Aston University biomass expert calls for more exploration of power bioenergy with carbon capture and storage
2023-04-04
Professor Patricia Thornley welcomes latest UK energy security plans
But calls for more exploration of bioenergy with carbon capture and storage
She believes plans shouldn’t concentrate solely on energy such as wind and solar power.
A leading biomass scientist at Aston University has welcomed the government’s announcement to ensure UK energy is more secure.
However, Professor Patricia Thornley, director of Aston University’s Energy and Bioproducts Research Institute (EBRI), believes the government ...
DMI allows magnon-magnon coupling in hybrid perovskites
2023-04-04
An international group of researchers has created a mixed magnon state in an organic hybrid perovskite material by utilizing the Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya-Interaction (DMI). The resulting material has potential for processing and storing quantum computing information. The work also expands the number of potential materials that can be used to create hybrid magnonic systems.
In magnetic materials, quasi-particles called magnons direct the electron spin within the material. There are two types of magnons – optical and acoustic – which refer to the direction of their spin.
“Both optical and acoustic magnons propagate ...
New study in JNCCN identifies approach for improving end-of-life conversations for people with cancer
2023-04-04
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [April 4, 2023] — New research in the April 2023 issue of JNCCN—Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network finds that specially trained oncology infusion room nurses can improve advance care planning (ACP) for patients with advanced cancer. In this study, oncology nurses underwent an immersive, three-day training session on palliative care. As compared to patients who received standard care, those who participated in this targeted and specialized intervention had a ...
Those who support Black Lives Matter tend to be less hesitant about vaccines, UCLA study finds
2023-04-04
Efforts to encourage vaccination might do well to take advantage of the positive feelings and actions between different social groups, according to a study of attitudes toward vaccines among supporters of the Black Lives Matter movement.
The study by UCLA psychologists, published in the journal Social Science and Medicine, found that across all racial, ethnic and income groups, people who expressed support for the BLM movement were less hesitant about receiving COVID-19 vaccines than those who did not. The evidence suggests that altruistic feelings about interactions between ...
Women’s geographic access to fertility treatment “significantly higher” in the richest parts of Britain, analysis shows
2023-04-04
Geographic access to IVF and other fertility services is significantly higher in the richest parts of Britain, a new study shows.
Researchers have warned the current locations of clinics is likely reducing opportunities for those living in more deprived parts of the country to get fertility treatment.
Opportunities to have a baby may thus be influenced by a geographical lottery.
In 2020 nearly a fifth of local authorities did not have fertility clinics within a radius of 25km, meaning 1.6m women of reproductive ages had no assisted fertility ...
Was plate tectonics occurring when life first formed on Earth?
2023-04-04
Earth is a dynamic and constantly changing planet. From the formation of mountains and oceans to the eruption of volcanoes, the surface of our planet is in a constant state of flux. At the heart of these changes lies the powerful force of plate tectonics—the movements of Earth’s crustal plates. This fundamental process has shaped the current topography of our planet and continues to play a role in its future.
But what was plate tectonic activity like during early Earth? And was the process even occurring during the time when life is thought to have formed?
“The dynamic tectonic ...
AI tool gains doctors’ trust by giving advice like a colleague
2023-04-04
ITHACA, N.Y. – A new Cornell University-led study suggests that if artificial intelligence tools can counsel a doctor like a colleague – pointing out relevant research that supports the decision – then doctors can better weigh the merits of the recommendation.
The researchers will present the new study in April at the Association for Computing Machinery CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems.
Previously, most AI researchers have tried to help doctors evaluate suggestions from decision support tools by explaining how the underlying algorithm works, or what data was used to train the AI. But an ...
The American College of Chest Physicians warns of impact of Braidwood Management ruling
2023-04-04
The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) opposes the federal court’s March 30, 2023, ruling in Braidwood Management Inc. v. Becerra and applauds the Department of Justice for acting so swiftly to appeal this decision. Judge O’Connor’s remedies strip the guarantee of no-cost preventative benefits away from the 151 million people insured by the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and currently have access to care, such as smoking cessation services, guideline-indicated lung cancer screening, and tuberculosis testing.
“CHEST’s ...
Chen Institute partners with ISSCR to establish fellowship for Stem Cell Reports Early Career Editorial Board
2023-04-04
The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) is delighted to announce a partnership with the Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute, establishing a fellowship program to support members of the Stem Cell Reports Early Career Editorial Board (ECEB). The program facilitates attendance at the ISSCR Annual Meeting, mentoring opportunities, and the development of scientific programs that will cultivate and deepen leadership skills.
