Patient and hospital characteristics associated with postpartum emergency department care
2023-03-21
About The Study: This study including 608,000 obstetric discharges found that Black and Hispanic patients experienced higher adjusted odds of postpartum emergency department visits across all hospital types, particularly at safety net hospitals and those disproportionately serving racial and ethnic minority populations. These findings support the urgent need to mitigate structural racism underlying maternal health disparities.
Authors: Michelle P. Lin, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., of Stanford ...
Associations between parent-adolescent relationships and young adult health
2023-03-21
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that adolescents’ positive perceptions of their relationships with their mothers and fathers are associated with a wide range of favorable outcomes in young adulthood. Investments in improving parent-adolescent relationships may have substantial benefits for young adult population health.
Authors: Carol A. Ford, M.D., of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.3944)
Editor’s ...
New possibilities in the theoretical prediction of particle interactions
2023-03-21
How does the world look like at the smallest scales? This is a question scientists are trying to answer in particle collider experiments like the Large Hadron Collider at CERN in Switzerland. To compare the results of these experiments, theoretical physicists need to provide more and more precise predictions based on our current model for the interactions of fundamental particles, the so called standard model. A key ingredient in these predictions are so called Feynman integrals. Recently, a team of the PRISMA+ Cluster of Excellence at Mainz University, consisting of Dr. Sebastian Pögel, Dr. Xing Wang and Prof. Dr. Stefan Weinzierl developed a method to efficiently ...
A new view of microscopic processes
2023-03-21
COLUMBIA, Mo. — For more than 20 years, Matt Maschmann, an associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the University of Missouri, has worked with materials that require specialized technology — electron microscopes — to be seen by the human eye.
“When we deal with materials interacting on a nanoscale level, we can’t physically see the processes that are occurring, like the charging and discharging of a battery, for instance, without the help of an electron microscope,” Maschmann said.
Now, with the support of a two-year, $800,000 grant from the National Science Foundation and an ...
Decline comes later than previously thought
2023-03-21
Utrecht, March 21, 2023 - Recent research from University Medical Center Utrecht (UMC Utrecht) shows that our brain declines later than previously thought. Instead of after our 25th year of life, it happens when we are between the ages of 30 and 40. The researchers published their results in Nature Neuroscience.
Clinical technologist Dorien van Blooijs and neurologist Frans Leijten, together with colleagues from UMC Utrecht and the Mayo Clinic, conducted research into the processing speed of our brain and how it changes as we age.
Faster ...
LSU Health New Orleans study suggests interprofessional team training could prove effective in AUD prevention & treatment
2023-03-21
New Orleans, LA – An LSU Health New Orleans study demonstrated the effectiveness of single, focused Interprofessional Education (IPE)-based exercises in preparing young health professions learners to limit or prevent alcohol use disorder (AUD). Students learned together as a foreshadowing of future interprofessional practice. This intervention produced significant decreases in the stigma associated with alcohol use, which is highly relevant for potential AUD patients. Results are published in BMC Medical Education, available here.
“These results may translate into more effective and collaborative ...
HonorHealth Research Institute is Arizona’s first to adopt new radiation protection technology in treatment of heart disease
2023-03-21
SCOTTSDALE, Ariz. — March 21, 2023 — HonorHealth Research Institute announced today that it is among the first healthcare providers in the U.S., and the first in Arizona, to use an advanced radiation protection system as part of the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease.
Modern cardiac catheterization laboratories use multiple X-ray beams from different angles to produce high-quality images of the heart, major arteries and other tissues. These low-level radiation beams enable physicians to guide catheters and other devices during interventional cardiology procedures, which are non-surgical, catheter-based therapies for ...
Insights into causes of rare genetic immune disorders
2023-03-21
The cellular glitches underlying a rare genetic disorder called activated PI3K Delta syndrome 2 (APDS2) have been identified by researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research. The disorder is caused by genetic variations that disrupt immune cell signalling through a protein called PI3K.
“This study tells us how signalling in the immune system needs to be tightly balanced to make an effective response to infection. Sometimes it’s turned down and you have a problem, and sometimes signalling being turned up can interfere with an immune ...
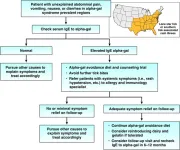
Lone star tick bites may be to blame for unexplained digestive problems
2023-03-21
Bethesda, MD (March 21, 2023) — The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has released new clinical guidance to help physicians and patients identify if unexplained digestive symptoms are due to alpha-gal syndrome, a food allergy that is caused by lone star tick bites. The AGA Clinical Practice Update was published today in Gastroenterology.
