NC State researchers assemble pathogen ‘tree of life’
2023-04-03
A new online tool – the first of its kind for plant pathogens – will help researchers across the globe identify, detect and monitor species of Phytophthora, which have been responsible for plant diseases ranging from the devastating 1840s Irish potato famine to sudden oak death that still plagues West Coast oak population.
The new pathogen “tree of life” provides a plethora of information about each of the more than 192 formally described species – including their evolutionary history and relationships within groups – as well as more than 30 other informally described taxa. It also includes ...
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research marks 75th anniversary
2023-04-03
Alexandria, VA – A symposium to kick off the year-long celebration of the 75th Anniversary of the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) was featured at the 52nd Annual Meeting & Exhibition of the AADOCR, held in conjunction with the 47th Annual Meeting of the CADR. The AADOCR/CADR Annual Meeting & Exhibition took place at the Oregon Convention Center in Portland on March 15-18, 2023.
The symposium explored a brief history of the founding of NIDCR and its early activities, followed by reflections of the former directors, Harold C. Slavkin, Lawrence A. Tabak and Martha ...
AADOCR announces 2023 AADOCR Hatton Competition and Award Winners
2023-04-03
Alexandria, VA – The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) has announced the winners of the 2023 AADOCR Hatton Competition. The winners were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the AADOCR, which was held in conjunction with the 47th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), that took place on March 15, 2023.
The Hatton Award was first presented as the "Novice Award" in 1953 and is the oldest IADR/AADOCR ...
AADOCR announces Winners of the 2023 AADOCR/CADR Joseph Lister Award for New Investigators
2023-04-03
Alexandria, VA – The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) has announced the winners of the 2023 AADOCR/CADR Joseph Lister Award for New Investigators. The winners were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the AADOCR, which was held in conjunction with the 47th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), that took place on March 15, 2023.
First given in 2018, the AADOCR/CADR Joseph Lister Award for New Investigators is managed by AADOCR and supported by Johnson & Johnson Consumer, Inc. It was created to award young investigators ...
AADOCR announces Winners of the 2023 Student Competition for Advancing Dental Research Application (SCADA)
2023-04-03
Alexandria, VA – The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) has announced the winners of the 2023 Student Competition for Advancing Dental Research Application (SCADA). The winners were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the AADOCR, which was held in conjunction with the 47th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), that took place on March 15, 2023.
In 2017, AADOCR and Dentsply Sirona joined forces to co-sponsor SCADA, which was previously known as the Student Clinicians of ...
Smart watches could predict higher risk of heart failure
2023-04-03
Wearable devices such as smart watches could be used to detect a higher risk of developing heart failure and irregular heart rhythms in later life, suggests a new study led by UCL researchers.
The peer-reviewed study, published in The European Heart Journal – Digital Health, looked at data from 83,000 people who had undergone a 15-second electrocardiogram (ECG) comparable to the kind carried out using smart watches and phone devices.
The researchers identified ECG recordings containing extra heart beats which are usually benign but, if they occur frequently, are linked to conditions such as heart failure and arrhythmia ...
Cold is beneficial for healthy aging
2023-04-03
Cold activates a cellular cleansing mechanism that breaks down harmful protein aggregations responsible for various diseases associated with aging. In recent years, studies on different model organisms have already shown that life expectancy increases significantly when body temperature is lowered. However, precisely how this works has still been unclear in many areas. A research team at the University of Cologne’s CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Aging Research has now unlocked one responsible mechanism. The study ‘Cold ...
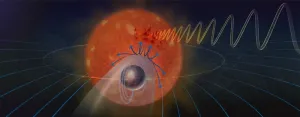
Tiny eye movements are under a surprising degree of cognitive control
2023-04-03
A very subtle and seemingly random type of eye movement called ocular drift can be influenced by prior knowledge of the expected visual target, suggesting a surprising level of cognitive control over the eyes, according to a study led by Weill Cornell Medicine neuroscientists.
The discovery, described Apr. 3 in Current Biology, adds to the scientific understanding of how vision—far from being a mere absorption of incoming signals from the retina—is controlled and directed by cognitive processes.
“These ...
Griffin Charitable Foundation donates $71,000 to the Masonic Medical Research Institute
2023-04-03
UTICA, NY –A $71,000 donation by the Griffin Charitable Foundation, based in Rome, New York, was awarded to the Masonic Medical Research Institute (MMRI) to purchase a new state-of-the-art microscope for imaging cells. “It came as wonderful news that the Foundation pledged this generous donation,” said Stephen F. Izzo, MMRI’s Development Director. “This gift will make a profound impact on our research capabilities.”
The Griffin Charitable Foundation supports not-for-profit entities serving Rome and select organizations ...
