Light-bending gravity reveals one of the biggest black holes ever found
2023-03-29
A team of astronomers has discovered one of the biggest black holes ever found, taking advantage of a phenomenon called gravitational lensing.
The team, led by Durham University, UK, used gravitational lensing - where a foreground galaxy bends the light from a more distant object and magnifies it – and supercomputer simulations on the DiRAC HPC facility, which enabled the team to closely examine how light is bent by a black hole inside a galaxy hundreds of millions of light years from Earth.
They found an ultramassive black hole, an object over 30 billion times the ...
Detecting coral biodiversity in seawater samples
2023-03-29
Researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have developed a method to measure coral biodiversity through extracting the environmental DNA (or eDNA) from a liter of surface seawater collected from above a reef. The method has been confirmed to work through observations made by scientific divers in the same areas of ocean. The research, conducted in collaboration with the Okinawa Prefecture Environmental Science Center and University of Tokyo, was published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. This has paved the way for large-scale comprehensive surveys of reef-building coral to take place and removes the reliance of ...
Research autopsies reveal how incurable skin cancer resists treatment
2023-03-29
Scientists have found out how some skin cancers stop responding to treatment at the end of life.
An in-depth analysis of 14 patients who died from incurable melanoma has revealed that changes to the order, structure and number of copies of tumour DNA could cause some skin cancers to resist treatment. These changes also explain how melanoma can spread to other parts of the body.
The research, published today (29th March) in the journal Cancer Discovery, was led by scientists and clinicians at the Francis Crick Institute, UCL and The Royal Marsden. It is part of the Cancer ...
COVID vaccine induces robust T cell responses in blood cancer patients
2023-03-29
Researchers found that, despite being heavily immunocompromised, haematology patients generate strong cellular immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 after vaccination, on par with that of healthy individuals.
Published today in Cell Reports Medicine, the research team, led by University of Melbourne Professor Katherine Kedzierska, a Laboratory Head at the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), undertook the most comprehensive analysis of adaptive SARS-CoV-2 immunity to ...
Revolutionary battery technology to boost EV range 10-fold or more
2023-03-29
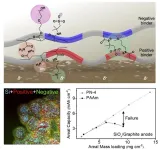
The electric vehicle market has been experiencing explosive growth, with global sales surpassing $1 trillion (approx. KRW 1,283 trillion) in 2022 and domestic sales exceeding 108,000 units. Inevitably, demand is growing for high-capacity batteries that can extend EV driving range. Recently, a joint team of researchers from POSTECH and Sogang University developed a functional polymeric binder for stable, high-capacity anode material that could increase the current EV range at least 10-fold.
A research team led by POSTECH professors Soojin Park (Department of Chemistry) and Youn Soo Kim (Department ...
Cooking up plasmas with microwaves
2023-03-29
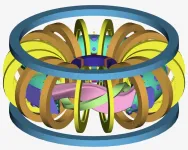
Kyoto, Japan -- Lead author Yurii Victorovich Kovtun, despite being forced to evacuate the Kharkiv Institute of Physics and Technology amid the current Russia-Ukraine war, has continued to work with Kyoto University to create stable plasmas using microwaves.
Getting plasma just right is one of the hurdles to harnessing the massive amounts of energy promised by nuclear fusion.
Plasmas -- soups of ions and electrons -- must be held at the right density, temperature, and duration for atomic nuclei to fuse together to achieve the desired release of energy.
One recipe involves the use of large, donut-shaped devices with powerful magnets ...
12th World Conference of Science Journalists opens under open skies
2023-03-29
The opening day of the World Conference of Science Journalists (WCSJ) 2023 in Medellín, Colombia saw hundreds of journalists from 62 countries come together in the stunning setting of the city’s Jardin Botanico.
Over 500 attendees will gather over three days to discuss science journalism, to challenge ideas and to reinforce their professional networks and friendships.
The day began with a keynote on biodiversity delivered by Brigitte Baptiste, a Colombian biologist and expert in biodiversity issues. And it closed with an opening ceremony and vibrant social event for attendees.
Both took place under open skies in the ...
Revealing the nature of fractures caused by hydrogen in high-strength steel
2023-03-29
One of the many ways to reduce the energy required for transportation is to make vehicles lighter. High-strength (HS) steels are perfect candidate materials for this purpose, as their higher weight-to-strength ratio allows for the use of less metal to achieve a similar structural integrity. Many automobile companies believe HS steels will be an essential component of various types of cars in the future. However, for this to become a reality, there is a glaring problem that needs to be solved.
When HS steel is exposed to rainwater (H2O) or hydrogen, a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement occurs. Hydrogen atoms diffuse into the lattice ...