Alpha-gal syndrome is an allergy that causes your body to react to eating meat from mammals and products made from mammals. Symptoms usually start 2-6 hours after eating the mammalian meat or food.
Clinicians should consider alpha-gal syndrome in patients ...
Forests reduce health risks, new global report confirms
2023-03-21
Forests, trees and green spaces play a vital role in ensuring a healthy life for all on a global scale.
The health benefits of forests and trees, ranging from physical and mental well-being to overall mortality reduction, far outweigh the adverse effects on health. As health threats, such as forest fires, are mainly caused by human activities, urgent action is needed.
In order to address health challenges, it is important to recognize the close links between human health and the health of other species, of ecosystems, and of the planet as a whole.
Vienna, March, 21, 2023 - The global scientific evidence of the multiple types of benefits ...
ASBMB cautions against drastic immigration fee increases
2023-03-21
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent recommendations to the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services related to the agency’s proposed changes to petition processing fees. The USCIS proposed increasing its filing fees for employment-based visas by up to 2,050%, a measure intended to remedy financial deficits at USCIS and ramp up hiring to improve services. The ASBMB expressed concern about how “the proposed rule is likely to harm the retention of highly skilled foreign-born scientific researchers.”
The ...
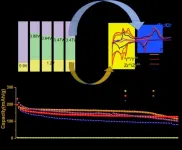
A new sight for the electrochemical stability in halide electrolytes
2023-03-21
They published their work on February in Energy Material Advances.
"Constructing an efficient ionic/electronic framework is crucial for the development of high-performance solid-state batteries," said Dr. Chuang Yu, a professor at the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Electromagnetic Engineering and Technology at Huazhong University of Science and Technology. "Currently, the application of solid-state batteries with inorganic electrolytes is challenging because most solid electrolytes have an unsatisfactory low oxidation potential."
According to Dr. Yu, halide electrolytes have been found to be cathode-stable materials with relatively wide electrochemical ...
Study confirms nitrate can release uranium into groundwater
2023-03-21
Eight years ago, the data was sound but only suggestive, the evidence strong but circumstantial.
Now, the University of Nebraska–Lincoln’s Karrie Weber and colleagues have experimentally confirmed that nitrate, a compound common in fertilizers and animal waste, can help transport naturally occurring uranium from the underground to groundwater.
Their new research backs a 2015 Weber-led study showing that aquifers contaminated with high levels of nitrate — including the High Plains Aquifer residing beneath Nebraska — also contain uranium concentrations far exceeding a threshold set by the Environmental Protection Agency. Uranium concentrations above that EPA threshold ...
PNAS announces six 2022 Cozzarelli Prize recipients
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, DC – The Editorial Board of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) has selected six papers published by PNAS in 2022 to receive the Cozzarelli Prize, an award that recognizes outstanding contributions to the scientific disciplines represented by the National Academy of Sciences (NAS). Papers were chosen from more than 3,200 research articles that appeared in the journal last year and represent the six broadly defined classes under which the NAS is organized. Additionally, the Editorial ...
Using optics to trace the flow of microplastics in oceans
2023-03-21
Microplastics are tiny plastic particles less than 5 mm in diameter that have emerged as a novel marine environment pollutant. Microplastics usually result from a breakdown of larger plastic debris but can also be generated from plastic microbeads used in personal care products. Over the years, there has been a significant buildup of microplastic pollutants in our oceans, with a recent estimate that the world’s oceans contain over 24.4 trillion pieces of microplastics weighing between 82,000 and 578,000 tons. It is highly likely that ...
First results from ESO telescopes on the aftermath of DART’s asteroid impact
2023-03-21
Using ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), two teams of astronomers have observed the aftermath of the collision between NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) spacecraft and the asteroid Dimorphos. The controlled impact was a test of planetary defence, but also gave astronomers a unique opportunity to learn more about the asteroid’s composition from the expelled material.
On 26 September 2022 the DART spacecraft collided with the asteroid Dimorphos in a controlled test of our asteroid deflection capabilities. The impact took place 11 million kilometres away ...
Obesity risk may pass from mothers to daughters
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON—Women with obesity may share risk for the disease with their daughters, but not their sons, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society’s Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
Obesity is a common, serious and costly disease affecting nearly half of the adults and 20 percent of children in the United States. It costs an estimated $173 billion in medical care costs. People with obesity are at higher risk of developing diabetes, high blood pressure, heart ...