Patients with schizophrenia have favorable surgical risk, opening the door for ethical consideration of neurosurgical interventions like Deep Brain Stimulation
2023-04-03
AURORA, Colo. (April 3, 2023) – A study published in Frontiers in Surgery finds that people with schizophrenia (SZ) and schizoaffective disorder (SAD) have overall lower surgical risk than people with Parkinson’s disease, which is reassuring when considering potential surgical interventions such as Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for the treatment of SZ and SAD.
DBS, a procedure that implants electrodes in the deeper structures of the brain connected to generators in the chest, is rare in treating SZ and ...
A 21st-century remedy for missed meds
2023-04-03
HOUSTON – (April 3, 2023) – Missing crucial doses of medicines and vaccines could become a thing of the past thanks to Rice University bioengineers’ next-level technology for making time-released drugs.
“This is a huge problem in the treatment of chronic disease,” said Kevin McHugh, corresponding author of a study about the technology published online in Advanced Materials. “It’s estimated that 50% of people don't take their medications correctly. With this, you’d give them one shot, and they’d be all set for the next couple of months.”
When patients fail to take prescription medicine or take it incorrectly, the costs can ...
Research suggests avenues toward gene therapies for polycystic kidney disease
2023-04-03
New Haven, Conn. — Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is the most common potentially lethal genetic disease—about a half million people in the United States alone suffer from the condition. There is no cure, but new research could open the door to new gene therapies for treating most cases of the disease.
For several decades, researchers have known that mutations in the PKD1 gene, which encodes the polycystin-1 (PC1) protein, can cause the disease in about 80% of cases. However, the protein is too big to be modified through gene therapy strategies. Now, a research ...
New research shows that bacteria get “hangry," too
2023-04-03
Have you ever been so hungry that you become angry, otherwise known as “hangry?” New research by Adam Rosenthal, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Microbiology and Immunology, has found that some bacteria cells get hangry too, releasing harmful toxins into our bodies and making us sick.
Rosenthal and his colleagues from Harvard, Princeton and Danisco Animal Nutrition discovered, using a recently developed technology, that genetically identical cells within a bacterial community have different functions, with some members behaving more docile and others producing the very toxins that make us feel ill.
“Bacteria behave much more ...
Mount Sinai awarded prestigious $1.3 million grant to expand research training program in skin biology
2023-04-03
The Kimberly and Eric J. Waldman Department of Dermatology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai will expand its research training program in skin biology with support from a five-year, $1.3 million T32 grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS).
The research training program in Systems Skin Biology will take a multidisciplinary approach in teaching scientists to holistically understand human physiology, health, and disease. As a recognized leader in research for skin biology and skin diseases, Mount Sinai will also become an incubator for future ...
MU grant will help ease nursing workforce shortage
2023-04-03
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- A recent grant from the Missouri Department of Economic Development will help train hundreds of MU students to become part-time nurse assistants at MU Health Care.
The three-year grant, which starts in fall 2023, will create a three-credit hour elective course within the MU Sinclair School of Nursing. The class will help nearly 100 MU students each year earn paid, part-time positions within MU Health Care as nurse assistants, also known as unlicensed assistive personnel (UAPs), certified nurse assistants (CNAs) and patient care technicians.
“We currently have nearly 800 pre-nursing undergraduate students at MU, and as a professor teaching a freshmen-level course, I ...
Yale-led team creates comprehensive resource for impact of genomic variants
2023-04-03
New Haven, Conn. — Each person has about 4 million sequence differences in their genome relative to the reference human genome. These differences are known as variants. A central goal in precision medicine is understanding which of these variants contribute to disease in a particular patient. Therefore, much of the human genome annotation effort is devoted to developing resources to help interpret the relative contribution of human variants to different observable phenotypes – i.e., determining variant impact.
Recently, Yale School of Medicine led a large NIH-sponsored study where multiple institutions and international collaborators came together ...
Illegal trade and poor regulation threaten pangolins in China
2023-04-03
Pangolins, unique scale-covered mammals, are drastically declining in numbers across Asia and Africa, largely due to illegal trade. Part of the trade, both legal and illegal, supports the traditional Chinese medicine market, which has attracted conservation attention. The level of demand for pangolins and other animals in traditional Chinese medicine, however, hasn’t been thoroughly studied.
In a new study published in the journal Nature Conservation, Dr Yifu Wang, currently a postdoc researcher at the University ...
DELLA proteins could hold key to the next Green Revolution
2023-04-03
A family of ‘promiscuous’ proteins found in all land plants is responsible for many different plant functions, despite remaining relatively unchanged for over 450 million years.
