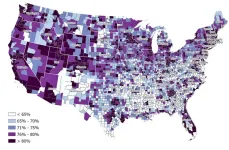
How one state beat national surgery opioid trends
2023-03-25
A statewide effort to treat the pain of surgery patients without increasing their risk of long-term dependence on opioids has paid off in Michigan, a study shows.
In less than two years, the effort led to a 56% reduction in the amount of opioids patients received after having six different common operations, and a 26% drop in the chance that they would still be filling opioid prescriptions months after their surgical pain should have eased.
Both of those drops beat national trends for similar patients, according to the new study published ...
Acquisitions can nix existing partnerships
2023-03-25
Business alliances are valuable because they help companies supplement critical skills, enter new markets, and gain competitive advantages.
In the pharmaceutical industry, strategic alliances are common because they help companies reduce risks and share the large R&D costs of bringing new drugs to market — like the partnership of Pfizer and BioNTech on vaccines. Such partnerships can take years to develop and are critical to a pharma company’s success.
But when biopharmaceutical companies merge, preserving their preexisting alliances isn’t always a priority, according to a new Texas McCombs study.
“High-performing alliances ...
Illinois Tech Assistant Professor Ren Wang receives prestigious National Science Foundation Award
2023-03-25
CHICAGO—March 24, 2023—Illinois Institute of Technology Assistant Professor Ren Wang has been honored with the National Science Foundation’s Computer and Information Science and Engineering Research Initiation Initiative (CRII) award. The two-year grant will support Wang’s groundbreaking research project, which aims to enhance the robustness of machine learning models by infusing key principles of the immune system into neural networks.
Wang’s innovative project, titled “Immune-Inspired Learning Foundations of Neural Network General Robustness,” not only advances the theory and ...
Antibiotics do not reduce risk of dying in adults hospitalised with common respiratory infections, suggests study
2023-03-25
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the congress if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Friday 24 March
Most patients admitted to hospital with acute viral respiratory infections are given antibiotics. Now new research to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April), suggests that prescribing antibiotic therapy to adults hospitalised with common viral respiratory infections such as influenza is unlikely to ...
Major European study confirms drop in suicides in last decade: may be linked to active measures to prevent suicide
2023-03-25
A major new study confirms the trend to fewer suicides in Europe. The findings show that suicide rates are down in 15 countries (including Germany and Italy), and stable elsewhere (including France, Spain and UK). Only Türkiye shows a significant increase. This work is presented for the first time at the European Congress of Psychiatry in Paris.
Suicide is one of the major causes of premature death, globally around 700,000 suicides are reported each year. European suicide rates have been generally ...
MSU researchers find clue to help plants grow with low phosphorus levels
2023-03-24
EAST LANSING, Mich. – Phosphorus is a natural mineral that is essential for plant growth and development, and Earth’s agricultural-grade phosphorus reserves are expected to be depleted in 50 to 100 years. A new discovery by researchers at Michigan State University and the Carnegie Institution for Science is changing their understanding of iron toxicity in plants caused by low phosphorus levels.
“Once the world’s supply is used up, we can’t make more phosphorus,” said Hatem Rouached, an assistant professor in MSU’s ...
New type of entanglement lets scientists ‘see’ inside nuclei
2023-03-24
The Science
Nuclear physicists have found a new way to see details inside atomic nuclei. They do so by tracking interactions between particles of light and gluons—the gluelike particles that hold together the building blocks of protons and neutrons. The method relies on harnessing a new type of quantum interference between two dissimilar particles. Tracking how these entangled particles emerge from the interactions lets scientists map out the arrangement of gluons.
The Impact
This technique is similar to how positron emission tomography (PET) scans image the brain and other body parts, but ...
NIH awards researchers $7.5 million to create data support center for opioid use disorder and pain management research
2023-03-24
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. – March 24, 2023 – Researchers at Wake Forest University School of Medicine have been awarded a five-year, $7.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Helping End Addiction Long-term (HEAL) initiative.
The NIH HEAL initiative, which launched in 2018, was created to find scientific solutions to stem the national opioid and pain public health crises. The funding is part of the HEAL Data 2 Action (HD2A) program, designed to use real-time data to guide actions and change processes toward reducing overdoses and improving opioid use disorder treatment ...
New study supports saving more lung tissue in lung cancer surgeries
2023-03-24
The traditional treatment for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer is a lobectomy, where a surgeon eradicates cancerous tissue by removing an entire lung lobe.
Yet, new research finds that select patients with early-stage disease who undergo a less invasive procedure have comparable outcomes, sparking hope for a less aggressive approach to lung cancer surgery.