The Chen Institute Fellowship is designed to directly support ECEB members financially and in career growth. Broadly, activities supported by ...
Oncotarget at AACR Annual Meeting 2023
2023-04-04
Impact Journals (Oncotarget's publisher) is proud to participate at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023, which convenes April 14-19 in Orlando, Florida.
BUFFALO, NY-April 4, 2023 – Impact Journals will be participating as an exhibitor at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023 from April 14-19 at the Orange County Convention Center in Orlando, Florida. This year, the AACR meeting theme is: “Advancing ...
Forsyth microbiologists discover a regulatory mechanism that keeps cancer-causing bacteria in check
2023-04-04
Cambridge, Mass. - Researchers at the Forsyth Institute have discovered an important mechanism that may have profound implications for how we prevent colorectal cancer. Oddly enough, their discovery began in the mouth.
Colorectal cancer is the second most deadly cancer, killing over 52,000 people a year. Increasing evidence indicates Fusobacterium nucleatum, an opportunistic oral pathogen is one of the factors causing colorectal cancer. Fusobacteria are often found in healthy mouths, living in balance ...
Traumatic brain injury interferes with immune system cells’ recycling process in brain cells
2023-04-04
Each year about 1.5 million people in the U.S. survive a traumatic brain injury due to a fall, car accident, or a sports injury, which can cause immediate and long-term disability.
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers wanted to better understand what happens in the brain during injury, so they conducted a study in mice to determine how different types of brain cells in mice react to severe trauma. In a new study published in the January issue of Autophagy, they found that after traumatic brain injury, the brain’s immune system cells’ internal recycling ...
Rats! Rodents seem to make the same logical errors humans do
2023-04-04
Animals, like humans, appear to be troubled by a Linda problem.
The famous “Linda problem” was designed by psychologists to illustrate how people fall prey to what is known as the conjunction fallacy: the incorrect reasoning that if two events sometimes occur in conjunction, they are more likely to occur together than either event is to occur alone.
Now, for the first time, UCLA psychology researchers have shown that this type of logical error isn’t the sole province of humans ...
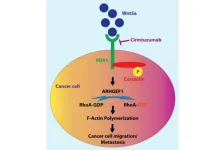
Impact of cortactin in cancer progression
2023-04-04
“Cortactin (also known as EMS1 or CTTN) is expressed broadly in a variety of cancers [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- April 4, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 21, 2023, entitled, “Impact of cortactin in cancer progression on Wnt5a/ROR1 signaling pathway.”
In this editorial, researchers Kamrul Hasan and Thomas J. Kipps from the University of California discuss cortactin—an intracellular cytoskeletal protein that can undergo tyrosine phosphorylation upon external stimulation and promote polymerization and the assembly of the actin filament that is required for cell migration. Upon stimulation, cortactin ...
Male beetles neglect their genomes when competing for females
2023-04-04
Male beetles face a trade-off between competing with other males for mating opportunities and repairing damage to their sperm DNA, according to a study publishing April 4th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Mareike Koppik from Uppsala University, Sweden, and colleagues.
Mutations in sperm and egg DNA can reduce the survival and fitness of offspring, so animals use a variety of repair and maintenance mechanisms in their reproductive cells. However, previous research has shown that sperm DNA has more mutations than egg DNA in a variety of ...
Studies ask: what does “multimorbidity” mean and how much does it cost us?
2023-04-04
The prevalence of multimorbidity, the co-occurrence of two or more chronic conditions, varies depending on exactly how it is defined. And the healthcare costs associated with many disease combinations cost more together than the sum of each individual disease. Those are the conclusions of two new studies, publishing April 4th in the open access journal PLOS Medicine, that broadly analyze the concept and costs of multimorbidity.
Multimorbidity is increasing in prevalence due to improved survival from chronic diseases and population aging, and now poses major challenges to healthcare systems worldwide. ...
SCI Canada Awards event to showcase country’s diverse scientific talent from Nunavut to Ontario
2023-04-04
SCI Canada Awards 2023 dinner, seminar and presentations to take place on 18 April in Toronto
Seminar theme is ‘Unlocking the potential of science talent enabling impact on Canada’s economic growth’
Award winners include the first indigenous community members
Dr Paul Smith, Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, will receive the 2023 Canada Medal
A panel representing the best of Canadian science and industry will discuss its role in boosting economic growth at a special awards event on 18 April in Toronto.
Winners of the 2023 SCI Canada Awards include ...
