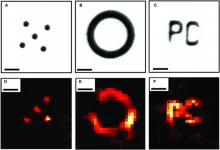
Can lymph nodes boost the success of cancer immunotherapy?
2023-03-20
Media contacts:
Robin Marks, 628-399-0370
Robin.Marks@ucsf.edu | @UCSF
Julie Langelier, 415-734-5000
julie.langelier@gladstone.org | @GladstoneInst
New Data Show Therapies May Activate Lymph Nodes to Produce Tumor-Tackling T Cells
Cancer treatment routinely involves taking out lymph nodes near the tumor in case they contain metastatic cancer cells. But new findings from a clinical trial by researchers at UC San Francisco and Gladstone Institutes shows that immunotherapy can activate tumor-fighting T cells in nearby lymph nodes.
The ...
Emergence of extensively drug-resistant Shigella sonnei strain in France
2023-03-20
Shigellosis, a highly contagious diarrheal disease, is caused by Shigella bacteria circulating in industrializing countries but also in industrialized countries. Scientists from the French National Reference Center for Escherichia coli, Shigella and Salmonella at the Institut Pasteur who have been monitoring Shigella in France for several years have detected the emergence of extensively drug-resistant (XDR) strains of Shigella sonnei. Bacterial genome sequencing and case characteristics (with most cases being reported in male adults) suggest that these strains, which originated in South Asia, mainly spread among men who have sex with men (MSM). This observation needs to ...
Speckle-illumination proves useful in photoacoustic microscopy
2023-03-20
Motivated by the limitations of scanning approaches to photoacoustic microscopy, an international group supervised by Emmanuel Bossy of Université Grenoble Alpes experimented with structured illumination using known and unknown speckle patterns. One of their experiments produced the first demonstration of the use of blind structured illumination for photoacoustic imaging through a diffuser.
The group’s research was published Jan. 11 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The research article concludes that “photoacoustic microscopy can harness many of the structured illumination methods developed initially for pure optical ...
Carnegie Mellon researchers develop head-worn device to control mobile manipulators
2023-03-20
More than five million people in the United States live with some form of paralysis and may encounter difficulties completing everyday tasks, like grabbing a glass of water or putting on clothes. New research from Carnegie Mellon University's Robotics Institute (RI) aims to increase autonomy for individuals with such motor impairments by introducing a head-worn device that will help them control a mobile manipulator.
Teleoperated mobile manipulators can aid individuals in completing daily activities, but many existing technologies like hand-operated joysticks or web interfaces require a user to have substantial fine motor skills to effectively ...
Excess calories during development alters the brain and spurs adult overeating
2023-03-20
People whose mothers are overweight during pregnancy and nursing may become obese as adults because early overnutrition rewires developing brains to crave unhealthy food, according to a Rutgers study in Molecular Metabolism.
Rutgers researchers traced this link from mother to child in mice with an experiment that began by letting some mice get obese on unlimited high-fat food during pregnancy and breastfeeding while keeping others slim on limitless healthy food. They found that mice born to obese mothers stay slim in adulthood on unlimited healthy food but overeat more than mice born to lean mothers when given access to unhealthy food.
The ...
Federal-local immigration enforcement policies designed to reduce crime found to raise victimization among Latinos
2023-03-20
Efforts to understand the effects of immigration enforcement on crime have largely been informed by police crime statistics. In a new study, researchers used longitudinal data from the U.S. National Crime Victimization Survey (NCVS) to assess the impact of federal immigration policies on local communities. They found that activation of two policies—the Secure Communities Program and 287(g) task force agreements—significantly increased the risk of violent victimization among Latinos.
The study, by researchers at Penn State University and the University of Maryland (UMD) at College Park, ...
Developing postoperative delirium is associated with a faster rate of cognitive decline
2023-03-20
BOSTON, MA -- Research published today in the JAMA Internal Medicine finds that developing postoperative delirium is associated with a 40% faster rate of cognitive decline over those who do not develop delirium.
“Delirium is associated with faster cognitive decline,” said Zachary J. Kunicki, PhD, MS, MPH Assistant Professor located at the Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, the first author. “Whether delirium causes this faster rate of decline, or is simply a marker of those who are at risk of experiencing faster ...
Daily step counts before, after onset of COVID-19
2023-03-20
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest a consistent, widespread, and significant decline in activity following the onset of COVID-19 in the United States. Vulnerable populations, including individuals at a lower socioeconomic status and those reporting worse mental health in the early COVID-19 period, were at the highest risk of reduced activity. The researchers found a significant decline in daily step counts that persisted even after most COVID-19–related restrictions were relaxed, suggesting COVID-19 affected long-term behavioral choices. It is currently unknown whether this reduction is steps is clinically meaningful over time.