The 10-year study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine and led by University of Chicago Medicine medical ...
If you build it, they will come
2023-03-24
Louisiana’s newly released draft of the state’s 2023 Coastal Master Plan proposes to spend $16 billion on the construction of new tidal marshes as a key strategy to combat coastal land loss. An important question is whether these newly created marshes will be similar in ecological value to the existing natural marshes. A new study published in the journal Ecosphere and funded by the NOAA RESTORE Science Program addresses this issue, and the results provide positive news for the state’s plans to rebuild the coastline.
“This work is really exciting because ...
With fewer salmon to eat, Southern Resident killer whales spend less time in the San Juan Islands
2023-03-24
NEWPORT, Ore. – As a key food supply declines, the endangered population of Southern Resident killer whales, known to frequent the Salish Sea off the coasts of Washington and British Columbia, is spending far less time in that region, a new study shows.
The Salish Sea around the San Juan Islands has traditionally been a hotspot for the whales. The Southern Residents would spend the summer months feeding on Chinook salmon, much of which belonged to the Fraser River stock that passes through the islands on its way to spawning grounds upriver.
But 17 years of whale sighting data shows that as the Fraser River Chinook salmon population dropped, the time spent ...
Where there’s smoke, there’s thiocyanate: McMaster researchers find tobacco users in Canada are exposed to higher levels of cyanide than other regions
2023-03-24
HAMILTON, ON – Mar 24, 2024 – Tobacco users in Canada are exposed to higher levels of cyanide than smokers in lower-income nations, according to a large-scale population health study from McMaster University.
Scientists made the discovery while investigating the molecule thiocyanate – a detoxified metabolite excreted by the body after cyanide inhalation. It was measured as a urinary biomarker of tobacco use in a study of self-reported smokers and non-smokers from 14 countries of varying socioeconomic status.
“We expected the urinary thiocyanate levels would be similar across regions and reflect primarily smoking intensity. However, ...
SIAM Conference on Applications of Dynamical Systems (DS23)
2023-03-24
The application of dynamical systems theory to areas outside of mathematics continues to be a vibrant, exciting, and fruitful endeavor. These application areas are diverse and multidisciplinary, covering areas that include biology, chemistry, physics, climate science, social science, industrial mathematics, data science, and more. This conference strives to amass a blend of application-oriented material and the mathematics that informs and supports the discipline. The goals of the conference are a cross-fertilization of ideas from different application areas and increased communication between ...
SIAM Conference on Mathematical & Computational Issues in the Geosciences (GS23)
2023-03-24
The study of geophysical systems at all scales, whether from a scientific or technological perspective, calls for sophisticated mathematical modeling, efficient computational methods, and pervasive integration with data. This effort is fundamentally interdisciplinary. This conference aims to stimulate the exchange of ideas among geoscientific modelers, applied mathematicians, statisticians, and other scientists, fostering new research in the mathematical foundations with an impact on geoscience applications. END ...
New experiment translates quantum information between technologies in an important step for the quantum internet
2023-03-24
Researchers have discovered a way to “translate” quantum information between different kinds of quantum technologies, with significant implications for quantum computing, communication, and networking.
The research, published in the journal Nature on Wednesday, was funded by the Army Research Office (ARO), the Air Force Office of Scientific Research (AFOSR), and the NSF Quantum Leap Challenge Institute for Hybrid Quantum Architectures and Networks (HQAN), which is led by the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. It represents a new way to convert quantum information from the format used by quantum computers to the format needed ...
NASA prepares for historic asteroid sample delivery on Sept. 24
2023-03-24
NASA's OSIRIS-REx spacecraft is cruising back to Earth with a sample it collected from the rocky surface of asteroid Bennu. When its sample capsule parachutes down into the Utah desert on Sept. 24, OSIRIS-REx will become the United States’ first-ever mission to return an asteroid sample to Earth.
After seven years in space, including a nail-biting touchdown on Bennu to gather dust and rocks, this intrepid mission is about to face one of its biggest challenges yet: deliver the asteroid sample to Earth while protecting it from heat, vibrations, and earthly contaminants.
“Once the sample capsule touches down, our team ...
11 ways to improve airlines for customers
2023-03-24
COLUMBIA, Mo— The name of the game is customer satisfaction, especially in the airline industry where companies are constantly jockeying for business by promising better service than their competitors. Now a professor at the University of Missouri has used artificial intelligence to sort through thousands of customer reviews and identify where airlines are falling short.
Sharan Srinivas, an assistant professor with a joint appointment in the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering and the Department of Marketing, used AI to analyze nearly 400,000 unique, ...
