Childhood asthma declines during COVID-19 pandemic
2023-03-31
Half as many children in the United States were diagnosed with asthma in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic compared to previous years, and Rutgers researchers think fewer colds may be part of the reason.
In a new Rutgers study, published in Respiratory Research, researchers examined the rates of new asthma diagnoses in a large commercial insurance claims database during the first year of the pandemic compared with rates of new diagnoses during the previous three years.
Using the Health Core Integrated Research ...
Study shows ketamine could be beneficial for treating brain injury in children
2023-03-31
A common anesthesia drug could be beneficial in reducing pressure inside the skull of children with traumatic brain injuries (TBI), according to a study published in Critical Care Medicine.
Ketamine, a drug that has been used for anesthesia since the 1970s, has traditionally been avoided for patients with TBI due to early studies suggesting that it could raise the pressure inside of the skull, known as intracranial pressure (ICP).
More recent studies have suggested otherwise, said lead author Michael Wolf, MD, assistant professor of Pediatrics and Neurological ...
Yak milk consumption among Mongol Empire elites
2023-03-31
Photos
For the first time, researchers have pinpointed a date when elite Mongol Empire people were drinking yak milk, according to a study co-led by a University of Michigan researcher.
By analyzing proteins found within ancient dental calculus, an international team of researchers provides direct evidence for consumption of milk from multiple ruminants, including yak. In addition, they discovered milk and blood proteins associated with both horses and ruminants. The team's results are published in Communication Biology.
The study presents novel protein findings from an elite Mongol Era cemetery ...
Hope for salamanders? Illinois study recalibrates climate change effects
2023-03-31
URBANA, Ill. – For tiny salamanders squirming skin-to-soil, big-picture weather patterns may seem as far away as outer space. But for decades, scientists have mostly relied on free-air temperature data at large spatial scales to predict future salamander distributions under climate change. The outlook was dire for the mini ecosystem engineers, suggesting near elimination of habitat in crucial areas.
Now, University of Illinois researchers are tuning into the microclimates that really matter to the imperiled amphibians and forecasting a somewhat more hopeful future.
“The ...
Engineered E. coli delivers therapeutic nanobodies to the gut
2023-03-31
BOSTON-- Humans are colonized with thousands of bacterial strains. Researchers are now focused on genetically modifying such bacteria to enhance their intrinsic therapeutic properties.
One goal is to develop smart microbes that release therapeutic payloads at sites of disease, thus maintaining therapeutic efficacy while limiting many of the side effects that can be associated with the systemic administration of conventional drugs.
Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), have engineered a strain of the probiotic Escherichia ...
New type of friction discovered in ligand-protein systems
2023-03-31
An interdisciplinary research team of the Institutes of Physical Chemistry and Physics of the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt-am-Main has discovered a new, direction-dependent friction in proteins called anisotropic friction. “Until now, nobody had observed that friction in biomolecules was dependent on direction,” says physicist Dr. Steffen Wolf of the University of Freiburg. The results have been published as cover story in the scientific journal “Nano Letters.”
Experiments on model complex of protein-ligands
Proteins constitute the microscopic machinery of cells. They perform work during their functional cycles. Accordingly, ...
New UNC Chapel Hill study quantifies $562M in financial risk from Hurricane Florence using novel modeling approach that evaluates risk of mortgage default and property abandonment
2023-03-31
When Hurricane Florence made landfall on North Carolina’s coast in 2018, it brought record rainfall causing catastrophic flooding and damages to communities across the eastern portion of the state.
Estimating the financial impacts of household flooding is complex because direct damages often snowball into other financial risks, like a decrease in property value or loss of equity. Generally, post-disaster damage assessments focus on insured and uninsured losses, but these numbers do not account for the secondary impacts to households, lenders, local governments and other stakeholders who may also share in the financial consequences if a property owner defaults ...
What is foreign exchange market or simply Forex?
2023-03-31
The Forex market, also known as the foreign exchange market or simply Forex (short for "foreign exchange"), is a decentralized global market where various currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. The primary purpose of the Forex market is to facilitate international trade and investment by allowing businesses, governments, and individuals to convert one currency into another.
Can cities make room for woodpeckers?
2023-03-31
Researchers are deploying the latest mapping techniques to identify the most important suburban habitat for North America’s largest woodpecker.
University of Cincinnati doctoral student Ruijia Hu said wildlife habitat in congested places like southwest Ohio is becoming increasingly fragmented as forests give way to new construction. Eventually, this could spell trouble to an animal with specific habitat needs like Ohio’s pileated woodpecker.
Pileated woodpeckers are crow-sized birds with colorful red crests and striking white facial stripes. They are found in forests from British Columbia to Florida. They have the ...
