Turn off porch light to aid caterpillars — and safeguard backyard ecosystems
2023-03-21
ITHACA, N.Y. – Moderate levels of artificial light at night – like the fixture illuminating your backyard – bring more caterpillar predators and reduce the chance that these lepidoptera larvae grow up to become moths and serve as food for larger prey.
This ecological impact was demonstrated in a new Cornell University study published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences.
The scientists placed more than 550 lifelike caterpillar replicas made of soft clay in a forest, setting to ascertain how the mockups were attacked and hunted by predators compared to a control group.
“We measured predation ...
Anne Kornahrens, Hertz Foundation Director of Community, selected as delegate to International Younger Chemists Network Assembly
2023-03-21
The Fannie and John Hertz Foundation is proud to announce that Anne Kornahrens, Director of Community, has been selected as a 2023 U.S. delegate to the International Younger Chemists Network (IYCN) Assembly.
Kornahrens will attend the 52nd International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) General Assembly and World Chemistry Congress, to be held in The Hague, Netherlands, August 18–25, 2023.
The IUPAC Young Observer Program strives to introduce the work of IUPAC to a new generation of distinguished researchers and to provide them with an opportunity to address international science policy issues. IYCN, an affiliated ...
Novel drug makes mice skinny even on sugary, fatty diet
2023-03-21
SAN ANTONIO (March 21, 2023) — Researchers from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) have developed a small-molecule drug that prevents weight gain and adverse liver changes in mice fed a high-sugar, high-fat Western diet throughout life.
“When we give this drug to the mice for a short time, they start losing weight. They all become slim,” said Madesh Muniswamy, PhD, professor of medicine in the health science center’s Joe R. and Teresa Lozano Long School of Medicine.
Findings by the collaborators, also from the University of Pennsylvania and Cornell University, were published Feb. 27 in the high-impact journal Cell ...
Department of Energy announces $150 million for research on the science foundations for Energy Earthshots
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Today, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) announced $150 million for research into the crosscutting foundational science for multiple Energy Earthshots. This funding, provided by the Office of Science, will support fundamental research to accelerate breakthroughs in support of the Energy Earthshots Initiative.
“Our Energy Earthshot solutions start with science,” said Asmeret Asefaw Berhe, DOE’s Director of the Office of Science. “The Office of Science is working to find those solutions by supporting research that will target the remaining and emerging scientific challenges underlaying ...
Turn up your favorite song to improve medication efficacy
2023-03-21
EAST LANSING, Mich. – While listening to a favorite song is a known mood booster, researchers at Michigan State University have discovered that music-listening interventions also can make medicines more effective.
“Music-listening interventions are like over-the-counter medications,” said Jason Kiernan, an assistant professor in the College of Nursing. “You don’t need a doctor to prescribe them.”
While previous research studies have used music-listening interventions as a tool to treat pain and anxiety, Kiernan took a novel approach by studying the effects of music-listening interventions ...
Local manure regulations can help reduce water pollution from dairy farms
2023-03-21
URBANA, Ill. – Animal agriculture is a major source of water pollution in the United States, as manure runoff carries excess nutrients into rivers and lakes. Because of their non-point source nature, most farms are not regulated under the federal Clean Water Act. This leaves pollution control up to the states, resulting in a patchwork of different approaches that are difficult to evaluate.
A new study from the University of Illinois focuses on local manure management regulations in Wisconsin and how they affect water ...
Analysis by NYUAD researchers offers new insights into causes of persistent inequities affecting non-white scientists and their research
2023-03-21
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 21, 2023 – A team of NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) researchers, including data and computational social scientists, is reporting new findings that highlight previously unknown ways through which non-White scientists suffer from inequalities when it comes to the process of having their research considered, published, and cited, potentially hindering the advancement of their academic careers. Specifically, the NYUAD team’s analysis found fewer non-White editors than would be expected based on their share of authorship. In addition, non-White scientists endure longer waiting times between the submission ...
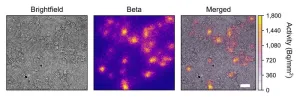
New compact and low-cost lensless radiomicroscope developed for nuclear medicine imaging
2023-03-21
Reston, VA—A novel imaging modality that can visualize the distribution of medical radiopharmaceuticals with very fine resolution has been developed and successfully tested, according to research published in the March issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. Known as the lensless radiomicroscope, the palm-sized instrument offers the same level of imaging performance as its closest imaging equivalent but comes with significantly larger field of view and costs less than $100.
“While many nuclear medicine imaging modalities can quantitively measure ...
