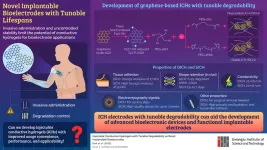
Is artificial intelligence better at assessing heart health?
2023-04-05
Who can assess and diagnose cardiac function best after reading an echocardiogram: artificial intelligence (AI) or a sonographer?
According to Cedars-Sinai investigators and their research published today in the peer-reviewed journal Nature, AI proved superior in assessing and diagnosing cardiac function when compared with echocardiogram assessments made by sonographers.
The findings are based on a first-of-its-kind, blinded, randomized clinical trial of AI in cardiology led by investigators in the Smidt Heart Institute and the Division of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine at Cedars-Sinai.
“The results have immediate implications for ...
Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology researchers correlate Arctic warming to extreme winter weather in midlatitude and its future
2023-04-05
Pictures of melting glaciers and stranded polar bears on shrinking sea ice in the Arctic are perhaps the most striking images that have been used to highlights the effects of global warming. However, they do not convey the full extent of the consequences of warmer Arctic. In recent years, there has been growing recognition of the Arctic’s role in driving extreme weather events in other parts of the world. While the Arctic has been warming at a rate twice as fast as the global average, winters in the midlatitude regions have experienced colder and more severe weather events. For instance, the winter of 2022-2023 saw record-breaking cold temperatures and snowfall ...
Finding a way to combat long COVID
2023-04-05
A new study has identified potential neurological biomarkers of long COVID-19 in nonhuman primates that may help physicians diagnose, monitor and treat this condition.
Over 65 million people worldwide have developed long COVID after being infected with SARS-CoV-2, and cases are only becoming more common. Long COVID symptoms can last weeks, months or years. Even more perplexing is the fact that symptoms can vary widely between individuals and consist of any combination of fatigue, fever, chest pain, trouble breathing, neurological symptoms such as ...
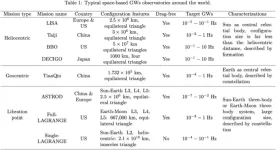
Overview of orbital mechanics for space-based gravitational wave observatories
2023-04-05
Gravitational waves (GWs) are “ripples in space-time”. The detection of gravitational waves (GWs) is critical to the understanding of the origin and evolution of stars, galaxies, and the Universe. At present, the laser interferometry is the most commonly use technology to detect GWs by measuring the phase change between two beams of coherent light. Due to the limitations of arm length, the ground-based GWs measurement is hard to detect the low-frequency GWs. While the space-based GWs observation is capable of longer arm length of the interferometer, the detection of GWs in space is expected to cover a greater number and variety of ...
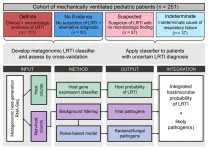
Cracking the puzzle of lower respiratory tract infections in children
2023-04-05
Lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI), which includes conditions such as pneumonia, has long been the leading cause of death from communicable agents and a leading cause of death in children worldwide. But despite its prevalence, LRTI is tricky for doctors to treat effectively because the current diagnostic approach often fails to conclusively determine whether an infection is present at all, and if so, what pathogen is causing it.
Now, in a study published April 3, 2023 in The Journal of Clinical Investigation, a team led by researchers at the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub San Francisco (CZ Biohub SF), UC San Francisco (UCSF), the University ...
Opening a new frontier: PdMo intermetallic catalyst for promoting CO2 utilization
2023-04-05
Being the most abundant and persistent greenhouse gas emitted, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the key driver of climate change. To address the pressing problems associated with climate change and fossil fuel depletion, scientists are looking for viable solutions that can minimize the amount of CO2 released into the atmosphere. One attractive solution to this problem is to convert atmospheric CO2 into more useful compounds. Towards this end, methanol ­- a raw material, fuel additive, and energy carrier, is widely being explored as a promising conversion option for CO2.
Now, while various catalysts ...
SwRI, Tec de Monterrey award funding for sustainable manufacturing research
2023-04-05
SAN ANTONIO — April 5, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute and Tecnológico de Monterrey (Tec de Monterrey) will jointly fund three research and development initiatives to advance sustainable manufacturing and technology in the United States and Mexico. The trio of projects are the first selected to receive support through the Sustainable Manufacturing Program, a transnational research and development collaboration established between SwRI and Tec de Monterrey — a private, nonprofit, independent university based in Monterrey, Mexico — in August 2022. The program provides grant opportunities funded ...
How were amino acids, one of the key building blocks of life, formed before the origin of life on Earth? Tiny particles from the near Earth asteroid Ryugu can help answer this profound question
2023-04-05
Our solar system formed from a molecular cloud, which was composed of gas and dust that was emitted into the interstellar medium (ISM), a vast space between stars. On collapse of the molecular cloud, the early sun was formed, with a large disk of gas and dust orbiting it. The dusty material collided to produce rocky material that would eventually grow in size to give large bodies called planetesimals.