Study: ChatGPT has potential to help cirrhosis, liver cancer patients
2023-03-31
A new study by Cedars-Sinai investigators describes how ChatGPT, an artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot, may help improve health outcomes for patients with cirrhosis and liver cancer by providing easy-to-understand information about basic knowledge, lifestyle and treatments for these conditions.
The findings, published in the peer-reviewed journal Clinical and Molecular Hepatology, highlights the AI system’s potential to play a role in clinical practice.
“Patients with cirrhosis and/or liver cancer and their caregivers often have unmet needs and insufficient knowledge about managing and preventing complications of their disease,” ...
A healthy microbiome may prevent deadly infections in critically ill people
2023-03-31
Twenty to 50 per cent of all critically ill patients contract potentially deadly infections during their stay in the intensive care unit or in hospital after being in the ICU – markedly increasing the risk of death.
“Despite the use of antibiotics, hospital-acquired infections are a major clinical problem that persists to be a huge issue for which we don’t have good solutions,” says Dr. Braedon McDonald, MD, PhD, an intensive care physician at the Foothills Medical Centre (FMC) and assistant professor at the ...
Academic institutions receive lower financial returns from biotechnology licenses than commercial firms
2023-03-31
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
The financial terms of biotechnology licenses from academic institutions are significantly less favorable than those of comparable licenses between commercial firms according to a new study from Bentley University’s Center for Integration of Science and Industry. The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, shows that the royalties and payments to academic institutions are significantly lower than those to commercial firms for similar licenses and products at the same stages of development.
The article, titled “Comparing the economic terms of biotechnology licenses from academic institutions with those ...
Harnessing nature to promote planetary sustainability
2023-03-31
As Earth’s population grows, the demands of modern lifestyles place mounting strain on the global environment. Proposed solutions to preserve and promote planetary sustainability can sometimes prove more harmful than helpful. However, technologies that harness natural processes could be more successful.
Such technologies are the focus of the latest issue of the open access journal PLOS Biology, which features a special collection publishing March 31st of papers highlighting biology-based solutions that could be applied to reduce carbon dioxide emissions, eliminate non-degradable plastics, produce food or energy ...
Study examines how social rank affects response to stress
2023-03-31
Can an individual’s social status have an impact on their level of stress? Researchers at Tulane University put that question to the test and believe that social rank, particularly in females, does indeed affect the stress response.
In a study published in Current Biology, Tulane psychology professor Jonathan Fadok, PhD, and postdoctoral researcher Lydia Smith-Osborne looked at two forms of psychosocial stress — social isolation and social instability — and how they manifest themselves based on social rank.
They conducted their research on adult female mice, putting them in pairs and allowing them to form a stable ...
The stars in the brain may be information regulators
2023-03-31
Long thought of as “brain glue,” the star-shaped cells called astrocytes—members of a family of cells found in the central nervous system called glial that help regulate blood flow, synaptic activity, keep neurons healthy, and play an important role in breathing. Despite this growing appreciation for astrocytes, much remains unknown about the role these cells play in helping neurons and the brain process information.
“We believe astrocytes can add a new dimension to our understanding of how external and internal information is merged in the ...
The Institut Pasteur and the University of São Paulo sign articles of association to establish the Institut Pasteur in São Paulo
2023-03-31
On Friday March 31st, 2023 at a ceremony in Paris, the Institut Pasteur President, Professor Stewart Cole, and the University of São Paulo (USP) Rector, Carlos Gilberto Carlotti Junior, signed articles of association for the Institut Pasteur in São Paulo, a private non-profit organization under Brazilian law. The mission of the institute, an associate member of the Pasteur Network, is to conduct research in the field of biology that contributes to the development of human health, and to promote outreach, education, innovation and knowledge transfer activities and public health measures.
The Institut Pasteur ...
Mathematical model provides bolt of understanding for lightning-produced X-rays
2023-03-31
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In the early 2000s, scientists observed lightning discharge producing X-rays comprising high energy photons — the same type used for medical imaging. Researchers could recreate this phenomenon in the lab, but they could not fully explain how and why lightning produced X-rays. Now, two decades later, a Penn State-led team has discovered a new physical mechanism explaining naturally occurring X-rays associated with lightning activity in the Earth’s atmosphere.
They published their ...
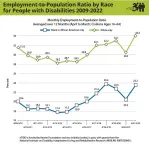
nTIDE March 2023 Deeper Dive: Intersection of race and disability perpetuate inequalities in employment impacting Black/African American people with disabilities
2023-03-31
East Hanover, NJ – March 31, 2023 – Since the pandemic, gains in the labor market have been slower to materialize for black/African American people with disabilities compared to their white counterparts, according to experts speaking last Friday during the nTIDE Deeper Dive Lunch & Learn Webinar. They discussed potential factors underlying why the disability employment gap is wider among members of the black/African American population when compared to the white population and how to integrate measures to effect change.