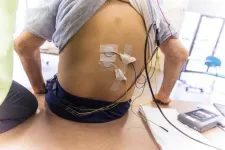
Patients with baclofen pumps may safely undergo transcutaneous spinal stimulation
2023-03-21
East Hanover, NJ. March 21, 2023. Researchers from Kessler Foundation and Kessler Institute for Rehabilitation (collectively “Kessler”) conducted the first prospective study to assess whether transcutaneous spinal stimulation (TSS) interacts with implanted intrathecal baclofen (ITB) pump delivery systems for managing spasticity. The article, "Transcutaneous spinal stimulation in patients with intrathecal baclofen pump delivery system: A preliminary safety study," (doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1075293), was published December 21, 2022, in Frontiers in Neuroscience. It is ...
Co-infection with ‘superbug’ bacteria increases SARS-CoV-2 replication up to 15 times, Western study finds
2023-03-21
Global data shows nearly 10 per cent of severe COVID-19 cases involve a secondary bacterial co-infection – with Staphylococcus aureus, also known as Staph A., being the most common organism responsible for co-existing infections with SARS-CoV-2. Researchers at Western have found if you add a ‘superbug’ – methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) – into the mix, the COVID-19 outcome could be even more deadly.
The mystery of how and why these two pathogens, when combined, ...
Advisory role: New research suggests peer-advisor relationship is key to success
2023-03-21
Collaborative research across the country has shown that strengthening the relationship between the student and advisor can increase retention rates in engineering doctoral studies.
Dr. Marissa Tsugawa, along with professors from Penn State, The University of Oregon, Indiana University Bloomington, University of Reno, Nevada and North Carolina State University, recently published a study with the Journal of Engineering Education on March 17. The study connects an engineering student’s identity and the intention to complete a Ph.D. in engineering. Identity is a role that students give themselves during their experiences in the lab and classroom. The authors argue ...
Researchers get to the “bottom” of how beetles use their butts to stay hydrated
2023-03-21
Beetles are champions at surviving in extremely dry environments. In part, this property is due to their ability to suck water from the air with their rear ends. A new collaborative study by researchers from the University of Copenhagen and the University of Edinburgh explains just how. Beyond helping to explain how beetles thrive in environments where few other animals can survive, the knowledge could eventually be used for more targeted and delicate control of global pests such as the grain weevil and red flour beetle.
Insect pests eat their way through thousands of tons of food around the world every year. Food security in developing ...
New MU study shapes understanding of adaptive clothing customer needs
2023-03-21
With the growth of the niche adaptive clothing market comes new challenges for retailers, including making the process of online shopping more inclusive for people with varying degrees of disability as well as expanding the functionality and aesthetic appeal of individual garments.
This study involved mining online reviews to understand the perspectives of adaptive clothing customers. University of Missouri researchers identified two main challenges for adaptive clothing consumers.
Customers said ...
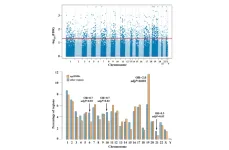
Aging | Age-related methylation changes in the human sperm epigenome
2023-03-21
“[...] we identified > 1,000 candidate genes with genome-wide significant age-related methylation changes in sperm.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 21, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 5, entitled, “Age-related methylation changes in the human sperm epigenome.”
Advanced paternal age is associated with increased risks for reproductive and offspring medical problems. Accumulating evidence suggests age-related changes ...
Study finds similar association of progestogen-only and combined hormonal contraceptives with breast cancer risk
2023-03-21
There is a relative increase of 20% to 30% in breast cancer risk associated with both combined and progesterone-only contraceptives, whatever the mode of delivery, though with five years of use, the 15-year absolute excess incidence is at most 265 cases per 100,000 users. The results appear in a new study publishing March 21st in the open access journal PLOS Medicine by Kirstin Pirie of University of Oxford, UK, and colleagues.
Use of combined oral contraceptives, containing both estrogen and progestogen, has previously been associated with a small increase in breast cancer risk but there is limited data about the ...
Exercise therapy is safe, may improve quality of life for many people with heart failure
2023-03-21
CONTENT UPDATED 3/17 - note new references to cardiac rehabilitation.
Statement Highlights:
A new scientific statement indicates supervised exercise therapy may help improve symptoms for people with one of the most common types of heart failure, known as heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), in which the heart muscle’s pumping strength is intact.
Exercise therapy had comparable or better results on improving exercise capacity for people with preserved EF compared to those who have heart failure with reduced ...
COVID-19 unemployment stigma is real and could threaten future job prospects: uOttawa study
2023-03-21
Regina Bateson, an Assistant Professor in the Faculty of Social Science’s Graduate School of Public and International Affairs, details the findings of her study, which shows the significant social and economic impacts to individuals who were out of work during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Below she answers questions about her study.
