At the end of the dry season: CO2 pulses over Australia
2023-03-31
End-of-dry-season CO2 pulses recur each year in the atmosphere above the Australian continent, a discovery made by an international research team led by environmental physicist Prof. Dr André Butz of Heidelberg University. To investigate the carbon fluxes over Australia, the researchers studied atmospheric CO2 measurements. Their analyses show that CO2 emissions spike when heavy rain falls on dried-out soil, thus activating microorganisms in that soil. The findings suggest that dry regions have a greater influence on the variations in the global carbon cycle than previously thought.
The Australian continent is dominated by dry ecosystems and widely varying precipitation patterns. ...
Ants took over the world by following flowering plants out of prehistoric forests
2023-03-31
Ants are pretty much everywhere. There are more than 14,000 different species, spread over every continent except Antarctica, and researchers have estimated that there are more than four quadrillion individual ants on Earth-- that’s 4,000,000,000,000,000. But how ants evolved to take over the world is still a mystery. In a new study in the journal Evolution Letters, scientists used a combination of fossils, DNA, and data on the habitat preferences of modern species to piece together how ants and ...
Welcome to the new Executive Editor of Forestry Research - Shihui Niu
2023-03-31
Now, Professor Niu serves as deputy director of the National Engineering Research Center of Tree Breeding and Ecological Restoration, deputy secretary general and standing member of the Pine Branch of the Chinese Society of forestry. He was selected as the national young top-notch talent of “Ten Thousand Talents Program”, leading talent of forest and grassland and technology innovation of the National Forestry and Grassland Administration (NFGA), outstanding young scholarship of “Beilin Scholars Program” of Beijing Forestry University, etc. He also served as an evaluation committee member ...
Study finds high rates of burnout across healthcare professions
2023-03-31
Burnout is associated with adverse outcomes including medical errors and lower quality of care. While many studies have focused on physician or nurse burnout, the COVID-19 pandemic increased stress across the healthcare workforce, including support staff and healthcare teams who have a crucial role in patient care. A new study of 206 healthcare organizations led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, identified high levels of burnout, intent to leave the profession, and work overload across all members of the healthcare ...
Oregon State researchers develop new model for quickly evaluating potential cervical cancer drugs
2023-03-31
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Researchers at Oregon State University have created a means of speeding up and improving the evaluation process for drugs used to combat cervical cancer.
The study led by Kaitlin Fogg, assistant professor of biological engineering in the OSU College of Engineering, is important because the American Cancer Society estimates that nearly 14,000 new cervical cancer cases will be diagnosed in the United States this year and that more than 4,000 women will die from the disease.
Findings were published in the Journal of Biomedical Materials Research.
Fogg and graduate students in the College of Engineering ...
Development of an artificial kidney for early detection of drug toxicity
2023-03-31
The kidney plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis within the body by eliminating toxic and superfluous substances in the bloodstream, including waste generated during metabolic processes, through urine. Nevertheless, toxicity can also be induced in the kidney from certain medications. Recently, a research team from POSTECH has engineered an artificial kidney that allows for the early detection of adverse drug reactions.
The POSTECH research team led by Professor Dong-Woo Cho and Professor Jinah Jang (Department ...
Do we understand the flickering flames?
2023-03-31
Overview
A research team, led by Professor Yuji Nakamura of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology, discovered that the flickering of flames can be freely controlled by moving two flames closer together or further apart. Until now, it had been known that interference between flames separated by a certain distance causes the flames to flicker during in-phase or anti-phase. However, it was not possible to stably express the state of “stopping the flickering of flames” that should occur under critical ...
DGIST Professor Yoonkyu Lee’s research team has developed a high-performance transparent-flexible electronic device based on a copper-graphene nanowire synthesized by scintillation
2023-03-31
□ DGIST Professor Yoonkyu Lee’s research team illuminated intense light on the surface of a copper wire to synthesize graphene, thereby increasing the production rate and lowering the production cost of the high-quality transparent-flexible electrode materials and consequently enabling its mass production. This technology is applicable to various 2D materials[1], and its applicability can be extended to the synthesis of various metal-2D material nanowires.
□ The research team used copper-graphene nanowires to implement high-performance transparent-flexible ...
DGIST held a graduation ceremony for the first half of 2023 (Feb.)
2023-03-31
□ On February 16 (Thursday), the DGIST held a graduation ceremony for the first half of 2023, that is, those who graduated in February, at the Convention Hall in the Office of the University. A total of 242 students—29 doctoral, 87 master’s, and 126 bachelor’s students—received academic degrees in science and technology fields.