Scientists use computational modeling to design “ultrastable” materials
2023-04-04
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Materials known as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have a rigid, cage-like structure that lends itself to a variety of applications, from gas storage to drug delivery. By changing the building blocks that go into the materials, or the way they are arranged, researchers can design MOFs suited to different uses.
However, not all possible MOF structures are stable enough to be deployed for applications such as catalyzing reactions or storing gases. To help researchers figure out which MOF structures might work best for a given application, MIT researchers have developed a computational approach that allows ...
Why do females prefer ornate male signals?
2023-04-04
Sexual selection provides an answer to the existence of lavishly ornate signals in animals, but not to the question of why such signals are attractive, why do females prefer the extravagant plumage of peacocks? As part of an international team, researchers at Eötvös Loránd University (ELTE) have shown that the reason is not the presumed wasteful cost of ornaments, as honest signals need not have to be costly at all as long as cheaters would have to pay to fake them. Researchers have developed a general formula to calculate honest equilibrium in any model, independent of the cost ...
How an autism gene contributes to infertility
2023-04-04
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- A University of California, Riverside, study has identified the biological underpinnings of a reproductive disorder caused by the mutation of a gene. This gene mutation also causes Fragile X Syndrome, a leading genetic cause of intellectual impairment and autism.
The researchers found mutations of the Fragile X messenger ribonucleoprotein 1 gene, or FMR1, contribute to premature ovarian failure, or POF, due to changes in neurons that regulate reproduction in the brain and ovaries. The mutation has been associated with early infertility, due ...
Penn Medicine researchers develop model to predict cardiovascular risk among chronic kidney disease patients
2023-04-04
PHILADELPHIA — Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a strong cardiovascular risk factor and is often accompanied by hypertension and diabetes. Despite the disease’s prevalence—10 percent of individuals across the globe suffer from CKD—there are limited tools for measuring cardiac risk for CKD patients, until now. A new proteomic risk model for cardiovascular disease was found to be more accurate than current methods of measuring cardiac risk, according to a new study led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The study published today in the European Heart Journal.
The Penn researchers developed ...
Overwhelmed? Your astrocytes can help with that
2023-04-04
How Little-Known Brain Cells Tamp Down Overexcited Neurons During Acute Stress
A brimming inbox on Monday morning sets your head spinning. You take a moment to breathe and your mind clears enough to survey the emails one by one. This calming effect occurs thanks to a newly discovered brain circuit involving a lesser-known type of brain cell, the astrocyte. According to new research from UC San Francisco, astrocytes tune into and moderate the chatter between overactive neurons.
This new brain circuit, described March 30, 2023 in Nature Neuroscience, plays a role in modulating attention and perception, and may hold a key to treating attention disorders like ...
WPI researcher leads project to determine how stretching and blood flow impact engineered heart valves
2023-04-04
Worcester, Mass. – April 4, 2023 – WPI Researcher Kristen Billiar has been awarded $429,456 from the National Institutes of Health to investigate how stretching and blood flow can inhibit or encourage cardiovascular cells to populate and grow in tissue-engineered heart valves.
The three-year project focuses on experimental valves that are not yet used in humans, and the work will expand understanding about how mechanical forces propel cells in the body.
“Existing heart valves have drawbacks, ...
Ethics & Human Research, March–April 2023 Issue
2023-04-04
Articles
Disclosing Conflicts of Interest to Potential Research Participants: Good for Nothing?
Inmaculada de Melo-Martín
The growing commercialization of science has raised concerns about financial conflicts of interest. Evidence suggests that such conflicts threaten the integrity of research and the well-being of research participants. Trying to minimize these negative effects, federal agencies, academic institutions, and publishers have developed conflict-of-interest policies. Among such policies, recommendations or requirements to disclose financial COIs to potential research participants ...
Sekazi K. Mtingwa Honored with AAAS Philip Hauge Abelson Prize at Annual Meeting
2023-04-04
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) has recognized physicist and humanitarian Sekazi Mtingwa for his invaluable work in the field of intrabeam scattering and particle accelerator research as well as his tireless efforts to promote accessibility, diversity, and equity in STEM. Mtingwa’s career and achievements exemplified the theme of this year’s meeting? “Science for Humanity.” Mtingwa has worked for many years in close collaboration with the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory and other science organizations around the world.
According ...
[1] ... [2002]
[2003]
[2004]
[2005]
[2006]
[2007]
[2008]
[2009]
2010
[2011]
[2012]
[2013]
[2014]
[2015]
[2016]
[2017]
[2018]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.