El Camino Health is first in the world to adopt FloPatch advanced ultrasound technology for sepsis management
2023-03-14
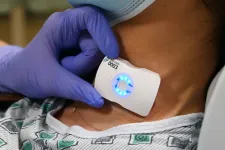
El Camino Health is the first health system in the world to adopt FloPatch, an innovative new technology that monitors blood flow in real time. Developed by Flosonics Medical, FloPatch is the world’s first wireless, wearable Doppler ultra-sound system that helps clinicians better manage intravenous (IV) fluid therapy earlier in the sepsis care pathway.
“Timing is crucial when caring for patients with sepsis. Our nurses have seen firsthand how effective FloPatch is in monitoring the effectiveness of treatment in deteriorating patients, especially those with sepsis and low blood pressure,” said Cheryl Reinking, chief nursing officer at El Camino Health. “We ...
Scientists reveal a potential new approach to treating liver cancer
2023-03-13
Scientists reveal a potential new approach to treating liver cancer
Results in cell and mouse studies may have implications for the development of a new class of anticancer drugs
Scientists at the National Institutes of Health and Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston have uncovered a potential new approach against liver cancer that could lead to the development of a new class of anticancer drugs. In a series of experiments in cells and mice, researchers found that an enzyme produced in liver cancer ...
City of Hope scientists reveal how XBP1s interacts with IL-15 to enhance the survival of natural killer cells
2023-03-13
FINDINGS
A new study published in Science Immunology points to a promising therapeutic approach for future cancer treatments based on natural killer cells (NK), which are immune cells that bind to tumor cells and destroy them.
City of Hope scientists created a knockout mouse model for a protein called XBP1s to explore the molecule’s effect on NK cells and its role in fighting cancer. Earlier studies showed that XBPIs strengthened the survival of NK cells, but precisely how was unclear.
The team identified a previously unknown mechanism in which interleukin-15 (IL-15) — a protein naturally ...
Unique image obtained by Brazilian scientists with high-speed camera shows how lightning rods work
2023-03-13
With a high-speed camera and the luck of being in the right place at the right time, physicist Marcelo Saba, a researcher at Brazil’s National Space Research Institute (INPE), and PhD candidate Diego Rhamon obtained a unique image of lightning strikes showing details of the connections to nearby buildings.
The image is so special that it appeared on the cover of the 28 December 2022 issue of Geophysical Research Letters (GRL) – one of the most important scientific journals in the field –, which featured an article with Saba as first author. ...
A new and better way to create word lists
2023-03-13
Word lists are the basis of so much research in so many fields. Researchers at the Complexity Science Hub have now developed an algorithm that can be applied to different languages and can expand word lists significantly better than others.
Many projects start with the creation of a word list. Not only in companies when mind maps are created, but also in all areas of research. Imagine you want to find out on which days people are in a particularly good mood by analyzing Twitter postings. Just looking for the word "happy" wouldn't be enough.
Instead, you would have to use an algorithm that detects all tweets that indicate that someone is happy. "So ...
The immune system does battle in the intestines to keep bacteria in check
2023-03-13
Yersinia bacteria cause a variety of human and animal diseases, the most notorious being the plague, caused by Yersinia pestis. A relative, Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, causes gastrointestinal illness and is less deadly but naturally infects both mice and humans, making it a useful model for studying its interactions with the immune system.
These two pathogens, as well as a third close cousin, Y. enterocolitica, which affects swine and can cause food-borne illness if people consume infected meat, have many traits in common, particularly their knack for interfering with the immune system’s ability to respond to infection.
The plague pathogen is blood-borne and transmitted by infected ...
Switching to hydrogen fuel could prolong the methane problem
2023-03-13
Hydrogen’s potential as a clean fuel could be limited by a chemical reaction in the lower atmosphere, according to research from Princeton University and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association.
This is because hydrogen gas easily reacts in the atmosphere with the same molecule primarily responsible for breaking down methane, a potent greenhouse gas. If hydrogen emissions exceed a certain threshold, that shared reaction will likely lead to methane accumulating in the atmosphere — with decades-long climate consequences.
“Hydrogen is theoretically the fuel of the future,” said Matteo Bertagni, a postdoctoral researcher at the High ...
Normalizing tumor blood vessels may improve immunotherapy against brain cancer
2023-03-13
BOSTON – A type of immune therapy called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy has revolutionized the treatment of multiple types of blood cancers but has shown limited efficacy against glioblastoma—the deadliest type of primary brain cancer—and other solid tumors.
New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and published in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer March 10, 2023, suggests that drugs that correct abnormalities in a solid tumor’s blood vessels can improve the delivery and function of CAR-T cell therapy.
With CAR-T cell therapy, immune cells are taken from a ...