New findings, published in Nature Plants and New Phytologist reveal new knowledge about how DELLA proteins regulate how much a plant grows, when germination occurs and how plants deals with threats such as drought and disease. The key is not in DELLA proteins’ ability to mutate over time, but instead in their ability to interact with dozens of different transcription factors, the proteins responsible for decoding DNA.
Understanding the mechanisms which underpin ...
Rising temperatures alter ‘missing link’ of microbial processes, putting northern peatlands at risk
2023-04-03
If you’re an avid gardener, you may have considered peat moss — decomposed Sphagnum moss that helps retain moisture in soil — to enhance your home soil mixture. And while the potting medium can help plants thrive, it’s also a key component of peatlands: wetlands characterized by a thick layer of water-saturated, carbon-rich peat beneath living Sphagnum moss, trees, and other plant life.
These ecosystems cover just 3% of Earth’s land area, but “peatlands store over one-third of all soil carbon on the planet,” explains Joel Kostka, professor and associate chair of Research in the School of Biological ...
Maclean studying paid sick leave mandates & mental health care service use
2023-04-03
Catherine Maclean, Associate Professor, Schar School of Policy and Government, received $641,155 from the National Institutes of Health for: "Paid Sick Leave Mandates and Mental Healthcare Service Use."
This project will provide the first causal estimates of the effect of state and local paid sick leave (PSL) mandates on access to PSL among those with mental health disorder(s), use of mental health care, and indicators of potential quality of mental health care received. It will also examine how community-level factors (e.g., mental health ...
How two different types of immune cells help two billion people keep tuberculosis in check
2023-04-03
More than 10 million people are sickened by tuberculosis (TB) globally each year, resulting in 1.5 million deaths. Yet, as many as two billion people are infected with Mycobaterium tuberculosis, the bacterium that causes tuberculosis, and are otherwise healthy and asymptomatic. Scientists who study TB look at those individuals who can tolerate and contain the infection in hopes of developing better treatments and vaccines.
The key feature of tuberculosis infection in humans is the formation of granulomas, or clusters of immune cells in the lungs that contain the infection. These granulomas contain B cells, all-purpose immune cells that perform a variety of functions, from producing ...
Do Earth-like exoplanets have magnetic fields? Far-off radio signal is promising sign
2023-04-03
Earth's magnetic field does more than keep everyone's compass needles pointed in the same direction. It also helps preserve Earth’s sliver of life-sustaining atmosphere by deflecting high energy particles and plasma regularly blasted out of the sun. Researchers have now identified a prospective Earth-sized planet in another solar system as a prime candidate for also having a magnetic field — YZ Ceti b, a rocky planet orbiting a star about 12 light-years away from Earth.
Researchers Sebastian Pineda and Jackie Villadsen observed a repeating radio signal emanating from the star YZ Ceti using the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array, a radio telescope ...
Higher lithium levels in drinking water may raise autism risk
2023-04-03
Pregnant women whose household tap water had higher levels of lithium had a moderately higher risk of their offspring being diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder, according to a new study led by a UCLA Health researcher.
The study, published April 3 in JAMA Pediatrics, is believed to be the first to identify naturally occurring lithium in drinking water as a possible environmental risk factor for autism.
“Any drinking water contaminants that may affect the developing human brain deserve intense scrutiny,” said lead study author Beate Ritz, MD, PhD, professor of neurology in the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA ...
Nasal vaccine to prevent COVID-19 passes first tests
2023-04-03
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers have been working on mucosal vaccines that can be administered through the nose. Now, scientists in Berlin have developed a live attenuated vaccine for the nose. In “Nature Microbiology”, they describe the special immune protection it induces.
Joint press release by Freie Universität Berlin, Max Delbrück Center and Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Coronaviruses spread primarily through the air. When infected people speak, cough, sneeze or laugh, they expel droplets of saliva containing the virus. Other people then breathe ...
Research finds global emissions of several banned ozone-destroying chemicals are increasing
2023-04-03
The research, published today in Nature Geoscience and led by the University of Bristol and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), puts the rise in part down to the chemicals, known as chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs, being used to make other ozone-friendly alternatives to CFCs. This is an exception allowed under the Montreal Protocol, but contrary to its wider goals.
Lead author Dr Luke Western, a Research Fellow at the University of Bristol and researcher at the NOAA’s Global Monitoring Laboratory (GML), said: “We’re paying attention to these emissions now because of the success of the Montreal Protocol. CFC ...
[1] ... [2006]
[2007]
[2008]
[2009]
[2010]
[2011]
[2012]
[2013]
2014
[2015]
[2016]
[2017]
[2018]
[2019]
[2020]
[2021]
[2022]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.