Propeller advance paves way for quiet, efficient electric aviation
2023-03-15
Electrification is seen as having an important role to play in the fossil-free aviation of tomorrow. But electric aviation is battling a trade-off dilemma: the more energy-efficient an electric aircraft is, the noisier it gets. Now, researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have developed a propeller design optimisation method that paves the way for quiet, efficient electric aviation.
In recent years, electrification has been described as having an important role in reducing emissions from future aviation. Due to the challenges posed by longer ranges, interest is chiefly focused on electric propeller planes covering shorter distances. Propellers connected to ...
People of color have been largely underrepresented among authors published in the American Journal of Archaeology
2023-03-14
A new demographic survey of authorship in the American Journal of Archaeology (AJA) reveals that people of color have been largely underrepresented among the scholars published in the journal. The results of the survey, which also found that authors who are the children of people without advanced degrees were also underrepresented in the journal’s pages, are published in the paper “Demographic Dynamics of Publishing in the American Journal of Archaeology.” The study was conducted ...
Common cold gives children immunity against COVID-19
2023-03-14
During the pandemic, medical doctors and researchers noticed that children and adolescents infected with COVID-19 became less ill than adults. A possible explanation for this is that children already had a prior level of immunity to COVID-19 provided by memory T cells generated by common colds.
After studying unique blood samples from children taken before the pandemic, researchers from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden have now identified memory T cells that react to cells infected with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Four coronaviruses cause common colds
A possible explanation for this immunity in children is that they already had colds caused by one of the four coronaviruses ...
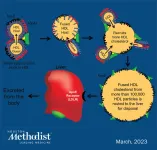
Researchers discover way to reverse infertility by reducing HDL cholesterol
2023-03-14
Houston Methodist scientists reversed infertility in sterile mice by reducing high-circulating cholesterol with a bacterial protein, showing further evidence that links high cholesterol to female infertility. This is a promising development, with one in every five women of childbearing age in the U.S. unable to get pregnant after trying for a year.
“We are working with a protein, called serum opacity factor, with unique characteristics,” said Corina Rosales, Ph.D., assistant research professor of molecular biology in medicine with the Houston Methodist ...
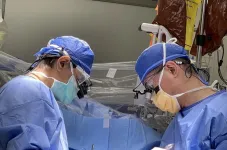
UK HealthCare’s Transplant Center celebrates 500th lung transplant
2023-03-14
LEXINGTON, Ky. (March 14, 2023) — The lung transplant team at UK HealthCare’s Transplant Center recently celebrated a major milestone, performing the 500th lung transplant since the lung transplant program was founded in 1991.
“This is an impressive milestone, and our whole staff — physicians, surgeons, nurse practitioners, nurse coordinators, pharmacists, nutritionists, social workers, therapists and support staff — should be very proud of their success,” said Sravanthi Nandavaram, M.D., medical director of the Lung Transplant Program. ...
How neuroimaging can be better utilized to yield diagnostic information about individuals
2023-03-14
Since the development of functional magnetic resonance imaging in the 1990s, the reliance on neuroimaging has skyrocketed as researchers investigate how fMRI data from the brain at rest, and anatomical brain structure itself, can be used to predict individual traits, such as depression, cognitive decline, and brain disorders.
Brain imaging has the potential to reveal the neural underpinnings of many traits, from disorders like depression and chronic widespread pain to why one person has a better memory than another, and why some people’s memories are resilient as they age. But how reliable brain imaging is for detecting traits has been a subject of wide debate.
Prior research ...
NASA’s Webb Telescope captures rarely seen prelude to supernova
2023-03-14
The rare sight of a Wolf-Rayet star – among the most luminous, most massive, and most briefly detectable stars known – was one of the first observations made by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in June 2022. Webb shows the star, WR 124, in unprecedented detail with its powerful infrared instruments. The star is 15,000 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius.
Massive stars race through their lifecycles, and only some of them go through a brief Wolf-Rayet phase before going supernova, making Webb’s detailed observations of this rare phase valuable to astronomers. Wolf-Rayet stars are in the process of casting off their outer layers, ...
Potential treatment target for drug-resistant epilepsy identified
2023-03-14
Researchers at Tufts University School of Medicine and colleagues have identified a small molecule that may help treat people with epilepsy whose condition has become resistant to the benzodiazepine drugs usually used in managing seizures. The research, conducted in laboratory cells and rodents, was published online March 7 in Cell Reports Medicine.
Uncontrolled epilepsy can lead to frequent and prolonged seizures lasting five minutes or more that can cause brain cell damage and even death. The condition affects an estimated 3.4 million people in the U.S. and millions more worldwide.
Epilepsy occurs ...