New program for veterans with high cholesterol, associated cardiovascular disease
2023-03-21
DALLAS, March 21, 2023 — More than 2 million veterans are living with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) and require management of their high cholesterol, according to the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). Left unaddressed, high cholesterol increases the chance of experiencing heart attack and stroke. To control high cholesterol among veterans, the American Heart Association, the world’s leading nonprofit organization focused on heart and brain health for all, in collaboration with the VA, ...
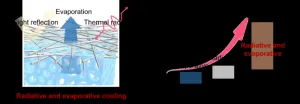
An integrated approach to cool: how evaporation and radiation can cool the world
2023-03-21
Large-scale, effective, and passive: these descriptions are aptly given to the integrated radiative and evaporative chiller (IREC), designed and tested by researchers at Tsinghua University in Beijing, China. The goal of this technology is to come up with an energetically affordable method of cooling to aid in the rising consumption of energy while still minimizing carbon emissions through the process.
“Energy scarcity is a universal challenge to global development. The demand for ...
TAMEST names MD Anderson’s Dr. Florencia McAllister recipient of the 2023 Mary Beth Maddox Award & Lectureship
2023-03-21
TAMEST (The Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology) has announced Florencia McAllister, M.D., The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, as the recipient of the 2023 Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship in cancer research. She was chosen for her seminal discoveries at the intersection of microbes, the immune system and pancreatic cancer, leading to insights into early detection, prevention and therapeutic strategies to fight the disease.
The Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship ...
Family Heart Foundation research finds high-risk Americans who do not maintain guideline recommend LDL-C targets have 44% higher rate of cardiovascular events
2023-03-21
SAN ANTONIO, March 21, 2023 – A real-world, retrospective analysis by the Family Heart Foundation, a leading non-profit research and advocacy organization, found that high-risk Americans who do not maintain levels of LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C) recommended in the 2018 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association cholesterol treatment guidelines, had a 44% higher rate of cardiovascular events compared to those who did achieve and maintained recommended LDL-C levels. The study findings, which were based on data from the Family Heart DatabaseTM of more than 300 million Americans, will be ...
Forest growing season in eastern U.S. has increased by a month
2023-03-21
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The growing period of hardwood forests in eastern North America has increased by an average of one month over the past century as temperatures have steadily risen, a new study has found.
The study compared present-day observations of the time span from budburst to peak leaf coloration in seven tree species to similar documentation that was collected by an Ohio farmer at the turn of the 20th century.
An analysis of changes in those leaf patterns along with decades of temperature data for northwest Ohio showed a clear connection between increased warming during winter and spring and an extended period of tree growth.
The implications of the longer growing period – ...
How the "marsupial sabertooth" thylacosmilus saw its world
2023-03-21
A new study investigates how an extinct, carnivorous marsupial relative with canines so large they extended across the top of its skull could hunt effectively despite having wide-set eyes, like a cow or a horse. The skulls of carnivores typically have forward-facing eye sockets, or orbits, which helps enable stereoscopic (3D) vision, a useful adaptation for judging the position of prey before pouncing. Scientists from the American Museum of Natural History and the Instituto Argentino de Nivología, ...
Molecular teamwork makes the organic dream work
2023-03-21
The virus responsible for E. coli infection has a secret weapon: teamwork.
Always scrappy in its bid for survival, the virus alights on an unassuming host cell and grips the surface with the business end of its tubular tail. Then, the proteins in the tail contract in unison, flattening its structure like a stepped-on spring and reeling the virus's body in for the critical strike.
Thanks to the proteins' teamwork, the tail can flex and flatten with ease. This process, called molecular cooperativity, is often observed in nature but rarely ...
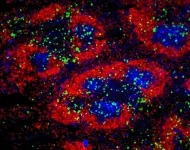
Wearable microscopes advance spinal cord imaging in mice
2023-03-21
LA JOLLA—(March 21, 2023) The spinal cord acts as a messenger, carrying signals between the brain and body to regulate everything from breathing to movement. While the spinal cord is known to play an essential role in relaying pain signals, technology has limited scientists’ understanding of how this process occurs on a cellular level. Now, Salk scientists have created wearable microscopes to enable unprecedented insight into the signaling patterns that occur within the spinal cords of mice.
This technological advancement, detailed in two papers published in Nature Communications ...
[1] ... [2034]
[2035]
[2036]
[2037]
[2038]
[2039]
[2040]
[2041]
2042
[2043]
[2044]
[2045]
[2046]
[2047]
[2048]
[2049]
[2050]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.