Boosting the body’s anti-viral immune response may eliminate aging cells
2023-03-30
BOSTON – Aging, or senescent cells, which stop dividing but don’t die, can accumulate in the body over the years and fuel chronic inflammation that contributes to conditions such as cancer and degenerative disorders.
In mice, eliminating senescent cells from aging tissues can restore tissue balance and lead to an increased healthy lifespan. Now a team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), has found that the immune response to a virus that is ubiquitously present in human tissues ...
Revealing the pattern between frontal polymerization and natural convection
2023-03-30
A self-propagating chemical reaction can transform a liquid monomer into a solid polymer and the interaction between the propagating front and the reaction’s natural convection leads to patterns in the resulting solid polymeric material. New University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign work has shown how the coupling between natural convection and frontal polymerization leads to those observed patterns.
This research was led by a unique team of researchers- Materials Science and Engineering professor Nancy Sottos, Aerospace Engineering professor Philippe Geubelle, and Mechanical Science and Engineering ...
New mechanisms and therapeutic possibilities for heart failure uncovered by scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University and Johns Hopkins University
2023-03-30
(Philadelphia, PA) – Greater awareness and advances in treatment have greatly improved survival rates following heart attack. With more survivors, however, has come the challenge of managing long-term impacts on heart function, especially chronic heart failure, in which the heart gradually loses its ability to pump blood.
Mortality among individuals affected by chronic heart failure following a heart attack – referred to medically as myocardial infarction (MI) – is high. But, according to new research from a major collaborative effort led by scientists at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, more effective treatments may soon ...
How to achieve a functional cure for chronic hepatitis B
2023-03-30
Geneva, March 30, 2023 – More than half of patients who suffer from chronic hepatitis B have the e antigen (HBeAg)-negative form of the disease. Even after many years of antiviral treatment with nucleos(t)ide analogues (NUC), lasting immune control is almost never seen. According to the current state of knowledge, those affected therefore require lifelong therapy. In the world’s first randomized controlled multicenter study – led by Leipzig University’s Faculty of Medicine and in partnership with the Centre for Clinical Studies (ZKS) – researchers have shown that many HBeAg-negative patients ...
New, exhaustive study probes hidden history of horses in the American West
2023-03-30
A team of international researchers has dug into archaeological records, DNA evidence and Indigenous oral traditions to paint what might be the most exhaustive history of early horses in North America to date. The group’s findings show that these beasts of burden may have spread throughout the American West much faster and earlier than many European accounts have suggested.
The researchers, including several scientists from the University of Colorado Boulder, published their findings today in the journal Science.
To tell the stories of horses in the West, the team closely examined about two dozen sets of ...
Newly discovered trigger for major depression opens new possibilities for treatments
2023-03-30
A common amino acid, glycine, can deliver a “slow-down” signal to the brain, likely contributing to major depression, anxiety and other mood disorders in some people, scientists at the Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation & Technology have found.
The discovery, outlined Thursday in the journal Science, improves understanding of the biological causes of major depression and could accelerate efforts to develop new, faster-acting medications for such hard-to-treat mood disorders, said neuroscientist Kirill Martemyanov, Ph.D., corresponding author of ...
Search for a major depression trigger reveals a familiar face: Discovery opens new possibilities for treatments
2023-03-30
JUPITER, Fla.— A common amino acid, glycine, can deliver a “slow-down” signal to the brain, likely influencing major depression, anxiety and other mood disorders in some people, scientists at The Herbert Wertheim UF Scripps Institute for Biomedical Innovation & Technology report online in the journal Science today.
The discovery improves understanding of the biological causes of major depression and could accelerate efforts to develop new, faster-acting medications for such hard-to-treat mood disorders, said neuroscientist Kirill Martemyanov, Ph.D., corresponding author of the study, appearing in Friday’s ...
AI predicts enzyme function better than leading tools
2023-03-30
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new artificial intelligence tool can predict the functions of enzymes based on their amino acid sequences, even when the enzymes are unstudied or poorly understood. The researchers said the AI tool, dubbed CLEAN, outperforms the leading state-of-the-art tools in accuracy, reliability and sensitivity. Better understanding of enzymes and their functions would be a boon for research in genomics, chemistry, industrial materials, medicine, pharmaceuticals and more.
“Just like ChatGPT uses data from written language to create predictive text, we are leveraging ...
Predatory dinosaurs such as T. rex sported lizard-like lips
2023-03-30
A new study suggests that predatory dinosaurs, such as Tyrannosaurus rex, did not have permanently exposed teeth as depicted in films such as Jurassic Park, but instead had scaly, lizard-like lips covering and sealing their mouths.
Researchers and artists have debated whether theropod dinosaurs, the group of two-legged dinosaurs that includes carnivores and top predators like T. rex and Velociraptor, as well as birds, had lipless mouths where perpetually visible upper teeth hung over their lower jaws, similar to the mouth of a crocodile.
