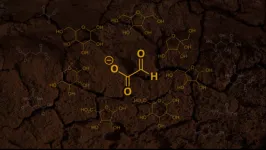
LA JOLLA, CA— Two prominent origin-of-life chemists have published a new hypothesis for how the first sugars—which were necessary for life to evolve—arose on the early Earth.
In a paper that appeared on April 13, 2023, in the journal Chem, the chemists from Scripps Research and the Georgia Institute of Technology propose that key sugars needed for making early life forms could have emerged from reactions involving glyoxylate (C2HO3–), a relatively simple chemical that plausibly existed on the Earth before life evolved.
“We show that our new hypothesis has key advantages over the more traditional view ...
Conservation: Red-throated loons avoid North Sea windfarms
2023-04-13
Offshore wind farms in the North Sea reduce the population of loons –fish-eating aquatic birds also known as divers – by 94% within a one-kilometre zone, according to new research published in Scientific Reports. The findings highlight the need to minimise the impact of offshore wind farms on seabirds, while balancing this effort with the demand for renewable energy.
Previous research has found that different seabird species respond to offshore windfarms differently – they may avoid the area which can lead to habitat displacement or they may be attracted to the area which can increase mortality via collisions with the turbines. However, it is difficult ...
Why orchid bees concoct their own fragrance
2023-04-13
Male bees display a remarkable passion for collecting scents: they deposit scents from various sources in special pockets on their hind legs, thus composing their own fragrance. This behaviour has been known since the 1960s. The reason why they do it has been the subject of much speculation just as long. Researchers from Ruhr University Bochum, Germany, in collaboration with colleagues from the University of California at Davis and the University of Florida at Fort Lauderdale, have finally solved the mystery. The bee fragrance serves as a sex attractant and increases the reproductive success of the males, as the team found out after three years ...
Uncovering hidden mitochondrial mutations in single cells
2023-04-13
A high-throughput single-cell single-mitochondrial genome sequencing technology known as iMiGseq has provided new insights into mutations of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and offers a platform for assessing mtDNA editing strategies and genetic diagnosis of embryos prior to their implantation.
An international team of researchers, led by KAUST stem cell biologist Mo Li, has now quantitatively depicted the genetic maps of mtDNA in single human oocytes (immature eggs) and blastoids (stem cell-based synthetic embryos)[1]. This has revealed molecular features of rare mtDNA mutations that cause maternally inherited diseases.
Mitochondria, the ...
Effectiveness of COVID-19 mRNA vaccination for children and adolescents confirmed by multi-state study
2023-04-13
A multi-state study from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC’s) VISION Network confirms that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine has provided children and adolescents, ages 5-17, with protection against both moderate and severe COVID-19 outcomes.
The study found that for 12-17 year olds, vaccine effectiveness was high against the Delta variant but lower during Omicron dominance, including BA.4 and BA.5. Due to the youngest age (5-11) group’s ineligibility for vaccination during Delta predominance, vaccine effectiveness could be estimated for these children only during the Omicron predominant ...
Four early-career cancer researchers earn prestigious annual award from NCCN Foundation
2023-04-13
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [April 13, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) and the NCCN Foundation® today announced four winners for the 2023 NCCN Foundation Young Investigator Awards. These annual awards honor up-and-coming leaders in oncology research working to investigate and advance cancer care. The honorees will each receive up to $150,000 in funding for projects that will run over two years. The selection process is overseen by the NCCN Oncology Research Program (ORP) which will also provide oversight.
“It is a privilege to support these emerging innovators ...
Some people may be attracted to others over minimal similarities
2023-04-13
We are often attracted to others with whom we share an interest, but that attraction may be based on an erroneous belief that such shared interests reflect a deeper and more fundamental similarity—we share an essence—according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Our attraction to people who share our attributes is aided by the belief that those shared attributes are driven by something deep within us: one’s essence,” said lead author Charles Chu, PhD, an assistant professor at the Boston University Questrom School of Business. “To put it concretely, we like someone who agrees with us on a political issue, shares our music ...