□ Jongho Lee (Minister of Science and ICT), Junghye Noh (the board chairman of DGIST and an honorary professor at SNU), Jonghan Kim (the administrative mayor of Daegu Metropolitan City), ...
DGIST Professor Minseok Kim’s team develops an electronic medicine technology that restores abnormal protein behavior, the cause of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease (CMT)
2023-03-31
□ The research team led by Professor Minseok Kim from the Department of New Biology at DGIST (President Yang Kuk) has developed a technology that can treat Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease, an incurable hereditary disease, with electric stimulation instead of drug therapy. The core of this technology is electric stimulation that restores the abnormal distribution of peripheral myelin protein 22 (PMP 22)[1], the cause of the disease, to normal. The research team discovered it by conducting a series of electric stimulation experiments using a CMT disease subtype ...
Can we connect to a virtual world as in the movie “The Matrix”? Microrobot technology has been developed for externally connecting in vivo neural networks.
2023-03-31
□ The research team led by Professor Hongsoo Choi from DGIST (President Kuk Yang) in the Department of Robotics and Mechatronics Engineering has developed a microrobot capable of forming neural networks and sectioning hippocampal tissues in an in vitro environment in an ex vivo[1] state. Through the joint research with the team led by Dr. Jongcheol Rah from Korea Brain Research Institute, the possibility of analyzing structurally and functionally connected neural networks using a microrobot in an in-vitro environment during cell delivery and transplantation has been confirmed. The research findings are ...
DGIST student startups received the Grand Prize and Excellence Award in the “LAB Start-up 2023” battle
2023-03-31
□ DGIST (President Kuk Yang) announced on March 7, 2023, that student startups, CURE and TIA, received the Grand Prize and Excellence Award, respectively, in the “LAB Start-up 2023” which is sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT and supervised by Commercialization Promotion Agency for R&D Outcome (COMPA) and Korea Entrepreneurship Foundation.
□ This event, which was held under the theme of "Scientific Technology, the Advocate of Entrepreneurship," involved IR and exhibitions of 146 teams that have been challenged to start a business through the ...
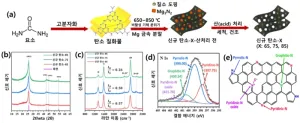
Professor Jong-Sung Yu’s team at DGIST develops a method for carbon support synthesis with higher stability and durability of fuel cell catalysts
2023-03-31
□ The research team led by Professor Jong-Sung Yu of the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST (President Kook Yang) has developed a low-temperature method to synthesize a highly graphitized[1] carbon support[2] that will greatly improve the lifespan of hydrogen fuel-cells[3]. They expect that the results of this study will greatly increase the possibility of commercialization by being used in fuel cells for vehicles, batteries for water electrolysis, and drones.
□ The importance of hydrogen fuel-cells is increasing with the burgeoning need for eco-friendly energy. Therefore, studies to improve the performance and lifespan of hydrogen fuel-cells ...
New trials aim to improve quality of life for autistic people as University of Warwick embraces neurodiversity this autism awareness month
2023-03-31
The University of Warwick is proud to stand with neurodiverse communities during Autism Awareness Month. This month, the University aims to raise autism awareness and acceptance, while celebrating the diversity of all individuals that make up the University of Warwick community. According to the National Autistic Society, there are around 700,000 autistic people in the UK.
As part of ongoing research into the best way to support neurodiverse individuals, academics at the Centre for Educational Development, Appraisal and Research (CEDAR) are launching two clinical trials and are encouraging autistic adults to consider ...
Smart robots to work with children to greatly improve human-machine communication
2023-03-31
A team of experts at The University of Manchester has been awarded major funding to help design smarter robots that will have more meaningfully dialogue with humans after developing improved insight into our inner feelings through language.
The European Research Council (ERC) has awarded Professor Angelo Cangelosi, co-director of the Manchester Centre for Robotics and AI, a total of €2.5million as part of the eTALK project.
The Manchester research team will combine expertise in AI ...
Latinx students reported higher depression and anxiety symptoms than other students during the pandemic
2023-03-31
Latinx children in the US experienced higher rates of depression and anxiety during the Covid-19 pandemic, a new study shows, as experts state the “pressing need” to examine the long-term impact.
Findings, published today in the peer-reviewed Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, follow the examination of early adolescent school data from the first two years of the pandemic, compared to pre-pandemic levels.
The results show Latinx students were 1.5 to 2 times more likely to present with risk for both depression and anxiety during every academic year cohort assessed.
The highest maladjustment was found among Latinx girls and gender non-conforming/binary ...
UC study: Engaging in civic leadership empowers refugees, immigrants
2023-03-31
Research led by a University of Cincinnati doctoral student shows that immigrants and refugees who participated in a civic leadership program felt more empowered after learning about their rights, civic entitlements and the social, cultural, and political context of Cincinnati.
