Honey, the 3D print--I mean, dessert--is ready!
2023-03-21
New York, NY—March 21, 2023—Cooking devices that incorporate three-dimensional (3D) printers, lasers, or other software-driven processes may soon replace conventional cooking appliances such as ovens, stovetops, and microwaves. But will people want to use a 3D printer--even one as beautifully designed as a high-end coffee maker--on their kitchen counters to calibrate the exact micro- and macro-nutrients they need to stay healthy? Will 3D food printing improve the ways we nourish ourselves? What sorts of ...
Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System awarded $30 million from NIH to support its Institute for Clinical and Translational Research
2023-03-21
March 21, 2023—BRONX, NY—Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System have received a seven-year, $30 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to continue support for the Harold and Muriel Block Institute for Clinical and Translational Research at Einstein and Montefiore (ICTR). The latest Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) will ensure the ICTR will further its vision to improve health in the Bronx, Westchester, and lower Hudson Valley by accelerating the translation of scientific discoveries into effective and equitable prevention and treatment approaches.
“Since establishing ...
Diet and exercise programs alone won’t tackle childhood obesity
2023-03-21
Focusing on immediate fixes such as diet and exercise programs alone won’t curb the tide of childhood obesity, according to a new study that for the first time maps the complex pathways that lead to obesity in childhood.
Coordinated by the University of Sydney’s Charles Perkins Centre the study finds children whose parents did not complete high school and who live with social disadvantage, were more likely to be affected by overweight or obesity in mid-adolescence. High school completion is a strong indicator of socio-economic status.
These factors were ‘on ramps’ which flow down to influence the body ...
New Yale study evaluates PAXLOVID’s use in Long COVID recovery
2023-03-21
New Haven, Conn. — Yale School of Medicine announces the initiation of a novel, randomized trial that will test whether receiving PAXLOVIDTM (nirmatrelvir tablets; ritonavir tablets) for 15 days can improve the health of highly symptomatic adults with Long COVID.
The trial, led by Yale School of Medicine Professors Harlan Krumholz and Akiko Iwasaki, has a decentralized design, meaning that participants do not have to travel to study sites. It also uses a novel, participant-centric, digital approach to data collection.
Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae SARS-CoV-2 ...
ESMT Berlin: New book on how industrial companies can survive deglobalization
2023-03-21
Deglobalization and the unpredictability of global business have led technology-based industries to review their overall strategies. Current geopolitical changes – the war in Ukraine, effects of the pandemic, and greenhouse gas emission targets – revived discussions about the value of globalization. However, international trade of goods and services has been slowing down significantly since 2011, with increasing nationalism being a factor. Additionally, lower salary differentials between developed and emerging economies have reduced overseas product shipments – which are increasingly criticized regarding environmental impact. So, how ...
Scientists find a common thread linking subatomic color glass condensate and massive black holes
2023-03-21
The Science
Physicists have discovered a remarkable correspondence between dense states of gluons—the gluelike carriers of the strong nuclear force within atomic nuclei—and enormous black holes in the cosmos. The dense walls of gluons, known as a color glass condensate (CGC), are generated in collisions of atomic nuclei. This CGC measures a mere 10-19 kilometers across—less than a billionth of a kilometer. Black holes, in contrast, span billions of kilometers across. The new work shows that both systems are made of densely packed, self-interacting force carrier particles. In CGC, those particles are ...
Vocal tract size, shape dictate speech sounds
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, March 21, 2023 – Only humans have the ability to use speech. Remarkably, this communication is understandable across accent, social background, and anatomy despite a wide variety of ways to produce the necessary sounds.
In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, researchers from University Hospital and Medical Faculty of the RWTH Aachen University explored how anatomical variations in a speaker’s vocal tract affect speech production.
The vocal tract looks like an air duct, starting at the vocal cords and moving vertically through the larynx before bending at the back of the mouth and running ...
Healthy men who have vaginal sex have a distinct urethral microbiome
2023-03-21
Contrary to common beliefs, your urine is not germ free. In fact, a new study shows that the urethra of healthy men is teeming with microbial life and that a specific activity—vaginal sex—can shape its composition. The research, published March 24 in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, provides a healthy baseline for clinicians and scientists to contrast between healthy and diseased states of the urethra, an entrance to the urinary and reproductive systems.
“We know where bugs in the gut come from; they primarily come from our surroundings ...
A recipe for 3D-printing food
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, March 21, 2023 – 3D-printing food could address global challenges in food supply and nutrition. But there are hurdles involved in adapting additive manufacturing to produce edible materials.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, University of Ottawa researchers Ezgi Pulatsu and Chibuike Udenigwe identify a range of factors that affect the print quality and shape complexity of food created with additive manufacturing. Accounting for these features can increase food quality, improve control, and speed up printing.