Implementing green corridors throughout Barcelona could reduce annual antidepressant use and visits to mental health specialists by 13%
2023-03-29
A health impact assessment led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation, has concluded that implementing green corridors throughout the city of Barcelona would result in a “considerable reduction” in mental disorder cases in adult residents as well as in direct and indirect costs associated to said cases. The study was published in the journal Environment International.
It is estimated that mental health disorders ...
AI shows the need for healthier diets in long-term care homes
2023-03-29
A detailed analysis of consumed food showed there is a need to improve diets in long-term care (LTC) homes to make them healthier for residents.
The analysis found that eating more whole grains, plant-based proteins, and plain fruits and vegetables would help residents meet government guidelines and reduce their risk of inflammation.
Researchers at the University of Waterloo developed new artificial intelligence (AI) technology to examine data on food and fluids consumed by more than 600 residents over three days at 32 LTC homes.
Results were compared to recommendations in the 2019 Canada’s Food Guide on healthy eating and expert ...
Eye-tracking during building inspections provides insight on how experts think
2023-03-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — After a building failure due to natural disasters or poor structural design, safety inspectors must enter a structure to assess the damage before occupants can return. Researchers in the Penn State Department of Architectural Engineering studied how building inspectors make their safety assessments, by analyzing their gaze patterns with eye-tracking software. Eventually, the eye-tracking data could be used to code autonomous robots, like drones, to conduct building assessments in place of humans.
The researchers' results were published in Scientific Reports.
“We ...
New soil sensor may improve efficiency of crop fertilization
2023-03-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Measuring temperature and nitrogen levels in soil is important for agriculture systems but detecting them apart from one another is difficult to do. Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, James L. Henderson, Jr. Memorial Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics at Penn State, led researchers in the development of a multi-parameter sensor that can effectively decouple temperature and nitrogen signals so that each can be measured accurately. The results were recently published by Advanced Materials.
“For efficient fertilization, ...
Story tip: A wise tool for modifying microbes
2023-03-28
A DNA editing tool adapted by Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists makes engineering microbes for everything from bioenergy production to plastics recycling easier and faster.
The Serine recombinase-Assisted Genome Engineering, or SAGE system, lets scientists quickly insert and test new DNA designs in a variety of microorganisms. Engineered microbes hold promise for making biofuels, recycling mixed plastics, aiding soil carbon storage and treating health disorders.
“SAGE works in virtually all microorganisms, revolutionizing what we’re able to do with microbes,” ...
Individualized brain fingerprints can help to uncover early signs of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-03-28
Neuroscientists from the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) report in Brain Connectivity that they have detected subtle differences in the way the brain functions in older adults with preclinical Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Adults with preclinical AD have the earliest signs of disease, such as buildup of amyloid-beta proteins in their brains. However, they have no noticeable symptoms of cognitive decline.
The research team, led by Andreana Benitez, Ph.D., and Stephanie Fountain-Zaragoza, Ph.D., used a novel brain imaging analysis technique to construct individualized maps of brain function. They then looked to see if there were ...
Tax on sugary drinks helps health during pregnancy
2023-03-28
Taxes on sugary drinks reduce the risk of gestational diabetes and unhealthy weight gain in pregnant women, reports a new UC San Francisco study of more than 5 million women.
Published by the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, this is the first study to examine how sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) taxes affect the health of mothers and children immediately before and after birth. Researchers compared mothers who were living in cities that had SSB taxes in effect while they were pregnant to mothers in cities with no SSB taxes. In addition to significantly lowering the risk of diabetes and unhealthy weight gain ...
Technology to protect bioactive compounds from food during digestion
2023-03-28
Bioactive compounds present mostly in fruit and vegetables perform different bodily functions relating to health and well-being. Their effects are considered antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiaging and anticancer, among others.
Many studies are looking for ways to optimize absorption of bioactive compounds by the organism and increase their bioavailability – the proportion that enters the bloodstream after absorption. One way is to coat the compounds with another material and package them on the nanometric scale (a nanometer is a billionth of a meter). Nanoencapsulation, as this technique is known, assures slow release of the compounds so that they take longer to digest and can survive ...
New drug combination holds unusually positive results for HPV-negative patients with advanced head and neck cancer
2023-03-28
WASHINGTON (March 28, 2023)— A new combination drug treatment showed promising results in patients with pan-refractory, recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer, according to a study published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Head and neck cancer is a deadly form of cancer that arises in the lining of the mouth and throat. Worldwide more than 700,000 people were diagnosed with head and neck cancer in 2021. The disease is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) or environmental carcinogens, including the regular use of tobacco or alcohol. When the cancer comes back after curative ...