Using data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) for persons ages 16-64, the monthly employment-to-population ratio averaged ...
Researchers uncover the first steps driving antibiotic resistance
2023-03-31
Antibiotic resistance is a global health threat. In 2019 alone, an estimated 1.3 million deaths were attributed to antibiotic resistant bacterial infections worldwide. Looking to contribute a solution to this growing problem, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have been studying the process that drives antibiotic resistance at the molecular level.
They report in the journal Molecular Cell crucial and surprising first steps that promote resistance to ciprofloxacin, or cipro for short, one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics. The findings point at potential ...
Study reveals new insights into body salt handling
2023-03-31
HUNTINGTON, W.Va. – A new study led by Marshall University researchers focuses on a novel mechanism of the body’s regulation of salt balance.
The kidney plays a central role in the body’s ability to maintain an appropriate sodium balance, which is critical for the determination of blood pressure. Disorders of sodium balance contribute to the development and progression of many common diseases, including hypertension, heart disease and stroke.
Na/K-ATPase (NKA) is the enzymatic machinery that drives absorption of sodium along the renal proximal tubule. As ...
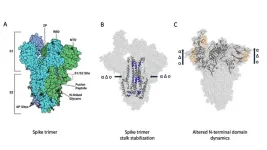
A tighter core stabilizes SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in new emergent variants
2023-03-31
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Just as a tight core is a component of good physical fitness for humans, helping to stabilize our bodies, mutations that tightened the core of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in new variants may have increased the virus’s fitness.
New research led by Penn State reveals that the stem region of the spike protein became progressively tighter over time, and the team thinks this likely improved the virus’s ability to transmit through nasal droplets and infect host cells once in the body. The team said the stem region of the protein that emerged in the most recent Omicron variants is as rigid as it can get, which could ...
Status epilepticus: New inflammatory markers to improve patient care
2023-03-31
A rare and nevertheless formidable event in the landscape of epilepsies, New-Onset Refractory Status Epilepticus (NORSE) is a form of prolonged seizure in which the neurons of the epileptic focus endure a continuous discharge of neurotransmitters. It is a medical emergency requiring intensive care management. Indeed, it can cause significant long-term neurological sequelae and is associated with an average mortality rate of 12% in children and 16 to 27% in adults. NORSE can occur in response to an infection or tumor development. However, its origin remains unknown in half of the affected patients despite extensive clinical and biological ...
Making rare cell types visible: Researchers are developing a new method
2023-03-31
The human body contains more than 30 trillion cells. Until recently, the sheer number of cells in the organism meant that approaches to understanding human diseases and developmental processes based on the analysis of single cells were a futuristic vision. The development of new sequencing methods is currently revolutionising our understanding of cellular heterogeneity. These technologies can detect rare or even new cell types by extracting and sequencing the genetic information from the cells based on ribonucleic acid chains.
In cooperation ...
More than 1,200 LOINC® registrants represent 78 countries for version 2.74 webinar
2023-03-31
INDIANAPOLIS -- LOINC®, an international data standard maintained at Regenstrief Institute, hosted an educational release webinar for version 2.74. More than 1,200 participants signed up, representing 78 countries.
The hour and a half webinar served as an opportunity for the LOINC team to introduce and explain the new concepts from the 2.74 release update. Participants were presented with opportunities to learn more about each new concept and ask questions.
LOINC, short for Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes, is a global standard for health terminology. Created and maintained at Regenstrief, LOINC enables the identification, exchange and collection of data across ...
NRG Oncology combined trial long-term results indicate that pathologic complete response is prognostic of outcomes for soft tissue sarcoma patients
2023-03-31
Combined long-term survival results from nonrandomized phase II trial NRG Oncology RTOG 0630 and the ancillary analysis of the combined NRG-RTOG 0630/9514 trials indicate that pathologic complete response (pCR) is associated with improved survival outcomes for patients with localized soft tissue sarcoma (STS) who receive preoperative chemoradiotherapy or radiotherapy. This data suggests that pCR can be used as a prognostic factor for clinical outcomes in future STS research. These results were recently published in the JAMA Oncology.
NRG-RTOG 0630 and 9514 both evaluated STS patients who were receiving either preoperative image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT; 0630) or neoadjuvant ...
[1] ... [2021]
[2022]
[2023]
[2024]
[2025]
[2026]
[2027]
[2028]
2029
[2030]
[2031]
[2032]
[2033]
[2034]
[2035]
[2036]
[2037]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.