New mining technology uses CO2 as tool to access critical minerals
2023-03-24
A mining technology pioneered by researchers at the Bureau of Economic Geology at The University of Texas at Austin could reduce the amount of energy needed to access critical minerals vital for modern energy technologies and capture greenhouse gases along the way.
Transitioning the world’s energy to technologies and sources with low-carbon emissions will take, in part, tremendous amounts of lithium, nickel, cobalt and other critical minerals that exist in low concentrations in the Earth’s crust. Mining those elements takes much energy and produces waste, which can negatively affect the environment and create significant amounts of greenhouse ...
Wastewater to energy: new treatment process can improve biorefinery sustainability
2023-03-24
Wastewater from biorefineries that convert plants into fuel is full of organic materials that cannot be efficiently treated with conventional wastewater systems, making it costly and energy-intensive to manage.
However, those rich organic materials are an untapped source of chemical energy that can be recovered as valuable products, including biogas, a clean-burning renewable fuel.
A study by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) found that recovering resources from wastewater can substantially improve the economic and environmental sustainability of second-generation ...
U.S. Department of Energy and Stellantis announce the Battery Workforce Challenge
2023-03-24
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and Stellantis today announced the launch of the Battery Workforce Challenge, which includes a three-year collegiate engineering competition; vocational training; youth education in science, technology, engineering and math (STEM); and career and technical education.
DOE has set a bold target to address the climate crisis and puts our nation on a path to achieve net-zero emissions, economy-wide, by 2050 for the benefit of all Americans. Key to this target goal are the design and development of advanced batteries to electrify ...
Study finds higher risk of sleep problems in gay, lesbian, and bisexual youth
2023-03-24
Toronto, ON - A new national study, published in LGBT Health, finds that lesbian, gay, and bisexual (LGB) youth are twice as likely to report trouble falling or staying asleep than their straight peers. Greater depression, stress, and family conflict contribute to the sleep problems of LGB youth.
“Young people who identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual may face discrimination and negative attitudes because of their sexual orientation. These experiences can make it harder for them to get a good night’s sleep,” says lead author, Jason Nagata, MD, assistant professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. “Difficulties getting ...
UW researchers identify cell type that could be key to preventing marrow transplant complication
2023-03-24
A bone marrow transplant can be a lifesaving treatment for people with relapsed blood cancers, but a potentially lethal complication known as graft-versus-host disease put limitations on this procedure. New research from the University of Wisconsin–Madison is helping to change that by identifying the cell population that causes GVHD, a target that may make bone marrow transplants safer and more effective.
An allogenic (from a donor) bone marrow transplant is a common treatment for blood cancers and other diseases of the immune system. During the transplant, the patient’s immune cells are replaced with the donor’s ...
Buprenorphine after nonfatal opioid overdose results in reduced risk of overdose death
2023-03-24
Receiving medication for opioid use disorders, such as buprenorphine after an overdose, leads to lower mortality risk, according to a Rutgers study.
Drug overdose deaths are a significant public health concern in the United States. According to the National Center for Health Statistics, there were more than 105,000 drug overdose deaths in 2021, which were largely attributed to opioids. Rutgers researchers found that opioid-involved overdose deaths following nonfatal overdose events are largely preventable with buprenorphine medication for opioid use disorder.
The medication, approved by the Food and Drug Administration, is a highly effective ...
Narrowing the digital divide for health care
2023-03-24
Many parts of rural America with less access to health care also have limited broadband internet that could help them take advantage of increasingly popular online health services.
A new study by the University of Cincinnati highlighted disparities in access to digital technology that could widen the gap in access to health care. The study found that socially vulnerable communities in the United States face more barriers to adequate health care, live in areas with fewer health care resources and have less access to high-speed internet.
UC researchers ...
Corporate investment could improve climate-tech innovation
2023-03-24
MADISON—Corporate investments in climate-tech start-ups are a growing but overlooked aspect of energy innovation. According to a new report from Morgan Edwards, a professor at the La Follette School of Public Affairs at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, and her lead co-author at University of Maryland, these investments should be more fully considered as methods to advance climate technology. The report was published in the journal Joule on March 17.
Start-up companies have the potential to rapidly commercialize innovation, but they don’t always have the resources to make such ventures successful. Corporations, on the other ...
[1] ... [2036]
[2037]
[2038]
[2039]
[2040]
[2041]
[2042]
[2043]
2044
[2045]
[2046]
[2047]
[2048]
[2049]
[2050]
[2051]
[2052]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.