The Biophysical Journal launches Postdoctoral Reviewer Program
2023-04-13
Today the Biophysical Journal is launching a new initiative, the Postdoctoral Reviewer Program. The program provides postdoctoral researchers in biophysics the opportunity to partner with Associate Editors and complete reviews that will be used in deciding whether articles will be accepted for publication.
Candidates for this program must be in a postdoctoral position during the 2023–2024 academic year and a member of BPS in good standing. Applications for the new program will be accepted through July 1 for a single-year term beginning in September 2023. Interested candidates can find more information about the program and application process online.
“I am extremely ...
Scientists create high-efficiency sustainable solar cells for IoT devices with AI-powered energy management
2023-04-13
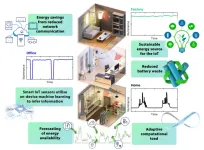
Newcastle University researchers have created environmentally-friendly, high-efficiency photovoltaic cells that harness ambient light to power internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Led by Dr Marina Freitag, the research group from the from School of Natural and Environmental Sciences (SNES) created dye-sensitized photovoltaic cells based on a copper(II/I) electrolyte, achieving an unprecedented power conversion efficiency of 38% and 1.0V open-circuit voltage at 1,000 lux (fluorescent lamp). The cells are non-toxic and environmentally friendly, setting a new standard for sustainable ...
A sharper look at the M87 black hole
2023-04-13
The iconic image of the supermassive black hole at the center of M87—sometimes referred to as the “fuzzy, orange donut”—has gotten its first official makeover with the help of machine learning. The new image further exposes a central region that is larger and darker, surrounded by the bright accreting gas shaped like a “skinny donut.” The team used the data obtained by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration in 2017 and achieved, for the first time, the full resolution of the array.
In 2017, the EHT collaboration used a network of seven pre-existing telescopes ...
Gentle method allows for eco-friendly recycling of solar cells
2023-04-13
By using a new method, precious metals can be efficiently recovered from thin-film solar cells. This is shown by new research from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden. The method is also more environmentally friendly than previous methods of recycling and paves the way for more flexible and highly efficient solar cells.
Today there are two mainstream types of solar cells. The most common is silicon-based and accounts for 90 percent of the market. The other type is called thin-film solar cells which in turn uses three main sub-technologies, one of which is known as CIGS ...
Infant formulas promise too much
2023-04-13
Many infant formulas promise a lot. Several products claim that they help develop the brain, increase immunity and promote children's growth and development, among other things.
Now a research group led by Imperial College London has looked at whether these promises have any substance to them. The article has recently been published in BMJ.
“Most of the claims about the health-giving and nutritional properties of breast milk substitutes seem to be based on little or no evidence,” the research group says.
Claims surrounding these replacement milk products are controversial. They can give the impression ...
CESJ selected for the ERC grant to launch a European program of science journalists in residence
2023-04-13
Milan (Italy), 13 April 2023 – The Center for Ethics in Science and Science Journalism (CESJ, www.cesj.eu) is among the partners of the FRONTIERS consortium that was selected by the European Research Council for a grant of 1.5 million euro to establish a residency program for science journalists in research institutions across Europe, and measure its impact on the lifelong professional development of science journalism in Europe. The consortium also includes the NOVA University of Lisbon (Portugal), ...
Living through high inflation increases home ownership
2023-04-13
People who experience periods of high inflation are more likely to buy a home, according to a new study from the University of California San Diego’s Rady School of Management.
The paper, to be published in The Journal of Finance, uses various sources of data which reveal households that have been exposed to high inflation are more likely to invest in real estate. The study suggests many homeowners buy because they are motivated to protect themselves from possible future price hikes.
The study is the first to reveal that personal ...
Eastern wolves evolved separately from grey wolves
2023-04-13
A new paper in Molecular Biology and Evolution, published by Oxford University Press, provides interesting new evidence about the evolution of North American wolves, which has been a subject of debate among conservationists and taxonomists.
Southeastern Canada is home to populations of wolves and coyotes whose origins and genetic relationships have long puzzled scientists. In particular, eastern wolves have been the subject of great dispute, and it remains unknown whether these canids represent ...
Visualizing differences in nuclear structure
2023-04-13
Helium usually has two protons and two neutrons strongly bound to each other, often forming a substructure within the nucleus. A nucleus composed of several such substructures is called a cluster structure. In the standard picture, nuclei are difficult to understand in terms of so-called shell structure; because there was no way to clearly distinguish whether each nucleus has a cluster or a shell structure.