Wayne State researchers develop new technology to easily detect active TB
2023-03-13
DETROIT – A team of faculty from Wayne State University has discovered new technology that will quickly and easily detect active Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) infection antibodies. Their work, “Discovery of Novel Transketolase Epitopes and the Development of IgG-Based Tuberculosis Serodiagnostics,” was published in a recent edition of Microbiology Spectrum, a journal published by the American Society for Microbiology. The team is led by Lobelia Samavati, M.D., professor in the Center for Molecular Medicine and Genetics in the School of Medicine. ...
Mahoney Life Sciences Prize awarded to UMass Amherst biologist Lynn Adler
2023-03-13
AMHERST, Mass. – University of Massachusetts Amherst biologist Lynn Adler has won the Mahoney Life Sciences Prize for her research demonstrating that different kinds of wildflowers can have markedly different effects on the health and reproduction rate of bumblebees.
“My lab studies the role that flowers play in pollinator health and disease transmission,” says Adler. “Flowers are of course a food source for pollinators, but, in some cases, nectar or pollen from specific plants can be medicinal. However, flowers are also high-traffic areas, and just like with humans, high-traffic areas can be hotspots for disease transmission. We’re tracing how different populations ...
Research highlights gender bias persistence over centuries
2023-03-13
New research from Washington University in St. Louis provides evidence that modern gender norms and biases in Europe have deep historical roots dating back to the Middle Ages and beyond, suggesting that DNA is not the only thing we inherit from our ancestors.
The findings — published on March 13, 2023 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) — highlight why gender norms have remained stubbornly persistent in many parts of the world despite significant strides made by the international ...
Swan populations grow 30 times faster in nature reserves
2023-03-13
Populations of whooper swans grow 30 times faster inside nature reserves, new research shows.
Whooper swans commonly spend their winters in the UK and summers in Iceland.
In the new study, researchers examined 30 years of data on swans at 22 UK sites – three of which are nature reserves managed by the Wildfowl and Wetlands Trust (WWT).
Survival rates were significantly higher at nature reserves, and population growth was so strong that many swans moved to non-protected sites.
Based on these findings, the research team – led by the universities of Exeter and Helsinki – project that nature reserves could help double the number ...
FSU researchers find decaying biomass in Arctic rivers fuels more carbon export than previously thought
2023-03-13
The cycling of carbon through the environment is an essential part of life on the planet.
Understanding the various sources and reservoirs of carbon is a major focus of Earth science research. Plants and animals use the element for cellular growth. It can be stored in rocks and minerals or in the ocean. Carbon in the form of carbon dioxide can move into the atmosphere, where it contributes to a warming planet.
A new study led by Florida State University researchers found that plants and small organisms in Arctic rivers could be responsible for more than half the particulate organic matter flowing to the Arctic Ocean. That’s a significantly ...
Statins may reduce heart disease in people with sleep apnea
2023-03-13
NEW YORK, NY (March 13, 2023)--A new study by Columbia University researchers suggests that cholesterol-lowering drugs called statins have the potential to reduce heart disease in people with obstructive sleep apnea regardless of the use of CPAP machines during the night.
CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) therapy improves sleep quality and reduces daytime fatigue in people with obstructive sleep apnea. But based on findings from several recent clinical trials, CPAP does not improve heart health as physicians originally hoped.
Alternative ...
New process could capture carbon dioxide equivalent to forest the size of Germany
2023-03-13
New research suggests that around 0.5% of global carbon emissions could be captured during the normal crushing process of rocks commonly used in construction, by crushing them in CO2 gas.
The paper ‘Mechanochemical processing of silicate rocks to trap CO2’ published in Nature Sustainability says that almost no additional energy would be required to trap the CO2. 0.5% of global emissions would be the equivalent to planting a forest of mature trees the size of Germany.
The materials and construction industry ...
City or country living? Research reveals psychological differences
2023-03-13
Living in the country, in rural areas, has long been idealized as a pristine place to raise a family. After all, open air and room to run free pose distinct advantages. But new findings from a University of Houston psychology study indicate that Americans who live in more rural areas tend to be more anxious and depressed, as well as less open-minded and more neurotic. The study also revealed those living in the country were not more satisfied with their lives nor did they have more purpose, or meaning in life, than people who lived in urban areas.
The ...
A potential new target for head and neck cancer immunotherapy
2023-03-13
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego Health have identified a strong association between the product of a gene expressed in most cancers, including the most common type of head and neck cancer, and elevated levels of white blood cells that produce antibodies within tumors.
The findings, published in the March 10, 2023 issue of PNAS Nexus, suggest a potential new target and approach for cancer immunotherapies that have thus far produced mixed results for certain head and ...
Impact of Covid-19 pandemic on incidence of long-term conditions in Wales
2023-03-13
A population data linkage study using anonymised primary and secondary care health records in Swansea University’s SAIL Databank has revealed that in 2020 and 2021, fewer people in Wales were being diagnosed with long-term conditions than expected.