However, an international team of researchers challenge some of the best-known depictions, and say these dinosaurs had lips similar to those ...
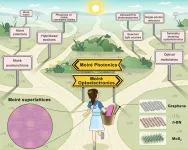
Moiré superlattices show superpower in photonics and optoelectronics
2023-03-30
Researchers from the Institute of Physics (IOP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, collaborating with international colleagues, have presented an overview of recent progress in emerging moiré photonics and optoelectronics.
The review was published in Science on March 30.
Moiré superlattices are artificial quantum materials formed by vertically stacking two or more two-dimensional (2D) layered materials with a slight lattice mismatch and/or a small rotational twist. They introduce a potential landscape of much larger length scale than the crystal periodicity ...
Increasing availability of non-alcoholic drinks may reduce amount of alcohol purchased online
2023-03-30
Increasing the proportion of non-alcoholic drinks on sale in online supermarkets could reduce the amount of alcohol people purchase, suggests a study published today led by researchers at the University of Cambridge.
The team used a simulated supermarket that presented shoppers with varying proportions of alcoholic and non-alcoholic drinks and asked them to select drinks to purchase for their next online shop. They found that shoppers who were exposed to more non-alcoholic drinks selected and purchased fewer units of alcohol. The findings are published in PLOS Medicine.
Excessive ...
The untold history of the horse in the American Plains, a new future for the world
2023-03-30
“Horses have been part of us since long before other cultures came to our lands, and we are a part of them,” states Chief Joe American Horse, a leader of the Oglala Lakota Oyate, traditional knowledge keeper, and co-author of the study. In 2018, at the instruction of her elder knowledge keepers and traditional leaders, Dr. Yvette Running Horse Collin contacted Prof Ludovic Orlando, French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS) scientist. She had completed her PhD, which focused on deconstructing the history of horses in the Americas. Up until that point, the field had been dominated by western academics, and Indigenous voices had been largely dismissed. She sought ...
T cells in human blood secrete a substance that affects blood pressure and inflammation
2023-03-30
Acetylcholine regulates blood flow, but the source of blood acetylcholine has been unclear. Now, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have discovered that certain T cells in human blood can produce acetylcholine, which may help regulate blood pressure and inflammation. The study, which is published in PNAS, also demonstrates a possible association between these immune cells in seriously ill patients and the risk of death.
Blood flow regulation by acetylcholine is long established and highlighted by the 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Yet the sources of acetylcholine ...
Interviews with icons yield lessons on productivity in ‘Wisdom Years’
2023-03-30
The Wonder Years can be great, sure: first loves, long summers, panoramic dreams exclusive to those with a lifetime of runway. The Working Years, too: established identity, new family and old friends, freedom to pursue personal goals and professional satisfaction.
The University of Nebraska–Lincoln’s Ken Kiewra just doesn’t want you to forget about the Wisdom Years. They got the name from famed psychologist Erik Erikson, who roughly defined them as starting at age 65, often considered a mile-marker of retirement in the United States. But whereas Erikson saw the Wisdom Years as ...
Conversion to Open Access using equitable new model sees upsurge in usage of expert scientific knowledge
2023-03-30
(San Mateo, CA, USA, March 30, 2023) — Leading nonprofit science publisher Annual Reviews has successfully converted the first fifteen journal volumes of the year to open access (OA) resulting in substantial increases in downloads of articles in the first month.
Through the innovative OA model called Subscribe to Open (S2O), developed by Annual Reviews, existing institutional customers continue to subscribe to the journals. With sufficient support, every new volume is immediately converted to OA under a Creative Commons license and is available for everyone to read and re-use. In addition, all articles from the previous nine volumes are also ...
Global breakthrough: Plants emit sounds!
2023-03-30
The sounds emitted by plants are ultrasonic, beyond the hearing range of the human ear.
Plant sounds are informative: mostly emitted when the plant is under stress, they contain information about its condition.
The researchers mainly recorded tomato and tobacco plants; wheat, corn, cactus, and henbit were also recorded.
The researchers: "Apparently, an idyllic field of flowers can be a rather noisy place. It's just that we can't hear the sounds!"
Global breakthrough: for the first time in the world, researchers at Tel Aviv University recorded and analyzed sounds ...
ATS publishes official statement on race, ethnicity and pulmonary function test interpretation
2023-03-30
March 30, 2023 – The American Thoracic Society has issued an official statement for clinicians that explains why race and ethnicity should no longer be considered factors in interpreting the results of spirometry, the most commonly used type of pulmonary function test (PFT). The statement was endorsed by the European Respiratory Society. The full statement is available online in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
Spirometry is a breathing test that measures how much air is going into an individual’s lungs, and how rapidly air is inhaled and exhaled. ...