Authors: Evan L. ...
Gender disparity in NIH funding among surgeon-scientists
2023-03-20
About The Study: The results of this study of National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded surgeons suggest that women surgeons remained underrepresented among surgeon-scientists over a 25-year period despite early career success in receiving NIH funding. These findings suggest that substantial additional support for women surgeon-scientists is necessary to achieve a gender-diverse surgical research workforce.
Authors: Mytien Nguyen, M.S., of the Yale School of Medicine in New Haven, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.3630)
Editor’s ...
Patients overwhelmingly prefer immediate access to test results, even when the news may not be good
2023-03-20
BOSTON – In April 2021, new federal rules went into effect mandating that healthcare providers make nearly all test results and clinical notes immediately available to patients. Evidence suggests that patients may gain important clinical benefits by reviewing their medical records, and access through electronic patient portals has been advocated as a strategy for empowering patients to manage their health care and for strengthening patient-clinician relationships. However, concerns remain about the effects of releasing test results to patients before clinicians offer counsel or interpretation.
In ...
PLOS announces newest joiners to the CRL/NERL Agreement
2023-03-20
SAN FRANCISCO – The Public Library of Science (PLOS) welcomes several new participants to its ongoing three-year consortial agreement with Center for Research Libraries (CRL) and the Northeast Research Libraries (NERL) program. Joining twenty fellow member institutions who signed on during the first year, newly participating institutions for the second year include Duke University, Macalester College, University of Arizona, University of Denver, and University of Southern California, University of Texas at Austin, and University of Washington.
This agreement provides researchers with unlimited publishing privileges in PLOS journals without incurring fees. All PLOS journals are underpinned ...
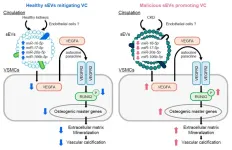
Link between chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease explained
2023-03-20
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) have uncovered a link between cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease, revealing novel disease biomarkers and therapeutic targets
Tokyo, Japan – Chronic kidney disease is linked to the formation of mineral deposits on blood vessel walls, known as “calcification”, causing cardiovascular disease. Small extracellular vesicles (sEVs)—small, enclosed structures outside cells—can transmit signaling molecules between cells, but their biological roles are not fully understood. Now, “malicious” sEVs ...
We have better solutions than chemical warfare to tackle climate-related pests and diseases
2023-03-20
Published on 10 March 2023 in Agronomy journal, the TMG Research gGmbH study team traced a highly destructive desert locust invasion in the Eastern Africa and Horn region between 2019-2021. Ethiopia and Kenya sprayed well over a million hectares of territory with damaging nerve agents malathion and chlorpyrifos, both from the organophosphate family of pesticides. The scale of the invasion – and subsequent choice of control measures – was magnified by unprecedented breeding due to changing climate conditions. Due to the inaccessible location of the breeding grounds, the scale of the threat ...
Discover BMB 2023 press materials available now
2023-03-20
Embargoed press materials are now available for Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. Top scientists and educators in the field will gather at the meeting, held March 25–28 in Seattle.
Reporters are invited to attend an exciting lineup of in-person scientific sessions in Seattle or access press materials electronically. Register now or find more information in the #DiscoverBMB newsroom.
Explore the schedule at a glance, full program, award lectures, or symposium sessions to see all the exciting research topics that will be covered at #DiscoverBMB.
Featured research findings are highlighted below:
New ...
Spherical particles growth with dynamics oscillation during lithium electrodeposition:Insights from numerical simulations
2023-03-20
They published their work on Feb. 6 in Energy Material Advances.
“Lithium-ion batteries are considered one of the most promising next-generation energy storage technologies,” said paper author Hui Xing, associate professor with MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary, Northwestern Polytechnical University. “to fully understand the dynamics of lithium dendrite growth during electrodeposition to inhibit the growth of lithium dendrite structure has been important in the field of battery safety and energy storage.”
Xing explained that Previous ...
Upgraded tumor model optimizes search for cancer therapies
2023-03-20
HOUSTON – (March 20, 2023) – Tumor cells won’t show their true selves in a petri dish, isolated from other cells.
To find out how they really behave, Rice University researchers developed an upgraded tumor model that houses osteosarcoma cells beside immune cells known as macrophages inside a three-dimensional structure engineered to mimic bone. Using the model, bioengineer Antonios Mikos and collaborators found that the body’s immune response can make tumor cells ...
Personality, satisfaction linked throughout adult lifespan
2023-03-20
Certain personality traits are associated with satisfaction in life, and despite the changes people may experience in social roles and responsibilities over the course of their adult lives, that association is stable regardless of age, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“Many studies have shown that people with certain personality profiles are more satisfied with their life than others. Yet, it had not been extensively studied whether this holds true across the lifespan. For example, extraverted – that is sociable, talkative – people might be particularly happy in young adulthood, ...