Diagnosis rates increased over the two-year period but for most conditions, they still lagged behind expectations at the end of 2021 implicating a potential backlog of undiagnosed patients who are unlikely to be receiving systematic monitoring and management for their conditions.
The study was led by researchers ...
Risk of death for people with dementia increases after a hurricane exposure
2023-03-13
Previous studies of hurricanes have shown general increases in mortality but little has been known about how mortality following hurricane exposure may differ among older adults living with dementia.
Their increased risk could be due to disruption of normal routine, such as access to caregiving, changes in living environment, loss in access to medications, and change in daily routines, said study first author Sue Anne Bell, assistant professor at the U-M School of Nursing.
The analysis focused on risk for mortality among people ...
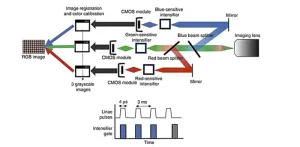
Cherenkov color imaging shows promise in enhancing radiation therapy effectiveness
2023-03-13
Cherenkov imaging is a valuable cancer treatment tool that can help doctors track and monitor radiation doses received by tissues during cancer therapy in real time. This imaging technique works by detecting Cherenkov radiation, which is emitted by tissues exposed to high-energy radiation, such as X-rays or electron beams from a linear accelerator. As high-energy charged particles from the incident radiation pass through biological tissue, either as primary or secondary radiation, they interact with the electromagnetic fields of the atoms and molecules in the tissue. These soft collision-type interactions ...
Abnormal biomarkers associated with obesity are identified in very young Latino children, study finds
2023-03-13
In the United States, low-income, Latino youth are disproportionately affected by obesity with 25.8% of Latino youth aged 2-19 considered to have obesity, which is approximately two times more likely when compared to their non-Latino white counterparts. A higher level of obesity results in an increased risk of cardiometabolic diseases, which are a group of related diseases caused by an unhealthy lifestyle and/or an increased genetic predisposition.
A new study by Allison McKay, RDN, department manager for the Department of Nutrition and Food Studies, identified elevated insulin, hemoglobin A1C, triglycerides, and other cardiometabolic ...
People should have right to shape marine environmental decisions
2023-03-13
Government and political institutions should do more to make citizens feel empowered within marine environment decisions and give them the right to participate, new research shows.
Marine Citizenship is the term used for people who get involved in changing how humans use the ocean. It has been investigated as a potential policy tool to engage the public in marine environmental issues through a new study by the University of Exeter and the University of Bristol Law School.
Despite efforts to tackle human causes such as overfishing, marine litter, microplastics, pollution, ocean acidity, global warming and climate change, there ...
New targets for CAR-T cell therapy against acute myeloid leukemia through AI-assisted analysis
2023-03-13
Unlike other forms of blood cancer, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cannot currently be treated with CAR-T cell immunotherapy. The reason is that specific molecular targets with which certain immune cells could specifically target AML cells are lacking, which would permit the immune system to attack cancer. Two research teams of Professor Dr. Sebastian Kobold with Dr. Adrian Gottschlich from the Division of Clinical Pharmacology at LMU University Hospital Munich and Dr. Carsten Marr with Moritz Thomas from the Institute of AI for Health at Helmholtz Munich have now ...
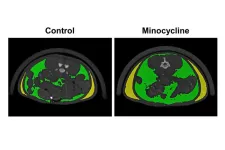
The fat tax: Long-term, systemic antibiotic use for the treatment of adolescent acne can promote fat accumulation
2023-03-13
A growing body of evidence is showing that the healthy gut microbiome – a community of microorganisms that live together in the gut – influences many aspects of human growth and development, especially during adolescence. While there are many physiologic changes during this time, one of the most outward facing, and sometimes distressing, is the development of acne.
Most individuals treat their acne with topical therapies; however, around 25% of adolescents require systemic antibiotics, such as minocycline, to help to alleviate symptoms and clear up the skin. These systemic antibiotic ...
Insilico Medicine brings AI-powered “ChatPandaGPT” to its target discovery platform
2023-03-13
Insilico Medicine, a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-powered drug discovery company, has integrated advanced AI chat functionality based on recent advances in large language models into its PandaOmics platform. The new feature, “ChatPandaGPT,” enables researchers to have natural language conversations with the platform and efficiently navigate and analyze large datasets, facilitating the discovery of potential therapeutic targets and biomarkers in a more efficient manner. Insilico Medicine is the first biotech company to implement chat functionality using large language models into its AI drug ...
[1] ... [2050]
[2051]
[2052]
[2053]
[2054]
[2055]
[2056]
[2057]
2058
[2059]
[2060]
[2061]
[2062]
[2063]
[2064]
[2065]
[2066]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.