'Other' race/ethnicity linked to higher suicide and overdose risk in military members with mild TBI
2023-03-08
March 8, 2023 – Previous studies have reported high rates of death by suicide and drug overdose – including opioid overdose – in military service members with a history of mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI). A new study finds that those risks are highest among military members with mTBI who identify their racial/ethnic status as "Other," as opposed to standard racial/ethnic categories, reports the March/April issue of the Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation (JHTR). The official journal of the Brain Injury Association of America, JHTR is ...
Cancer Grand Challenges announces global research funding opportunity with nine new challenges
2023-03-08
The National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health, and Cancer Research UK have announced nine new research challenges aimed at tackling some of the most profound problems in cancer research. The global funding opportunity is part of the Cancer Grand Challenges program, an initiative launched by NCI and Cancer Research UK in 2020.
The research initiative aims to inspire bold new ideas that have the greatest potential for advancing cancer research and improving outcomes for people affected by cancer. The new round of challenges, announced March 8, 2023, during the Cancer Grand Challenges Annual Scientific Summit in London, is open until June ...
Genes in beans! Bean genome sequenced for improved nutrition
2023-03-08
The faba bean genome, which at 13 billion bases is more than four times the size of the human genome, has been sequenced for the first time and is published today (08 March 2023), in Nature. This is an extraordinary technical achievement and crucial to efforts to breed beans with optimum nutritional content and sustainability of production.
A consortium of scientists from Europe and Australia, led by the University of Reading (UK), Aarhus University (Denmark) and the University of Helsinki (Finland), worked together on this large scale sequencing project.
The project to fully decode the genome went on to test out its usefulness by searching for genes involved ...
MD Anderson research highlights for March 8, 2023
2023-03-08
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center’s Research Highlights showcases the latest breakthroughs in cancer care, research and prevention. These advances are made possible through seamless collaboration between MD Anderson’s world-leading clinicians and scientists, bringing discoveries from the lab to the clinic and back.
Recent developments include overlooked proteins from long noncoding RNAs that likely play a functional role in breast cancer, inhibiting tumor-associated neuronal cells to improve treatment response in pancreatic cancer, ...
Discovery of T cells’ role in Alzheimer’s, related diseases, suggests new treatment strategy
2023-03-08
Nearly two dozen experimental therapies targeting the immune system are in clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease, a reflection of the growing recognition that immune processes play a key role in driving the brain damage that leads to confusion, memory loss and other debilitating symptoms.
Many of the immunity-focused Alzheimer’s drugs under development are aimed at microglia, the brain’s resident immune cells, which can injure brain tissue if they’re activated at the wrong time or in the wrong way. A new study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis ...
Newborn drug testing by race, ethnicity before and after recreational cannabis legalization
2023-03-08
About The Study: Researchers found in this examination of newborn drug testing at a Midwestern academic medical center before and after statewide legalization of recreational cannabis that clinicians ordered newborn drug tests more frequently for Black newborns when no drug testing was done during pregnancy. These findings call for further exploration of how structural and institutional racism contribute to disproportionate testing and subsequent Child Protective Services investigation, surveillance, and criminalization of Black parents.
Authors: Lauren Oshman, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of Michigan ...
Major North American oil source yields clues to one of earth’s deadliest mass extinctions
2023-03-08
The Bakken Shale Formation—a 200,000-square-mile shale deposit below parts of Canada and North Dakota—has supplied billions of barrels of oil and natural gas to North America for 70 years. A new discovery reveals that the rocks also open a uniquely informative window into Earth’s complicated geological history.
A research team, which included geologists from the University of Maryland, George Mason University and the Norwegian oil and gas company Equinor, developed a new framework for analyzing paleontological and biogeochemical data extracted from the formation’s rock. Using this technique, the team pinpointed a major trigger of several closely spaced ...
Study reveals new understanding of how androgen therapy affects breast tissue
2023-03-08
New insights into the effects of a hormonal treatment for transgender men, discovered by Cedars-Sinai investigators, could have implications for the treatment of breast cancer.
Transgender men who were assigned female at birth and identify today as male may take hormones called androgens to induce physical changes that help them align their physical appearance with their identified gender. Androgens such as testosterone are involved primarily in the development of male traits, although females also produce androgens.
Molecular changes observed in the breast tissue of transgender men undergoing androgen therapy may signal the potential ...