Question: How was this research performed?
Regina Bateson: “In this study, I conducted a pre-registered survey experiment with a nationally representative sample of 974 U.S. adults. ...
Ultra-lightweight multifunctional space skin created to withstand extreme conditions in space
2023-03-21
A new nano-barrier coating could help protect ultra-lightweight carbon composite materials from extreme conditions in space, according to a study from the University of Surrey and Airbus Defence and Space.
The new functionality added to previously developed ‘space skin’ structures adds a layer of protection to help maintain space payloads while travelling in space, similar to having its very own robust ultralight protective jacket.
The research team has shown that their innovative nano-barrier would help drastically increase the stability of carbon fibre materials, while reducing radiation ...
Researchers identify new genes that modulate the toxicity of the protein β-amyloid, responsible for causing Alzheimer’s disease
2023-03-21
An international study led by the Molecular Physiology Laboratory at the UPF Department of Medicine and Life Sciences (MELIS) identifies new genes that modulate the toxicity of the protein β-amyloid, responsible for causing Alzheimer’s disease. Combining molecular biology, genomics and bioinformatics techniques, 238 amyloid toxicity protective or activator genes have been identified. Among them, the gene Surf4 stands out. It is involved in the control of intracellular calcium and, by increasing the toxicity of the β-amyloid protein, contributes to the disease.
The research has been carried out thanks to the support ...
Smart light traps
2023-03-21
Plants use photosynthesis to harvest energy from sunlight. Now researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have applied this principle as the basis for developing new sustainable processes which in the future may produce syngas (synthetic gas) for the large-scale chemical industry and be able to charge batteries.
Syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, is an important intermediate product in the manufacture of many chemical starter materials such as ammonia, methanol and synthetic hydrocarbon fuels. "Syngas is currently made almost exclusively using fossil raw materials," ...
Visualization of electron dynamics on liquid helium for the first time
2023-03-21
An international team led by Lancaster University has discovered how electrons can slither rapidly to-and-fro across a quantum surface when driven by external forces.
The research, published in Physical Review B, has enabled the visualisation of the motion of electrons on liquid helium for the first time.
The experiments, carried out in Riken, Japan, by Kostyantyn Nasyedkin (now at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, USA) in the lab of Kimitoshi Kono (now in Taiwan at Yang Ming Chiao Tung University) detected unusual oscillations whose frequencies varied in time. Although it was unclear how ...
Argonne is helping U.S. companies advance battery recycling technology and strengthen the nation’s battery supply chain
2023-03-21
Argonne received $3.5 million in funding to help accelerate battery production in America, lower costs, provide a domestic source of materials and reduce the environmental impact of electric vehicle batteries.
Batteries are critical to powering a clean energy economy. This is especially true in the transportation sector, where electric vehicles (EVs) are on track to make up half of all new vehicle sales by 2030. In order to meet this rapidly increasing demand, the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is distributing funding to advance domestic recycling and reuse of electric vehicle batteries. Managed by DOE’s Vehicle ...
Machine learning programs predict risk of death based on results from routine hospital tests
2023-03-21
If you’ve ever been admitted to hospital or visited an emergency department, you’ve likely had an electrocardiogram, or ECG, a standard test involving tiny electrodes taped to your chest that checks your heart’s rhythm and electrical activity.
Hospital ECGs are usually read by a doctor or nurse at your bedside, but now researchers are using artificial intelligence to glean even more information from those results to improve your care and the health-care system all at once.
In recently published findings, the research team built and trained machine learning programs based on 1.6 ...
Imaging the proton with neutrinos
2023-03-21
The Science
Protons and neutrons, the building blocks of atomic nuclei, are themselves made up of strongly interacting quarks and gluons">quarks and gluons. Because the interactions are so strong, the structure of protons and neutrons is difficult to calculate from theory. Instead, scientists must measure it experimentally. Neutrino experiments use targets that are nuclei made of many protons and neutrons bound together. This complicates interpreting those measurements to infer proton structure. ...
To ward off aging, stem cells must take out the trash
2023-03-21
In humanity’s ongoing quest for the elixir of life, the science keeps pointing to stem cells. Research increasingly shows that maintaining stem cell fitness promotes a long healthspan, and new findings show keeping stem cells clean and tidy is an integral step.
In a study published March 21, 2023 in Cell Stem Cell, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that blood stem cells use an unexpected method to get rid of their misfolded proteins, and that this pathway’s ...
[1] ... [2045]
[2046]
[2047]
[2048]
[2049]
[2050]
[2051]
[2052]
2053
[2054]
[2055]
[2056]
[2057]
[2058]
[2059]
[2060]
[2061]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.