NASA wallops supports second rocket lab electron launch
2023-03-28
NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility supported the successful launch of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket at 6:39 p.m. EDT, Thursday, March 16, from Virginia’s Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport on Wallops Island, Virginia.
The mission, named “Stronger Together,” carried two, 100-kilogram commercial satellites to low-Earth orbit for Capella Space.
“I’m extremely proud of the NASA team that helped ensure a safe and successful launch operation today,” said ...
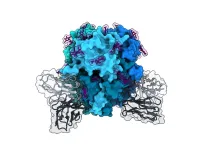
Researchers find new molecule that shows promise in slowing SARS-CoV-2
2023-03-28
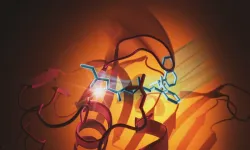
Researchers have designed a molecule that slows the effects of one of SARS-CoV-2's more dangerous components – an enzyme called a protease that cuts off the immune system's communications and helps the virus replicate.
While much more needs to happen to develop a drug, scientists can begin to imagine what that drug could look like – thanks to new images of the molecule bound to the protease.
“We have been searching for an effective molecule like this one for a while,” said Suman Pokhrel, a Stanford University graduate student in chemical and systems biology and one of the paper’s lead authors. “It is ...
Rural educators find solutions to support multilingual learners
2023-03-28
A new study found a professional development program helped teachers in a rural school district in the Southeast to collaborate and identify innovative solutions to serve multilingual learners, or students learning English as a second language.
The study, published in the Journal of Research in Rural Education, suggests professional development can help prepare teachers in rural districts that have fewer resources and a growing need to support multilingual learners.
“Professional development is essential in rural communities, where you might not have resources for specialists like a literacy coach, bilingual school psychologist, or bilingual family engagement specialist,” ...
Retinal scans: A non-invasive, inexpensive method to track human aging
2023-03-28
Buck Institute professor Pankaj Kapahi thinks the eye is a window to aging. His lab, in collaboration with Google Health and Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, has shown how imaging of the fundus, the blood vessel-rich tissue in the retina, can be used to track human aging, in a way that is noninvasive, less expensive and more accurate than other aging clocks that are currently available. Publishing in eLife, researchers also did a genome-wide association study (GWAS) to establish the genetic basis for such a clock, which they call eyeAge.
“This type of imaging could be really ...
New additives could turn concrete into an effective carbon sink
2023-03-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Despite the many advantages of concrete as a modern construction material, including its high strength, low cost, and ease of manufacture, its production currently accounts for approximately 8 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions.
Recent discoveries by a team at MIT have revealed that introducing new materials into existing concrete manufacturing processes could significantly reduce this carbon footprint, without altering concrete’s bulk mechanical properties.
The findings are published today in the ...
Fluorescent visualization and evaluation of NPC1L1-mediated cholesterol absorption at the levels of endocytic vesicles
2023-03-28
Excessive cholesterol absorption from intestinal lumen contributes to the pathogenesis of hypercholesterolemia, which is a well-established risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The absorption of intestinal cholesterol is primarily mediated by Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) protein, which is responsible for about 70% cholesterol absorption. NPC1L1-deficient mice are resistant to diet-induced hypercholesterolemia, which provides a compelling strategy for intervention the related diseases through inhibiting NPC1L1 expression or activity.
NPC1L1 protein is expressed in the brush border membrane of small intestine. The protein is extensively N-glycosylated ...
Biden-Harris Administration announces recipients of the Enrico Fermi Award
2023-03-28
Today, the Biden-Harris Administration announced Darleane C. Hoffman and Gabor A. Somorjai as recipients of the Enrico Fermi Presidential Award, one of the oldest and most prestigious science and technology honors bestowed by the U.S. government.
“Dr. Hoffman and Dr. Somorjai’s work to open the frontiers of radiochemistry and surface chemistry helped change what was possible, and advanced efforts to tackle some of the world’s greatest challenges,” said Assistant to the President and Director of the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy Arati Prabhakar. “They are world-class ...
We've learned a lot from lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus—now the time has come to fight it
2023-03-28
Key findings:
There are no vaccines or therapies available for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection. This pathogen spreads easily and is extremely common in people worldwide.
Infection with LCMV can cause birth defects in developing fetuses, and severe illness and even death in the immuncompromised.
New findings from La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) scientists show how an engineered antibody can target LCMV and neutralize the virus. They found this antibody has the potential to both prevent infection and treat an already established infection.
With this better understanding of LCMV's weak spots, scientists can move forward ...
[1] ... [2029]
[2030]
[2031]
[2032]
[2033]
[2034]
[2035]
[2036]
2037
[2038]
[2039]
[2040]
[2041]
[2042]
[2043]
[2044]
[2045]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.