“The most salient change participants reported in connection to their involvement in the program were changes in consciousness related to power, rights and opportunities which immigrants and refugees are entitled to,” says ...
Alcohol increases risk for gun-involved suicide among Americans
2023-03-30
TORONTO, March 30, 2023 – A CAMH-led study just published in the journal JAMA Network Open has found that the probability of using a gun as a means of suicide among Americans increases the more alcohol they drink.
The study looked at all suicides in a national surveillance system in the United States over a 17-year period for people 18 and older who had alcohol in their system at the time of death. It found that the more alcohol they drank, the greater the probability that they would use a gun as the means of suicide, highlighting the need ...
White-tailed deer blood kills bacteria that causes Lyme disease
2023-03-30
As tick season kicks in across the country, the executive director of the University of Massachusetts Amherst-based New England Center of Excellence in Vector-Borne Diseases (NEWVEC) and his team have completed research that offers a promising lead in the fight against Lyme disease.
The study, published recently in the journal Vector-borne and Zoonotic Diseases, demonstrates that the blood of the white-tailed deer kills the corkscrew-shaped bacterium that causes Lyme disease, a potentially debilitating illness. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that each year some 476,000 people are diagnosed with and treated for Lyme, the ...
Kessler Foundation scientists receive $500,000 in grants to address early intervention after spinal cord injury
2023-03-30
East Hanover, NJ – March 30, 2023 –Three Kessler Foundation scientists have received grants totaling $500,000 from the New Jersey Commission on Spinal Cord Research to advance exploratory pilot studies in early intervention after spinal cord injury. Two studies will focus on areas of rehabilitation using spinal cord transcutaneous stimulation and another will test the impact of a BrainHQ cognitive training program in improving processing speed abilities shortly after SCI.
Fan Zhang, PhD, research scientist in the ...
New procedure helps patients avoid leg amputation
2023-03-30
More than 75% of patients facing amputation from the most severe form of peripheral artery disease were able to keep their limb after an innovative treatment as part of a multicenter study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The alternative to amputation, known as “limb salvage,” for patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI) came from the PROMISE II U.S. clinical trial assessing LimFlow technology and its use in performing transcatheter arterialization of the deep vein system.
The trial completed recently, and results were formally presented at the VIVA (Vascular InterVentional Advances) meeting in Las ...
Prototype taps into the sensing capabilities of any smartphone to screen for prediabetes
2023-03-30
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control, one out of every three adults in the United States has prediabetes, a condition marked by elevated blood sugar levels that could lead to the development of Type 2 diabetes. The good news is that, if detected early, prediabetes can be reversed through lifestyle changes such as improved diet and exercise. The bad news? Eight out of 10 Americans with prediabetes don’t know that they have it, putting them at increased risk of developing diabetes ...
Doctoral candidate creates technique to improve AI energy efficiency
2023-03-30
An engineering doctoral student is shedding light on the reliability of today’s modern-day artificial intelligence with an issue most do not think about: energy efficiency.
Noel Daniel Gundi, who will defend his dissertation later in the semester, was the lead collaborator on research addressing reliability and faults in artificial intelligence. The research paper will be presented and published at the Design Automation Conference in July. It focuses on the computer chip used for artificial intelligence software, such as Google’s search engines. When at low power, the chip ...
New ideas for biodiversity research: ecologist Jonathan Chase receives ERC Advanced Grant
2023-03-30
The European Research Council (ERC) announced that Professor Jonathan Chase will be awarded one of the prestigious ERC Advanced Grants. The scientist will receive almost 2.5 million euros over the next five years to fund his research project "MetaChange". With this project, he plans to develop new concepts, tools and analyses for a better understanding of biodiversity and its change. Chase has been conducting research and teaching at Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg (MLU) and the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv) Halle-Jena-Leipzig since 2014.
"Jonathan ...
Breaking the barrier: Low-temp ammonia synthesis with iron catalysts and barium hydride
2023-03-30
The Haber-Bosch (HB) process is one of the most important industrial chemical reactions. It combines nitrogen and hydrogen gases in the presence of an iron-based catalyst at high temperatures and pressures to produce ammonia fertilizer which helps provide food for over five billion people. Over the decades, researchers have tried to bring down the reaction temperature of the HB process to increase the ammonia yield while reducing energy consumption. To this end, they have recently developed new catalysts based on other transition metals, ...
[1] ... [2010]
[2011]
[2012]
[2013]
[2014]
[2015]
[2016]
[2017]
2018
[2019]
[2020]
[2021]
[2022]
[2023]
[2024]
[2025]
[2026]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.