Pediatric Investigation review takes stock of history and current status of long-acting growth hormone therapy
2023-03-13
In 1957, Maurice Raben successfully isolated and purified the growth hormone (GH) from the pituitary gland, opening up a potential avenue of GH therapies. Children who were born with a deficiency of this hormone could now receive medical intervention in the form of daily injections to substitute the product into their body, thus avoiding the ill-effects of GH deficiency. However, given that it was a product that had to be meticulously extracted from the pituitary of dead bodies, and was time-consuming as well as labor- and resource-intensive process, it remained ...
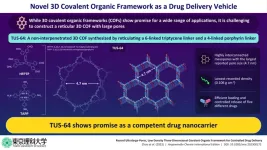
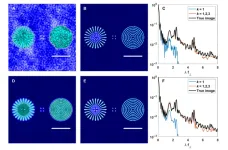
Towards a novel 3D covalent organic framework with record large pores for efficient drug delivery
2023-03-13
Materials science is constantly evolving research area as researchers strive to discover and synthesize novel functional materials with desirable properties suited to a variety of applications. One example on this front is furnished by covalent organic frameworks (COFs), a class of materials characterized by crystalline porous polymers connected in the form of a network via covalent bonds.
Owing to their structural diversity, high porosity, and easily accessible active sites, COFs can be designed for a range of applications such as gas storage and separation, catalysis, and drug delivery. ...
Equipping employers to address costly health inequities, improve workforce well-being
2023-03-13
Embargoed until 8:00 a.m. CT / 9:00 a.m. ET Monday, March 13, 2023
DALLAS and ALEXANDRIA, Va., March 13, 2023 — Health inequities can be detrimental to employees’ emotional, psychological and physical health and place a significant economic burden on employers. To improve employee well-being and reduce health inequities nationwide, the American Heart Association—a global force for longer, healthier lives for all—introduces the Health Equity in the Workforce initiative in collaboration with the Deloitte Health Equity Institute and the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM) Foundation.
The Health Equity ...
Too hot to handle
2023-03-13
Metal organic frameworks, or MOFs, are kind of like LEGOs.
The pieces are simple to connect, yet they’re capable of building highly sophisticated structures. These structures can be used to filter toxic gasses out of the air or to store fuel for natural or hydrogen gas-powered engines.
LEGOs melt when they interact with heat. But, what happens to MOFs?
A new study from the University of Pittsburgh Swanson School of Engineering found that MOFs heat up significantly when they soak up gasses and if they ...
Brown widow spiders' aggression likely driver of black widow decline
2023-03-13
Annapolis, MD; March 13, 2023—Black widow spiders have earned a fearsome reputation for their venomous bite. But in parts of the southern United States these spiders have much to fear themselves—from spider relatives who really don't like their company.
In the past couple decades, researchers have noticed black widow spiders commonly being displaced by the brown widow, a fellow species in the same genus, Latrodectus. But new research suggests this isn't a just simple case of one species winning the competition for food or habitat. Instead, a study shows brown widow spiders have a striking propensity to seek out and kill nearby ...
The best of both worlds: a new algorithm fuses quantum and classical information for high-quality imaging
2023-03-13
Researchers from Colorado State University and the Colorado School of Mines have thought up a new computational imaging strategy that exploits the best of both the quantum and classical worlds. They developed an efficient and robust algorithm that fuses quantum and classical information for high-quality imaging. The results of their research were published Dec. 21 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
Recently, the quantum properties of light have been exploited to enable super­resolution microscopy. While quantum information brings new possibilities, it has its own set of limitations.
The researchers’ approach is based on classical and quantum ...
Triggering bitter taste receptors could someday treat asthma, COPD
2023-03-13
Surprisingly, bitter taste receptors are not only located in the mouth, but also elsewhere in the body, including the airways. Activating those receptors opens up lung passageways, so they’re a potential target for treating asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Now, researchers report in ACS’ Journal of Medicinal Chemistry that they have designed a potent and selective compound that could lead the way to such therapies.
Among the 25 different types of bitter taste receptors, the TAS2R14 subtype is one of the most widely distributed in tissues outside the mouth. Scientists are uncertain about ...
Evaluation of DNA metabarcoding for identifying fish eggs: a case study on the West Florida Shelf
2023-03-13
A new study published in PeerJ Life & Environment and featured in the International Association for Biological Oceanography Hub evaluates the use of DNA metabarcoding to identify fish eggs. The study assessed the performance of DNA metabarcoding to increase throughput and reduce financial and labor costs associated with a long-term fish egg monitoring program.