The planetesimals that formed far enough from the sun, also contained large quantities of ice. The ice consisted of water and other volatile compounds, such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), methanol (CH3OH) and ammonia (NH3), as well as ...
Air pollution is linked to lower COVID-19 vaccine responses
2023-04-05
People exposed to higher levels of air pollution before the pandemic had lower antibody responses to COVID-19 vaccines, according to a study led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), an institution supported by “la Caixa” Foundation, in collaboration with the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP). In particular, exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and blank carbon (BC) was associated with about a 10% decrease in IgM and IgG antibody responses in people without prior infection. The findings, published in Environmental Health Perspectives, ...
More than a third of children worry at least once a week, with their tendency to worry progressing with age, according to national survey by Nemours KidsHealth(R)
2023-04-05
WILMINGTON, Del. (April 5, 2023) – More than one in three children ages 9 to 13 (37%) worry at least once a week, primarily about school (64%) and friendships (41%), with their tendency to worry progressing with age. Older children (age 13) are more likely than their younger counterparts to report feeling as though they will never stop worrying (48% vs. 22% for 9-year-olds). This is according to the results of What’s Worrying America’s Kids, a national survey conducted by The Harris Poll on behalf of Nemours KidsHealth. The survey results ...
TOS endorses global editorial on people-first language and pediatric obesity
2023-04-05
ROCKVILLE, Md.—The Obesity Society (TOS) has joined several European, US and Canadian obesity organizations in an editorial statement published in the journal Pediatric Obesity championing the use of people-first language for pediatric overweight and obesity to address weight stigma and bias.
Professor David Thivel, president of the European Childhood Obesity Group and coordinator of the joint statement, said, "This paper emphasizes the importance of considering the use of people-first language when it comes to pediatric obesity, by all who work with, care for or support children and adolescents, in order to avoid stigmatization and to create an appropriate and optimal ...
Complications for procedure to open clogged pulmonary arteries decrease significantly
2023-04-05
For patients with high blood pressure in their pulmonary arteries caused by chronic blood clots, complications after a minimally invasive balloon angioplasty have decreased substantially over the last decade, a Michigan Medicine-led study finds.
Researchers examined over 7,500 cases of balloon pulmonary angioplasty for patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension, an elevated blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries due to persistent blockages known as CTEPH, between 2013 and 2022. The procedure, which is offered ...
New tool shows progress in fighting spread of invasive grass carp in Great Lakes
2023-04-05
New research reveals the progress scientists at The University of Toledo are making in their ongoing efforts to capture and remove invasive grass carp from the Great Lakes.
Researchers based at the UToledo Lake Erie Center created a new way to estimate the abundance of invasive “sleeper” species in freshwater ecosystems and help guide management strategies.
Using data collected during their efforts to remove invasive grass carp from Lake Erie and its tributaries, the aquatic ecologists and environmental ...
Recent advances in space chemistry research
2023-04-05
Space is the great unknown — very few of us will ever experience what it’s like to visit another planet or moon, and so much is yet to be discovered. Below are some recent papers published in ACS journals that report advances toward understanding whether certain minerals, compounds or even life itself could form on other worlds. Reporters can request free access to these papers by emailing newsroom@acs.org.
“Immunoanalytical Approach for Detecting and Identifying Ancestral Peptide Biomarkers in Early Earth Analogue Environments”
Analytical Chemistry
March 16, 2023
These authors reasoned that if they could analyze “resurrected” ...
Survey of allergists/immunologists reveals management of hereditary angioedema differs by region
2023-04-05
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (April 5, 2023) – Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is a disease that, due to its rare nature, can pose difficulties for both patients and medical professionals. A new survey of allergists/immunologists from the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI) shows that diagnosing, treating and managing this condition can be challenging for patients and healthcare providers - including patients in rural areas. An article about the survey is published in Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, ACAAI’s scientific journal.
HAE is caused by a genetic mutation, and there are different types. It is a hereditary disease. The symptoms of HAE ...
SynGAP Research Fund awards a collaborative grant to Tang Lab & AXONIS Therapeutics
2023-04-05
PALO ALTO, Calif. (April 5, 2023) – SynGAP Research Fund (SRF), a 501(c)(3) public charity whose mission is to improve the quality of life for SYNGAP1 patients through the research and development of treatments, therapies and support systems, today announced they have awarded a $130,000 collaborative grant to the lab of Xing Tang, PhD at Boston Children's Hospital & AXONIS Therapeutics to investigate the treatment effects of KCC2-enhancing small molecule compounds in SYNGAP1 haploinsufficiency.