Additive manufacturing of food involves designing (3D shapes and their geometric codes), ...
Cascading failures in urban traffic systems tied to hidden bottlenecks
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, March 21, 2023 – Transportation systems in urban settings are vulnerable to a variety of factors including weather, traffic congestion, and special events. Bottlenecks, in particular, can cause major problems and lead to cascading failure of the entire system.
Scientists from Fudan University and Shanghai University of Electric Power in China developed a modeling technique to study urban traffic flows and verified it with real-world data from Shanghai. They describe their approach in Chaos, by AIP Publishing, and show that their model can be used to find previously unknown bottlenecks that could ...
Pew funds 7 researchers to advance ocean conservation
2023-03-21
PHILADELPHIA—Today, The Pew Charitable Trusts announced the seven recipients of the 2023 Pew Fellowship in Marine Conservation. The researchers—from Australia, Brazil, Cape Verde, China, the United Kingdom, and the United States—join a network of 202 Pew marine fellows from 42 countries.
“Pew has long supported experts whose considerable talents and solution-oriented approaches help address complex challenges in the marine environment,” said Susan K. Urahn, Pew’s president ...
CHOP researchers find strong adolescent-parent relationships lead to better long-term health outcomes in young adults
2023-03-21
Philadelphia, March 21, 2023 – Researchers from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have found that adolescents who report strong relationships with their parents have better long-term health outcomes. Study findings, published today in JAMA Network Open, suggest that investments in improving parent–adolescent relationships could help improve general health, mental health and sexual, health while also reducing substance use in young adulthood.
Prior research shows that positive ...
Association between rates of down syndrome diagnosis in states with vs without 20-week abortion bans
2023-03-21
About The Study: In this study of 31 million births in the United States from 2011 to 2018, neonatal Down syndrome diagnoses increased more in states that enacted 20-week abortion bans compared with states that did not enact bans. Because these abortion bans were enacted throughout the study period and are known to inhibit choice in patient decision-making, it is possible that the difference in the rates of diagnosis is associated with these policies.
Authors: Sarina R. Chaiken, B.A., and Aaron B. Caughey, M.D., Ph.D., of the Oregon Health & Science University in Portland, is the corresponding author.
To ...
Patient and hospital characteristics associated with postpartum emergency department care
2023-03-21
About The Study: This study including 608,000 obstetric discharges found that Black and Hispanic patients experienced higher adjusted odds of postpartum emergency department visits across all hospital types, particularly at safety net hospitals and those disproportionately serving racial and ethnic minority populations. These findings support the urgent need to mitigate structural racism underlying maternal health disparities.
Authors: Michelle P. Lin, M.D., M.P.H., M.S., of Stanford ...
Associations between parent-adolescent relationships and young adult health
2023-03-21
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that adolescents’ positive perceptions of their relationships with their mothers and fathers are associated with a wide range of favorable outcomes in young adulthood. Investments in improving parent-adolescent relationships may have substantial benefits for young adult population health.
Authors: Carol A. Ford, M.D., of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.3944)
Editor’s ...
New possibilities in the theoretical prediction of particle interactions
2023-03-21
How does the world look like at the smallest scales? This is a question scientists are trying to answer in particle collider experiments like the Large Hadron Collider at CERN in Switzerland. To compare the results of these experiments, theoretical physicists need to provide more and more precise predictions based on our current model for the interactions of fundamental particles, the so called standard model. A key ingredient in these predictions are so called Feynman integrals. Recently, a team of the PRISMA+ Cluster of Excellence at Mainz University, consisting of Dr. Sebastian Pögel, Dr. Xing Wang and Prof. Dr. Stefan Weinzierl developed a method to efficiently ...
A new view of microscopic processes
2023-03-21
COLUMBIA, Mo. — For more than 20 years, Matt Maschmann, an associate professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the University of Missouri, has worked with materials that require specialized technology — electron microscopes — to be seen by the human eye.
“When we deal with materials interacting on a nanoscale level, we can’t physically see the processes that are occurring, like the charging and discharging of a battery, for instance, without the help of an electron microscope,” Maschmann said.
Now, with the support of a two-year, $800,000 grant from the National Science Foundation and an ...
Decline comes later than previously thought
2023-03-21
Utrecht, March 21, 2023 - Recent research from University Medical Center Utrecht (UMC Utrecht) shows that our brain declines later than previously thought. Instead of after our 25th year of life, it happens when we are between the ages of 30 and 40. The researchers published their results in Nature Neuroscience.