The study found:
Egg identifications were consistent with prior species distributions observed from individual egg DNA barcoding, and spatial ...
ESC Preventive Cardiology 2023: how to maintain heart health throughout life
2023-03-13
Date: 13 March 2023, 08:30 CET
13 to 15 April in Malaga, Spain
Get ready for practice-changing science at ESC Preventive Cardiology 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).
The annual congress of the European Association of Preventive Cardiology (EAPC), a branch of the ESC, takes place 13 to 15 April at the Trade Fair and Congress Centre of Malaga (FYCMA - Palacio de Ferias y Congresos de Malaga) in Malaga, Spain. Explore the scientific programme.
Novel research ...
Arctic climate modelling too conservative
2023-03-13
Climate models used by the UN’s IPCC and others to project climate change are not accurately reflecting what the Arctic’s future will be. Researchers at the University of Gothenburg argue that the rate of warming will be much faster than projected.
Due to the Arctic´s sea ice cover and its harsh climate, relatively few observations are made in that part of world. This means that the climate models used for projecting the future of the Arctic have not been calibrated to the same extent there as in other parts of the world.
Two recent ...
New drug to lower brain pressure could treat blinding IIH headaches, trial finds
2023-03-13
Patients with ‘blinding’ headaches known as Idiopathic Intercranial Hypertension (IIH) could be treated with an injectable peptide used for type 2 diabetes, a new trial has found.
The study, published in the journal Brain, today reports on a phase two trial of a drug called exenatide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, as a potential treatment for IIH.
The IIH Pressure Trial led by a team of neurologists from the University of Birmingham and University Hospitals Birmingham found that for the seven ...
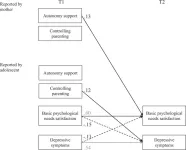
Links between maternal autonomy support and controlling parenting and adolescents’ depressive symptoms
2023-03-13
The relationship between adolescents and their parents has always been an intriguing issue in psychological research. Several studies underscore the significance of parenting behavior in the development of young people. Parental autonomy support, in particular, has been considered essential for adolescents’ growth and healthy functioning. Parental autonomy support and controlling parenting are the two most important facets of parenting. The former refers to parents supporting the independence of their children, including listening carefully, providing choices, perspective-taking, and offering valid reasoning for particular behaviors. On the contrary, controlling parenting refers to parental ...
Organosulfur content of vegetables quantified
2023-03-13
Osaka, Japan – The health-promoting effects of sulfur-rich vegetables such as onions and garlic have been known for a long time. How food containing sulfur compounds promotes health has not been easy to explore, as the levels—and types—of reactive polysulfides found in different vegetables had not been accurately measured.
A research team, led by Assistant Professor Shingo Kasamatsu from the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Science, has established a method for selective and sensitive detection of reactive ...
Scientists to examine whether SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy affects a child’s risk for neurodevelopmental disorders
2023-03-13
BALTIMORE, Md. (March 13, 2023) – Scientists led by the Lieber Institute for Brain Development are studying how a mother’s SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy affects the biology of the placenta and the corresponding trajectory of the child’s brain development, including the risk for neurodevelopmental disorders such as schizophrenia and autism. The work is made possible by a $3 million, five-year grant from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health & Human Development, part ...
How new multi-sport facilities can be used after major events
2023-03-13
Communities that are constructing new multi-sport facilities for major events could run the risk of ending up with expensive under-used complexes, but a new study suggests there are several factors that can keep them productive in the long run.
Researchers found that factors such as the location and design of the facility, the formal agreements between operating groups and the breadth of sport and recreation programming offered at the facility all contributed to promoting a legacy of participation post-event.
“Major sporting ...
New technique reduces postoperative complications in prostate cancer surgery
2023-03-12
Surgeons in Germany have shown a small technical change to keyhole surgery for prostate cancer can more than halve one of the most common post-operative complications – where lymphatic fluid collects in the pelvis.
The technique involves creating a small flap in the peritoneum – the lining of the abdomen – and attaching this flap down into the pelvis. This creates a route for lymphatic fluid to escape from the pelvis into the abdomen where it can be more easily absorbed.
The findings ...
UK study finds vasectomies are even safer than reported
2023-03-12
Vasectomies are much less likely to cause complications than expected, according to a new UK study reviewing the outcomes from over 90,000 vasectomies performed over 15 years.
The study, led by researchers from Gloucestershire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, is being presented today at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Congress in Milan.
It shows that existing leaflets explaining the potential complications to patients are based on outdated figures.