DART VADAR harnesses the force of enzymes for better RNA drugs
2023-03-20
More than twelve billion doses of mRNA vaccines have been administered globally since the start of the COVID pandemic, saving millions of lives. But RNA-based therapies for other diseases have so far proven more challenging to develop. The full-body immune response caused by mRNA vaccines is fantastic for fighting off invading pathogens, but many other conditions only affect a single organ or cell type. Engineering RNA molecules to only activate their therapeutic payloads when they find themselves in the right conditions is the key to the next generation ...
Researchers create breakthrough spintronics manufacturing process that could revolutionize the electronics industry
2023-03-20
University of Minnesota Twin Cities researchers, along with a team at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), have developed a breakthrough process for making spintronic devices that has the potential to become the new industry standard for semiconductors chips that make up computers, smartphones, and many other electronics. The new process will allow for faster, more efficient spintronics devices that can be scaled down smaller than ever before.
The researchers’ paper is published in Advanced Functional Materials, a peer-reviewed, top-tier materials science journal.
“We believe we’ve found a material and ...
Can synthetic polymers replace the body's natural proteins?
2023-03-20
Most life on Earth is based on polymers of 20 amino acids that have evolved into hundreds of thousands of different, highly specialized proteins. They catalyze reactions, form backbone and muscle and even generate movement.
But is all that variety necessary? Could biology work just as well with fewer building blocks and simpler polymers?
Ting Xu, a University of California, Berkeley, polymer scientist, thinks so. She has developed a way to mimic specific functions of natural proteins using only two, four or six different building blocks — ones currently used in ...
The dark figure of crime
2023-03-20
AMES, IA – In his new book, Matt DeLisi, a world-renowned criminologist at Iowa State University, lays out evidence that Ted Bundy’s criminal career was far lengthier and deadlier than the official record from 1974 to 1978.
“Ted Bundy and the Unsolved Murder Epidemic: The Dark Figure of Crime” underscores how most crime is never known to law enforcement. The book also emphasizes that a small percentage of individuals in society commit a much larger share of violent crime. With an estimated 250,000 to 350,000 unsolved homicide cases in the U.S., DeLisi offers solutions ...
JMIR Medical Education invites submissions for its new theme issue "ChatGPT: Generative Language Models and Generative AI in Medical Education"
2023-03-20
JMIR Medical Education is excited to announce the launch of a new theme issue, ChatGPT, Generative Language Models, and Generative AI in Medical Education. The Call for Papers is now open and submissions are due by July 31st.
Guest editors Kaushik P Venkatesh, MBA, MPH, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA, and Maged N Kamel Boulos, MBBCh, MSc, PhD, FHEA, SMIEEE, of Sun Yat-sen University, China, are encouraging both empirical and theoretical submissions, including original research, systematic reviews, viewpoints, and tutorials.
The objective of this theme issue ...
Few people seem to find real joy in JOMO
2023-03-20
PULLMAN, Wash. – Most people who ranked high in “joy of missing out” or JOMO also reported high levels of social anxiety in a recent Washington State University-led study.
The term JOMO has been popularized as a healthy enjoyment of solitude in almost direct opposition to the negative FOMO, the “fear of missing out” people may have when seeing others having fun experiences without them. In an analysis of two samples of adults, researchers found mixed results when it comes to JOMO with evidence that there is some anxiety behind the joy.
“In general, a lot of people like being connected,” said ...
Does discrimination accelerate aging in African American cancer survivors?
2023-03-20
Study reveals link between major discrimination and frailty
Cancer and its treatment can accelerate the rate of aging because they both destabilize and damage biological systems in the body. New research published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society, found that African American cancer survivors who reported high levels of discrimination exhibited greater aging and frailty than those reporting lower levels of discrimination.
For the study, Jeanne Mandelblatt, MD, MPH, director of the Institute for Cancer and Aging Research at Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center in Washington, ...
Study finds relationship between discrimination and frailty in Black cancer survivors
2023-03-20
WASHINGTON — Discrimination experienced by Black people can affect their health and increase their frailty, which can be particularly impactful for cancer survivors, according to a new study by researchers at Georgetown University’s Lombardi Comprehensive Cancer Center and colleagues at the Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Institute in Detroit. The researchers assessed frailty by a number of factors, including whether a participant had several chronic diseases, poor muscle strength and difficulty performing activities of daily living.
The ...
[1] ... [2037]
[2038]
[2039]
[2040]
[2041]
[2042]
[2043]
[2044]
2045
[2046]
[2047]
[2048]
[2049]
[2050]
[2051]
[2052]
[2053]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.