Principal Investigator of translational neuroscience at AXONIS, Dr. Kadam, has been working with the SRF community for many years. While at Johns Hopkins, she gave a popular SRF ...
Manganese in Central Valley water threatens fetuses and children
2023-04-05
Water in California’s Central Valley contains enough manganese to cause cognitive disabilities and motor control issues in children, and Parkinson’s-like symptoms in adults.
A naturally occurring metal, manganese is found in water supplies throughout the world. It is regulated as a primary contaminant in many Southeast Asian countries where the climate causes it to leach into groundwater. However, in the U.S. it is regulated only as a secondary contaminant, meaning no maximum level is enforced.
A ...
Do altered gut microbes affect risk of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder?
2023-04-05
New research published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry suggests that the microbial composition of the gut may affect a child’s susceptibility to attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
The human gastrointestinal tract hosts a large population of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. When investigators compared fecal samples from 35 children with ADHD and 35 healthy controls, samples from children with ADHD had higher levels of certain species of fungi and lower levels of other species.
In experiments with cells grown in the lab, one species in abundance in ...
Can a drug used to treat liver disease help prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections and lessen COVID-19 severity?
2023-04-05
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, attaches to a cellular receptor called angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and activation of the farnesoid X receptor increases ACE2 expression. New research published in the Journal of Internal Medicine suggests that a drug that inhibits the farnesoid X receptor and is used to treat liver disease may decrease SARS-CoV-2 infections and reduce the severity of COVID-19.
The study ran from March 2020 to February 2022 and included 3,214 patients with liver disease, half of whom were taking the drug, called ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). ...
Can some snakes do cartwheels to escape or startle predators?
2023-04-05
In research published in Biotropica, investigators report that the Dwarf Reed Snake (Pseudorabdion longiceps) performs cartwheels when threatened. This is the first time such an active rolling motion has been documented in snakes, with images and a detailed description.
The Dwarf Reed Snake is a nocturnal, small snake that lives in regions of Southeast Asia. Typical defense mechanisms that small snakes use against predators include fleeing, camouflage, coloration, odors, death-feigning, and intimidation. ...
Can phototherapy improve cognitive function in patients with dementia?
2023-04-05
In an analysis of published clinical trials, investigators found that phototherapy—or exposure to sessions of bright light—may be a promising non-pharmacological intervention for lessening symptoms of dementia.
The analysis in Brain and Behavior included 12 randomized clinical trials. Results indicated that phototherapy improved cognitive function in patients with dementia, but it did not affect symptoms of depression or sleep quality.
“Further well-designed studies are needed to explore the most effective clinical implementation ...
Could a novel small molecule slow or reverse the effects of Duchenne muscular dystrophy?
2023-04-05
In a new study published in The FASEB Journal, investigators demonstrated the potential of a molecule that may help overcome some of the devastating symptoms of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), the most common life-limiting congenital neuromuscular disorder. The agent promotes the activity of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an important fuel-sensing enzyme that is present in all mammalian cells.
Previous research has shown that stimulating AMPK can mitigate the dystrophy—or wasting—of muscles, but AMPK activators have failed to reach the clinic due to either their lack of potency or toxic off-target effects.
In ...
CycPeptMPDB: A database aimed at promoting drug design using cyclic peptides
2023-04-05
CycPeptMPDB, a novel database—created by Tokyo Tech researchers—focused on the membrane permeability of cyclic peptides, could accelerate the development of drugs based on these promising compounds. This database was created by gathering published information on thousands of cyclic peptides and organizing it neatly in an online-accessible platform. Thanks to its search and visualization capabilities, CycPeptMPDB could pave the way to new computational and machine learning methods for screening and designing drugs with cyclic peptides.
One of the ...
Brain injury toolkit helps support domestic violence survivors
2023-04-05
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A new approach to trauma-informed care developed by domestic violence survivor advocates and researchers at The Ohio State University has been found in a new study to improve support organizations’ care for survivors by better recognizing brain injury and addressing its often long-lasting repercussions.
The study appears in the Journal of Head Trauma and Rehabilitation.
CARE is the first trauma-informed approach that considers brain injury in the complex set of circumstances to be addressed and accommodated in order ...
Aging at AACR Annual Meeting 2023
2023-04-05
Impact Journals (Aging's publisher) is proud to participate at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023, which convenes April 14-19 in Orlando, Florida.
BUFFALO, NY-April 4, 2023 – Impact Journals will be participating as an exhibitor at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023 from April 14-19 at the Orange County Convention Center in Orlando, Florida. This year, the AACR meeting theme is: “Advancing the Frontiers of Cancer Science and Medicine.”
Impact ...
[1] ... [2013]
[2014]
[2015]
[2016]
[2017]
[2018]
[2019]
[2020]
2021
[2022]
[2023]
[2024]
[2025]
[2026]
[2027]
[2028]
[2029]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.