Around 11,000 vasectomy operations are performed every year ...
Difference between “growers” and “showers” revealed
2023-03-12
A scientific definition to determine whether a man’s erection can be deemed a "grower " or a "shower" has been produced by researchers.
The findings are presented today at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Congress in Milan.
Urologists based at three hospitals and a clinic in Madrid conducted ultrasound scans on 225 men in both flaccid and then erect states.
The researchers, led by Dr Manuel Alonso-Isa, a urologist at the University Hospital HM Puerta del Sur in Madrid, Spain, had hoped to find factors among the men that would predict if they fell into one of these ...
Delaying treatment for localised prostate cancer does not increase mortality risk, trial shows
2023-03-12
Active monitoring of prostate cancer has the same high survival rates after 15 years as radiotherapy or surgery, reports the largest study of its kind today.
The latest findings from the ProtecT trial, led by the Universities of Oxford and Bristol, are presented today at the European Association of Urology (EAU) Congress in Milan and published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trial was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).
Although men on active monitoring – which involves regular tests to check on the cancer – were more likely to see it progress ...
Clinical trial shows wrist device significantly reduces tics in Tourette syndrome
2023-03-12
The results of the clinical trial of a new wrist device designed to help control the symptoms of Tourette syndrome have shown it significantly reduces the severity and frequency of tics.
The prototype wrist device, which was recently tried out by Lewis Capaldi, delivers electrical pulses to reduce the amount and severity of tics experienced by individuals with Tourette’s and was trialed by 121 people across the UK. The results have been announced in MedRxive.
The device has been developed by scientists at the University of Nottingham and spin-out company Neurotherapuetics Ltd who have recently secured £1m in additional funding to ...
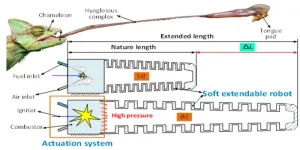
Design of a fuel explosion-based chameleon-like soft robot aided by the comprehensive dynamic model
2023-03-11
A research paper by scientists at the Beijing Institute of Technology and University of Lancaster displayed a recent advancement of using fuel explosion as the power of source to achieve the rapid and powerful motion for the medium-size robots.
The new research paper, published in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems, provided a new kind of actuation system for the robotic system, providing a promising patentability to largely improve the working length of the conventional medium-size robotic systems.
“Achieving the rapid and fast motion of the medium-size robot has been a challenging task for many years, …” ...
Looking for risky viruses now to get ahead of future pandemics
2023-03-11
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Most of what scientists know about viruses in animals is the list of nucleotides that compose their genomic sequence – which, while valuable, offers very few hints about a virus’s ability to infect humans.
Rather than let the next outbreak take the world by surprise, two virologists say in a Science Perspective article published today (March 10, 2023) that the scientific community should invest in a four-part research framework to proactively identify animal viruses that might infect humans.
“A lot of financial investment has gone into sequencing viruses in nature and thinking that from sequence alone we’ll be ...
MSU-led international research network welcomes new Ibero-American partner to advance nuclear astrophysics
2023-03-11
EAST LANSING, MI – The International Research Network for Nuclear Astrophysics (IReNA), supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and headquartered at Michigan State University (MSU), brings together nuclear physicists, astronomers, and computational scientists to try to answer a long-standing question in science: Where do the elements that make up our world come from?
Founded in 2019, IReNA continues to expand its global reach for cooperation to advance knowledge in nuclear astrophysics, and now welcomes a new network partner: the Ibero-American Network of Nuclear ...
Aging | Cognitive aging and dementia prevention: The time for psychology?
2023-03-11
“[...] there is a need to explore brain mechanisms through which psychological processes may exert their protective or deleterious effects.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 10, 2023 – Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) published a new editorial paper in Volume 15, Issue 4, entitled, “Cognitive aging and dementia prevention: the time for psychology?”
Modifiable risk and protective factors (e.g. engaging in active lifestyles ...
New platform allows researchers to listen in on cell-cell crosstalk
2023-03-11
Inflammatory neurological diseases, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), can arise when cell-to-cell communication between cells in the central nervous system (CNS) goes awry. But exactly how this cellular crosstalk leads to the molecular changes that drive disease remain unknown. To address this, researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, developed a platform that allows them to perform genetic screens of cell-cell interactions to identify genes that control biologic processes. ...
[1] ... [2052]
[2053]
[2054]
[2055]
[2056]
[2057]
[2058]
[2059]
2060
[2061]
[2062]
[2063]
[2064]
[2065]
[2066]
[2067]
[2068]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.