Associate Professor Wataru Horiuchi and Professor Naoyuki Itagaki from the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Science, have developed an ...
The Lancet Neurology: Identifying ‘hallmark’ Parkinson’s disease protein build-up could aid early detection and pave way for improved diagnosis and treatment
2023-04-13
Cross-sectional study of 1,123 participants confirms α-synuclein seed amplification assay (αSyn-SAA) technique is highly accurate at identifying people with Parkinson’s disease.
The technique detects at-risk individuals and those with early, non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease prior to diagnosis, suggesting that a positive result on αSyn-SAA may be an early indicator of disease onset.
Differences in the frequency of a positive αSyn-SAA result were detected based on age and sex, and if people ...
Free trade deal is a major threat to UK public health, warn experts
2023-04-13
The UK’s decision to join one of the world’s largest free trade agreements, known as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement on Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), poses a major threat to UK public health, warn experts in The BMJ today.
In acceding to the CPTPP, the government hopes to boost trade, improve economic growth, and strengthen the UK’s strategic position as a global rule setter.
But Courtney McNamara and colleagues argue that free trade deals have serious and wide ranging implications for public health and ...
Female healthworkers need better radiation protection to minimise breast cancer risk
2023-04-13
Women working in healthcare who are regularly exposed to radiation from x-rays and other imaging procedures need better ionising radiation protection to help minimise their risk of developing breast cancer, argue doctors in The BMJ today.
Ionising radiation is a known human carcinogen and breast tissue is highly radiation sensitive. As such, there are concerns that regular exposure to ionising radiation during image guided procedures may be linked to a higher risk of breast cancer in female healthcare workers.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) such as lead gowns are used to shield the body from harmful radiation during these ...
Higher dose corticosteroids associated with a 60% increased risk of death in hypoxic COVID-19 patients requiring only non-invasive oxygen therapy (The Lancet / RECOVERY trial)
2023-04-13
*Note: this is a joint press release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) and The Lancet. Please credit both the congress and the journal in your stories*
A new study to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen 15-18 April), and published in The Lancet, shows that, compared with standard care that included low dose corticosteroid use, treating hypoxic COVID-19 patients needing ...
Assisted reproduction kids grow up just fine – but it may be better to tell them early about biological origins, twenty-year study suggests
2023-04-13
Paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1y9GfgYkRdUtwyq6nBhySePTUHZYP6iAj?usp=share_link
Landmark study finds no difference in psychological wellbeing or quality of family relationships between children born by assisted reproduction (egg or sperm donation or surrogacy) and those born naturally at age 20.
However, findings suggest that telling children about their biological origins early – before they start school – can be advantageous for family relationships and healthy adjustment.
The study, by University of Cambridge researchers, is the first to examine the long-term ...
The hidden culprit behind nitrogen dioxide emissions
2023-04-13
Nitrogen dioxide is one of the criteria air pollutants that plays an important role as a precursor gas of fine particulate matter and ozone. NO2 emissions are known to be primarily generated by industrial facilities or vehicle exhausts. Recently, a research team from POSTECH analyzed satellite remote sensing data from the European Space Agency (ESA) and released results showing that food processing facilities and high-rise apartments that are 10 stories or higher are significant sources of NO2 emissions. Their findings have drawn attention from NASA.
A ...
Notable birth cohort effects on the incidence trend of renal replacement therapy in Japan
2023-04-13
Niigata, Japan - A new Japanese study reveals significant birth cohort effects on the incidence trend of ESKD requiring RRT.
“Different birth cohorts may have different levels of exposure to a particular risk factor, which may produce a change in disease incidence for individuals born at a particular time, i.e. a cohort effect,” said Dr. Wakasugi, the corresponding author of the study. “Age-Period-Cohort (APC) analysis, a statistical method to distinguish between age, period, and ...
[1] ... [1997]
[1998]
[1999]
[2000]
[2001]
[2002]
[2003]
[2004]
2005
[2006]
[2007]
[2008]
[2009]
[2010]
[2011]
[2012]
[2013]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.