How the Brain Senses Infection
2023-03-08
At a glance:
A small population of airway neurons alerts the brain about a flu infection, according to a new study in mice
The results help explain how drugs like ibuprofen and aspirin reduce flu symptoms
The findings could help scientists develop more-effective flu therapies
A new study led by researchers at Harvard Medical School illuminates how the brain becomes aware that there is an infection in the body.
Studying mice, the team discovered that a small group of neurons in the airway plays a pivotal role in alerting the brain about ...
ALMA traces history of water in planet formation back to the interstellar medium
2023-03-08
Scientists studying a nearby protostar have detected the presence of water in its circumstellar disk. The new observations made with the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) mark the first detection of water being inherited into a protoplanetary disk without significant changes to its composition. These results further suggest that the water in our Solar System formed billions of years before the Sun. The new observations are published today in Nature.
V883 Orionis is a protostar located roughly 1,305 light-years from Earth in the constellation Orion. ...
Study shows racial inequities in newborn drug testing
2023-03-08
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – If a newborn tests positive for certain drugs after birth, mandated reporters in many states – including health care professionals and social workers – are required to report it to Child Protective Services.
But guidelines on what should trigger these tests are often unclear and inconsistent, which studies have shown may contribute to racial inequities in who gets tested.
Residents, faculty, medical students and researchers at Michigan Medicine’s Department of Family Medicine and Antiracism and Health Equity Program wanted to determine rates of newborn drug testing and if these rates varied by ...
During COVID, Black children were 100x more likely than White children to experience gun injuries
2023-03-08
EMBARGOED UNTIL 11:00 AM EST Wednesday, March 8, 2023
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Gun violence—and racial disparities in gun violence—have increased substantially during the pandemic, particularly among children. Now a new study led by a Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) researcher shows just how stark these differences in risk of firearm injury are between White and non-White children.
Published as a research letter in JAMA Network Open, the study examined gun injuries among children in four major US cities—New York City, Chicago, Los Angeles, and Philadelphia—and ...
Eyes in the sky: using drones to assess the severity of crop diseases
2023-03-08
Rice is one of the most important crops in the world and constitutes the primary food source for over half of Earth’s population. Protecting rice plantations from disease is therefore an essential endeavor in modern agriculture. Of the many pathogens that can infect rice plants, the bacterium Xanthomonas oryzae, which is responsible for bacterial blight (BB), is among the worst. Hundreds of millions of dollars’ worth of crops are lost each year due to BB, and millions of dollars are spent in preventive measures and research.
One of the most fruitful strategies to control BB and other crop diseases is to grow genetically resistant cultivars. However, as pathogens can ...
New Insights by Mass General on the molecular mechanism of hydrocephalus could lead to the first-ever non-surgical treatment
2023-03-08
BOSTON – Mass General researchers have discovered a novel molecular mechanism responsible for the most common forms of acquired hydrocephalus, potentially opening the door to the first-ever nonsurgical treatment for a life-threatening disease that affects about a million Americans. As reported in the journal Cell, the team uncovered in animal models the pathway through which infection or bleeding in the brain triggers a massive neuroinflammatory response that results in increased production of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) ...
Analyzing child firearm assault injuries by race, ethnicity during pandemic
2023-03-08
About The Study: Child firearm assaults increased substantially during the COVID-19 pandemic in four major U.S. cities, according to the results of this study. Racial and ethnic disparities increased, as Hispanic, Asian, and especially Black children experienced disproportionate shares of the increased violence.
Authors: Jonathan Jay, Dr.P.H., J.D., of the Boston University School of Public Health in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.3125)
Editor’s ...
eDNA holds the key to safeguarding pollinators amid global declines: Study
2023-03-08
Curtin researchers have uncovered new evidence of western pygmy possums interacting with native flowers, providing the first eDNA study to simultaneously detect mammal, insect and bird DNA on flowers.
The new research, published today in Environmental DNA, examined DNA traces left by animal pollinators on native flora and detected both insect and animal pollinators from multiple flowering plant species at once - a game changer in the face of declining animal pollinators globally.
In North America, some pollinator species have fallen by more than 95 per cent while ...
SIAM Conference on Computational Geometric Design (GD23)
2023-03-08
The 2023 SIAM Conference on Computational Geometric Design, organized by the SIAM Activity Group on Geometric Design, is part of the International Geometry Summit bringing together the Symposium on Physical and Solid Modeling 2023, Shape Modeling International 2023, EG Symposium on Geometry Processing 2023, and Geometric Modeling and Processing 2023.
The 2023 SIAM Conference on Computational Geometric Design seeks high quality, original research contributions that strive to advance all aspects ...