New model provides improved air-quality predictions in fire-prone areas
2023-03-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Globally, wildfires are becoming more frequent and destructive, generating a significant amount of smoke that can be transported thousands of miles, driving the need for more accurate air pollution forecasts. A team of Penn State researchers developed a deep learning model that provides improved predictions of air quality in wildfire-prone areas and can differentiate between wildfires and non-wildfires.
“As climate change continues to cause ecological changes and challenges, it is likely that wildfire ...
New study finds early warning signs prior to 2002 Antarctic ice shelf collapse
2023-03-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In 2002, an area of ice about the size of Rhode Island dramatically broke away from Antarctica as the Larsen B ice shelf collapsed. A new study of the conditions that led to the collapse may reveal warning signs to watch for future Antarctic ice shelf retreat, according to a Penn State-led team of scientists.
“The collapse of the Larsen B ice shelf is generally thought of as an independent event,” said Shujie Wang, assistant professor of geography at Penn State. “Our ...
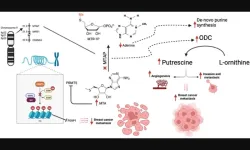
Oncotarget | MTAP loss in metastatic breast cancer patients: Genomic landscape
2023-03-14
“In breast cancer, MTAP downregulation activates ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) which in turn leads to formation of putrescine which promotes tumor migration, invasion and angiogenesis [15].”
BUFFALO, NY- March 14, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 11, 2023, entitled, “Genomic landscape of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients with methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) loss.”
Homozygous deletion of methylthioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) upregulates de novo synthesis ...
Tim Michalski selected as Jefferson Lab’s engineering manager
2023-03-14
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility has selected Tim Michalski to lead its Engineering Division as the Engineering Division Manager. In this role, Michalski oversees all aspects of the management and operation of the Engineering Division. The division includes more than 200 staff members and supports the Continuous Electron Beam Accelerator Facility and the lab’s growing project portfolio.
“I am proud to name Tim as our newest Engineering Division Manager,” said Jefferson Lab Director Stuart Henderson. “Tim has ...
Princeton Chem, IAS uncover spatial patterns in distribution of galaxies
2023-03-14
In late 2021, Salvatore Torquato, on sabbatical from Princeton’s Department of Chemistry, reached across the aisle as it were and invited a young astrophysicist at the Institute for Advanced Study to apply the tools of statistical mechanics to his own work on the distribution of galaxies.
The astrophysicist, Oliver Philcox, now a postdoc at the Simons Foundation, was intrigued. A year-long collaboration ensued.
The questions at the heart of their unusual partnership were straightforward: can the statistical descriptors Torquato has worked with throughout his career find application in unlikely places like cosmology, and can they accurately characterize the complexity in the distribution ...
Researchers look to AI for decision-making in extreme situations
2023-03-14
Imagine you are a doctor managing the emergency room of a large hospital. You suddenly get a call reporting a mass shooting at a nearby concert. In 20 minutes, you will be responsible for triaging more than 200 patients with a range of injuries. You do not have enough staff or resources and the hospital policies are not designed for a situation this dire.
“When people respond to emergencies, many decisions they face are quite predictable. They’re trained on them, and there’s policy,” said UMass Lowell’s Neil Shortland, associate professor in the School of Criminology and Justice Studies. “But every now and then, they get stuck with a really ...
Mix-and-match kit could enable astronauts to build a menagerie of lunar exploration bots
2023-03-14
When astronauts begin to build a permanent base on the moon, as NASA plans to do in the coming years, they’ll need help. Robots could potentially do the heavy lifting by laying cables, deploying solar panels, erecting communications towers, and building habitats. But if each robot is designed for a specific action or task, a moon base could become overrun by a zoo of machines, each with its own unique parts and protocols.
To avoid a bottleneck of bots, a team of MIT engineers is designing a kit of universal ...
Common dry cleaning chemical linked to Parkinson’s
2023-03-14
A common and widely used chemical may be fueling the rise of the world’s fastest growing brain condition – Parkinson’s disease. For the past 100 years, trichloroethylene (TCE) has been used to decaffeinate coffee, degrease metal, and dry clean clothes. It contaminates the Marine Corps base Camp Lejeune, 15 toxic Superfund sites in Silicon Valley, and up to one-third of groundwater in the U.S. TCE causes cancer, is linked to miscarriages and congenital heart disease, and is associated ...
Molecular component of caffeine may play a role in gut health
2023-03-14
Brigham researchers studying how and why certain cell types proliferate in the gut found that xanthine, which is found in coffee, tea and chocolate, may play a role in Th17 differentiation
Insights may help investigators better understand gut health and the development of conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease
The gut is home to a cast of microbes that influence health and disease. Some types of microorganisms are thought to contribute to the development of inflammatory conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), but the exact cascade of events that leads from microbes to immune cells to disease remains ...