Researchers reveal real-time glimpse into growth habits of nanoparticles
2023-03-30
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — For the first time, researchers have observed the process of nanoparticles self-assembling and crystalizing into solid materials. In new videos produced by the team, particles can be seen raining down, tumbling along stairsteps and sliding around before finally snapping into place to form a crystal’s signature stacked layers.
Led by Qian Chen at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and Erik Lutijen at Northwestern University, the study used liquid-phase transmission electron microscopy and computational modeling to gain an unprecedented view of the self-assembly ...
How plants cope with the cold light of day - and why it matters for future crops
2023-03-30
On bright chilly mornings you can either snuggle down under the duvet or leap up and seize the day.
However, for photosynthesising plants, this kind of dawn spells danger, so they have evolved their own way of making cold mornings tolerable.
Research led by the John Innes Centre has discovered a cold “coping” mechanism that is under the control of the plant biological clock and could offer solutions to breeding more resilience into crops less suited to cold climates.
“We’ve identified a new process that helps plants ...
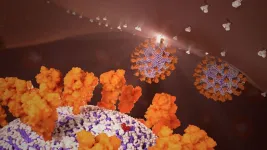
WPI-led team uncovers new details of SARS-COV-2 structure
2023-03-30
Worcester, Mass. – March 30, 2023 – A new study led by Worcester Polytechnic Institute (WPI) brings into sharper focus the structural details of the COVID-19 virus, revealing an elliptical shape that “breathes,” or changes shape, as it moves in the body. The discovery, which could lead to new antiviral therapies for the disease and quicker development of vaccines, is featured in the April edition of the peer-reviewed Cell Press structural biology journal Structure.
“This is critical knowledge we need to fight future pandemics,” said Dmitry Korkin, Harold L. Jurist ’61 and Heather E. Jurist Dean’s ...
University Hospitals research published in New England Journal of Medicine shows minimally invasive procedure saves most patients with severe vascular disease from amputation
2023-03-30
CLEVELAND – A study published in the March 30 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine has shown that there may finally be an alternative to amputation for patients suffering from chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI), the most severe form of peripheral artery disease. This study, co-led by University Hospitals (UH) Harrington Heart & Vascular Institute, could lead to the first FDA approval of a therapy giving thousands of patients hope for an alternative to limb loss.
THERAPY SAVES MOST PATIENTS FROM AMPUTATION
The PROMISE II U.S. pivotal clinical trial found that minimally ...
Columbia establishes the Center for the Transition to Parenthood with funding from the Bezos Family Foundation
2023-03-30
NEW YORK, NY (March 30, 2023)--With a transformational gift from the Bezos Family Foundation, Columbia will launch the Center for the Transition to Parenthood (TtP) in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology (Ob/Gyn). Supported by the most advanced scientific knowledge in the field, the TtP Center seeks to reinvent prenatal care, address the mental health of parents, improve the overall health of their infants, and promote family well-being.
The Center, established with a gift of $21 million from the Bezos Family Foundation, will develop, test, and put into practice a range ...
Form is (mal)function: Protein’s shape lets bacteria disarm it
2023-03-30
Shigella bacteria can infect humans but not mice. In the March 29 issue of Nature, a team from UConn Health explains why. Their findings may explain the multifariousness of a key weapon of our immune system.
Shigella infections cause fever, stomach pain, and prolonged, sometimes bloody diarrhea for as long as a week. The bacteria sicken 450,000 people each year in the US alone. Although most people recover on their own, children and those with weakened immune systems are at risk of Shigella ...
Thermal paint — MXene spray coating can harness infrared radiation for heating or cooling
2023-03-30
An international team of researchers, led by Drexel University, has found that a thin coating of MXene — a type of two-dimensional nanomaterial discovered and studied at Drexel for more than a decade — could enhance a material’s ability to trap or shed heat. The discovery, which is tied to MXene’s ability to regulate the passage of ambient infrared radiation, could lead to advances in thermal clothing, heating elements and new materials for radiative heating and cooling.
The group, including materials science ...
An improved, visible light-harvesting catalyst to speed up reactions
2023-03-30
Photocatalysis is the use of light to accelerate the rate of a reaction in the presence of a photocatalyst. The catalyst plays a crucial role in this process—it absorbs the light being shined onto it and makes it available in way that can help accelerate the chemical reaction and also enhance it. These catalysts are used for a variety of light-dependent reactions ranging from the production of paper to the conversion of carbon dioxide to fuel. Given these applications, the development of ideal photocatalysts is important. An ideal ...
[1] ... [2011]
[2012]
[2013]
[2014]
[2015]
[2016]
[2017]
[2018]
2019
[2020]
[2021]
[2022]
[2023]
[2024]
[2025]
[2026]
[2027]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.