Study associates long COVID with physical inactivity
2023-03-08
The link between symptoms of COVID-19 and physical inactivity is increasingly evident. An article recently published in the journal Scientific Reports by researchers at the University of São Paulo (USP) in Brazil describes a study in which COVID-19 survivors with at least one persistent symptom of the disease were 57% more likely to be sedentary, and the presence of five or more post-acute sequelae of infection by SARS-CoV-2 increased the odds of physical inactivity by 138%.
“Although this was a cross-sectional study, the findings underscore the importance of discussing and encouraging physical activity at all times, including during the pandemic,” ...
Scientists uncover the unexpected identity of mezcal worms
2023-03-08
Mezcal is a distilled alcohol made from the boiled and fermented sap of agave plants. Most mezcal beverages — including all brands of tequila — are sold as pure distillates, but a few have an added stowaway bottled inside: worms.
Called gusanos de maguey (Spanish for agave worms), these odd organic chasers aren’t actually worms, but instead a type of insect larva, and their addition to mezcal is a recent one. Mezcal production has a storied history, dating back to the first Spanish inhabitants of Mexico, but larvae were only added to the drink in ...
AERA announces 2023 fellows
2023-03-08
WASHINGTON, March 8, 2023—The American Educational Research Association (AERA) has announced the selection of 24 exemplary scholars as 2023 AERA Fellows. The AERA Fellows Program honors scholars for their exceptional contributions to, and excellence in, education research. Nominated by their peers, the 2023 Fellows were selected by the Fellows Committee and approved by the AERA Council, the association’s elected governing body. They will be inducted during a ceremony at the 2023 Annual Meeting in Chicago on April 14. They join a total of 714 AERA Fellows.
“AERA Fellows demonstrate the highest standards ...
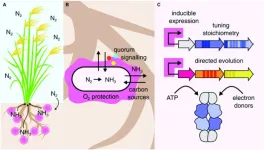
A better way to produce fertilizers
2023-03-08
Fertilizers are one of the main reasons that we are able to grow enough crops to feed the almost 8 billion humans living on Earth. Modern agriculture depends largely on nitrogen-based fertilizers, which significantly increase the yield of crops. Unfortunately, a great portion of these fertilizers are produced at an industrial level, consuming fossil fuel energy and causing nitrogen pollution.
One attractive way to minimize our use of industrially produced fertilizers is to harness the power of nitrogenases. ...
University of Cincinnati study finds little federal funding for incarceration-related research
2023-03-08
Research from the University of Cincinnati finds a lack of federal funding for incarceration-related research. The study looked at data from the Department of Justice, National Institutes of Health (NIH) and National Science Foundation, some of which dated back to 1985.
The study was published recently in the journal JAMA Network Open.
“We have very little evidence-based research on how and when to intervene with children and families when someone is removed from the home due to incarceration, especially on how to ...
How nanoplastics can influence metabolism
2023-03-08
PET, the plastic used to make bottles, for example, is ubiquitous in our natural environment. In a joint study, scientists from Leipzig University and the Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research (UFZ) investigated the negative effects that tiny plastic PET particles can have on the metabolism and development of an organism. Their findings have now been published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The increasing use of plastic is threatening ecosystems around the world. One of the big concerns is the presence of plastics in the form of small particles, also called microplastics and nanoplastics. ...
Virginia Tech researchers study PTSD effects on bystanders
2023-03-08
The traditional line of thought is that post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is caused by directly experiencing the traumatic event. However, about 10 percent of diagnosed PTSD occurs when people witness these events versus experiencing it directly themselves.
Little is known about these cases of PTSD, but that’s something that Tim Jarome, an associate professor in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences School of Animal Sciences, is aiming to change with a $430,000 grant from the National Institute ...
New pain medications are still widely inaccessible to individuals living with sickle cell disease
2023-03-08
(WASHINGTON, March 8, 2023) – Sickle cell disease (SCD), a rare chronic, progressive, life-threatening, inherited blood disorder, often affects individuals with chronic pain that can be debilitating to their quality of life. Yet less than 4% of people living with SCD who experience chronic pain episodes have prescriptions for newer FDA-approved pain-relieving drugs, including l-glutamine, voxelotor, and crizanlizumab, according to a new study published in Blood Advances. Further, researchers found that less than a third of patients with pain episodes have prescriptions for hydroxyurea, ...
[1] ... [2059]
[2060]
[2061]
[2062]
[2063]
[2064]
[2065]
[2066]
2067
[2068]
[2069]
[2070]
[2071]
[2072]
[2073]
[2074]
[2075]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.