Clinical technologist Dorien van Blooijs and neurologist Frans Leijten, together with colleagues from UMC Utrecht and the Mayo Clinic, conducted research into the processing speed of our brain and how it changes as we age.
Faster ...
LSU Health New Orleans study suggests interprofessional team training could prove effective in AUD prevention & treatment
2023-03-21
New Orleans, LA – An LSU Health New Orleans study demonstrated the effectiveness of single, focused Interprofessional Education (IPE)-based exercises in preparing young health professions learners to limit or prevent alcohol use disorder (AUD). Students learned together as a foreshadowing of future interprofessional practice. This intervention produced significant decreases in the stigma associated with alcohol use, which is highly relevant for potential AUD patients. Results are published in BMC Medical Education, available here.
“These results may translate into more effective and collaborative ...
HonorHealth Research Institute is Arizona’s first to adopt new radiation protection technology in treatment of heart disease
2023-03-21
SCOTTSDALE, Ariz. — March 21, 2023 — HonorHealth Research Institute announced today that it is among the first healthcare providers in the U.S., and the first in Arizona, to use an advanced radiation protection system as part of the diagnosis and treatment of heart disease.
Modern cardiac catheterization laboratories use multiple X-ray beams from different angles to produce high-quality images of the heart, major arteries and other tissues. These low-level radiation beams enable physicians to guide catheters and other devices during interventional cardiology procedures, which are non-surgical, catheter-based therapies for ...
Insights into causes of rare genetic immune disorders
2023-03-21
The cellular glitches underlying a rare genetic disorder called activated PI3K Delta syndrome 2 (APDS2) have been identified by researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research. The disorder is caused by genetic variations that disrupt immune cell signalling through a protein called PI3K.
“This study tells us how signalling in the immune system needs to be tightly balanced to make an effective response to infection. Sometimes it’s turned down and you have a problem, and sometimes signalling being turned up can interfere with an immune ...
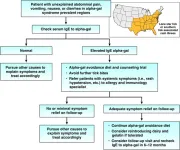
Lone star tick bites may be to blame for unexplained digestive problems
2023-03-21
Bethesda, MD (March 21, 2023) — The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) has released new clinical guidance to help physicians and patients identify if unexplained digestive symptoms are due to alpha-gal syndrome, a food allergy that is caused by lone star tick bites. The AGA Clinical Practice Update was published today in Gastroenterology.
Alpha-gal syndrome is an allergy that causes your body to react to eating meat from mammals and products made from mammals. Symptoms usually start 2-6 hours after eating the mammalian meat or food.
Clinicians should consider alpha-gal syndrome in patients ...
Forests reduce health risks, new global report confirms
2023-03-21
Forests, trees and green spaces play a vital role in ensuring a healthy life for all on a global scale.
The health benefits of forests and trees, ranging from physical and mental well-being to overall mortality reduction, far outweigh the adverse effects on health. As health threats, such as forest fires, are mainly caused by human activities, urgent action is needed.
In order to address health challenges, it is important to recognize the close links between human health and the health of other species, of ecosystems, and of the planet as a whole.
Vienna, March, 21, 2023 - The global scientific evidence of the multiple types of benefits ...
ASBMB cautions against drastic immigration fee increases
2023-03-21
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent recommendations to the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services related to the agency’s proposed changes to petition processing fees. The USCIS proposed increasing its filing fees for employment-based visas by up to 2,050%, a measure intended to remedy financial deficits at USCIS and ramp up hiring to improve services. The ASBMB expressed concern about how “the proposed rule is likely to harm the retention of highly skilled foreign-born scientific researchers.”
The ...
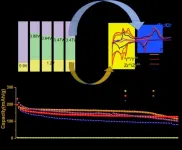
A new sight for the electrochemical stability in halide electrolytes
2023-03-21
They published their work on February in Energy Material Advances.
"Constructing an efficient ionic/electronic framework is crucial for the development of high-performance solid-state batteries," said Dr. Chuang Yu, a professor at the State Key Laboratory of Advanced Electromagnetic Engineering and Technology at Huazhong University of Science and Technology. "Currently, the application of solid-state batteries with inorganic electrolytes is challenging because most solid electrolytes have an unsatisfactory low oxidation potential."
According to Dr. Yu, halide electrolytes have been found to be cathode-stable materials with relatively wide electrochemical ...
[1] ... [2046]
[2047]
[2048]
[2049]
[2050]
[2051]
[2052]
[2053]
2054
[2055]
[2056]
[2057]
[2058]
[2059]
[2060]
[2061]
[2062]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.