Ochsner Health announces new Aortic Center; subscribes to cutting-edge imaging with Cydar Technology
2023-03-14
NEW ORLEANS, La. – Global death rates from aortic diseases have steadily increased over the past two decades. Studies show up to 8% of individuals will develop an aortic aneurysm during their lifetime, higher than rates of colon and lung cancer combined, and over 80% of ruptured aortic aneurysms cause sudden death.
To save lives and improve outcomes for patients with aortic disease of all kinds, Ochsner Health is excited to announce the establishment of The Ochsner Aortic Center. Outfitted with cutting-edge imaging technology that allows medical staff to make faster, easier, and safer decisions, this dedicated, comprehensive aortic center is now the ...
Aston Pharmacy School researchers develop new technique mixing oil and water to improve drug delivery
2023-03-14
A team of researchers from Aston University has developed a new technique that could be a game changer for the medical and drinks industries.
The technology enables insoluble drug/oil to be dissolved in water. The technique is novel because it doesn’t just mix the two together to make an emulsion, it makes oil soluble in water and has the potential to revolutionise a variety of medical treatments and improve drug delivery.
The technique was developed with Max Bio+ a spin out company founded by Professor Sunil Shah, a consultant ...
New guideline introduces recommendations for optimal timing of elective hip or knee arthroplasty
2023-03-14
ATLANTA — The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and the American Association of Hip and Knee Surgeons (AAHKS) released a summary of its new guideline titled “the Optimal Timing of Elective Hip or Knee Arthroplasty for Patients with Symptomatic Moderate to Severe Osteoarthritis or Osteonecrosis Who Have Failed Nonoperative Therapy.” The ACR and AAHKS have worked together before, creating guidelines for Perioperative Management of Antirheumatic Medication in Patients with Rheumatic Diseases Undergoing Elective Total Hip or Total Knee Arthroplasty in 2017 and 2022. While those guidelines focus on which medications ...
Solving the Alzheimer’s disease puzzle: One piece at a time
2023-03-14
Researchers from Drexel University have uncovered a novel regulatory mechanism in the brain that is essential for making the right kinds of proteins that promote healthy brain function, and its malfunctioning may be an early contributor of the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Brain cells are continuously undergoing changes in response to environmental stimuli and to record new memories. Such complex brain capability relies on the ability of brain cells to generate different functional variants of the same protein using a process known as alternative RNA splicing.
Recent studies have reported defects ...
Stephen Fantone elected chair of Hertz Foundation’s board of directors
2023-03-14
The Fannie and John Hertz Foundation, a nonprofit organization dedicated to empowering the most promising innovators in science and technology, has announced the election of Stephen D. Fantone as chair of its board of directors.
Fantone is the founder and president of Optikos Corporation, which provides innovative applications of optical technology, both products and services, to commercial, government and consumer products organizations worldwide. Fantone is a recognized expert in optical engineering and optical product ...
WVU lab’s game-changing high-performance semiconductor material could help slash heat emissions
2023-03-14
Researchers at West Virginia University have engineered a material with the potential to dramatically cut the amount of heat power plants release into the atmosphere.
A team led by Xueyan Song, professor and George B. Berry Chair of Engineering at the Benjamin M. Statler College of Engineering and Mineral Resources, has created an oxide ceramic material that solves a longstanding efficiency problem plaguing thermoelectric generators. Those devices can generate electricity from heat, including power plant heat emissions, which contribute to global warming.
The breakthrough ...
William Evans joins Hertz Foundation board of directors
2023-03-14
The Fannie and John Hertz Foundation, a nonprofit organization dedicated to empowering the most promising innovators in science and technology, has announced the election of William Evans to its board of directors.
Evans is the physics division leader in the Physical and Life Sciences Directorate at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL), which works to enable United States security and global stability and resilience by empowering multidisciplinary teams to pursue bold and innovative science and technology.
“It is imperative that the Hertz Foundation’s board of directors ...
COVID-19 pandemic has long-lasting effects on adolescent mental health and substance use
2023-03-14
March 14, 2023-- The COVID-19 pandemic has had a long-lasting impact on adolescent mental health and substance use according to a new population-based study are based on survey responses from a nationwide sample of over 64,000 13–18-year-old North American and Icelandic adolescents assessed prior to and up to two years into the pandemic. The study was conducted by faculty at Columbia University Teachers College and Mailman School of Public Health and a team of Icelandic and other North American clinical, behavioral and social scientists. The findings are published in published in The Lancet Child & Adolescent Health.
This same research team ...
[1] ... [2047]
[2048]
[2049]
[2050]
[2051]
[2052]
[2053]
[2054]
2055
[2056]
[2057]
[2058]
[2059]
[2060]
[2061]
[2062]
[2063]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.