Two-pronged immunotherapy eliminates metastatic breast cancer in mice
2023-03-08
Metastatic breast cancer has no cure and has proven stubbornly resistant to one of the most innovative and promising new cancer treatments: immunotherapy.
Now, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a way to treat the area surrounding breast tumors that have spread to bone so that such tumors become vulnerable to attack by the body’s immune system. When the researchers boosted the activity of certain immune cells, called T cells and macrophages, these immune cells worked together to clear metastatic breast tumors that had spread to the bones of mice, and continued to eliminate tumor cells ...
Researchers take a step towards turning interactions that normally ruin quantum information into a way of protecting it
2023-03-08
Researchers have found a way to predict the behavior of many-body quantum systems coupled to their environment. The work represents a way to protect quantum information in quantum devices, which is crucial for real-world applications of quantum technology.
In a study published in Physical Review Letters, researchers at Aalto University in Finland and IAS Tsinghua University in China report a new way to predict how quantum systems, such as groups of particles, behave when they are connected to the external environment. ...
Long-term exposure to nitrate in drinking water may be a risk factor for prostate cancer
2023-03-08
The nitrate ingested over the course of a person’s adult lifetime through the consumption of tap water and bottled water could be a risk factor for prostate cancer, particularly in the case of aggressive tumours and in younger men. This is the conclusion of a study conducted in Spain and led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation. The findings have been published in Environmental Health Perspectives.
The study also suggests that diet plays an important role. The researchers found that eating plenty of fibre, fruit/vegetables and vitamin C could reduce the negative effect ...
UNIST receives generous gift from BNK Kyongnam Bank
2023-03-08
UNIST and BNK Kyongnam Bank recently held a donation agreement ceremony in pursuit of creating a beautiful, biodiverse, and sustainable kitchen garden on UNIST campus.
A ceremony to commemorate and display gratitude for BNK Kyongnam Bank also took place on Friday, February 24, 2023. As part of its Carbon Neutral Campus Project, UNIST has been implementing a number of projects to improve sustainability on campus and in the surrounding community, including the creation of an ecological garden that ...
Seeking leukemia’s Achilles heel
2023-03-08
A team of researchers has discovered a potential therapeutic that can synergize with existing drugs to more effectively kill certain leukemia cells. The authors published their results on Jan. 19 in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Acute myeloid leukemia is a cancer of developing immune cells. It can manifest in all individuals, including the elderly and children. Only 30% of patients survive beyond five years of diagnosis
Unlike cancers of solid organs, AML is found in bodily fluids, such as blood. Like passengers ...
Men over 65 are at greater risk than women of skull fractures from falls
2023-03-08
Each year, more than 3 million people ages 65 and older are treated in emergency departments for fall injuries. Head trauma is the leading cause of serious injury with skull fractures being reported as a serious outcome. According to the 2016 National Trauma Database annual report, females account for 58 percent of these falls.
Because geriatric females have an increased rate of falls and facial fractures, determining if they also are at an increased risk of skull fractures is crucial. Currently, research ...
Highlight facts or appeal to feelings? The psychology of persuading individuals to contribute to a collective goal
2023-03-08
Researchers from Fudan University, China Europe International Business School, and Peking University published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines how marketers can use different messaging to persuade individuals to contribute to a collective goal. The study addresses the specific question of the type of message—fact-based vs. affected-based—that is more effective in eliciting participation based on how near the goal is to completion.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal ...
Just add water: How diluting ouzo liquor could lead to better emulsions
2023-03-08
It sounds like a party trick: Add water to the clear, licorice-flavored ouzo liquor, and watch it turn cloudy. This “ouzo effect” is an example of an easy way to make highly stable emulsions — or mixtures of liquids that don’t like being together, like vinaigrettes — but nobody has yet fully understood how it works. Now, researchers report in ACS Central Science that the secret may lie in the unique structure of the emulsion’s droplets.
Ouzo is a popular liquor enjoyed throughout Greece, ...
Paving a smoother path to manuscript publication
2023-03-08
Shane Harper, DMS, PA-C, knows how difficult it is to launch a medical research journal and get it into the orbit of the scientific community. In 2022 he became the founding editor-in-chief for the West Texas Journal of Medicine, which published its inaugural issue in December.
By establishing a medical research publication, Harper and the journal’s editorial board seek to provide an online publication that distributes original medical and health sciences-related research in a forum free of common predatory publication practices to ...
Paleontologists flip the script on anemone fossils
2023-03-08
Billions of sea anemones adorn the bottom of the Earth’s oceans — yet they are among the rarest of fossils because their squishy bodies lack easily fossilized hard parts. Now a team of paleontologists has discovered that countless sea anemone fossils have been hiding in plain sight for nearly 50 years.
In a newly published paper in the journal Papers in Palaeontology, University of Illinois Chicago’s Roy Plotnick and colleagues report that fossils long-interpreted ...
Mezcal worm in a bottle: DNA evidence suggests a single moth species
2023-03-08
A new study published in PeerJ Life & Environment looked to identify the species of larva found in bottles of Mezcal. Mezcal is a distilled alcoholic beverage made from any type of agave.
Are people consuming larvae of the skipper butterfly Aegiale hesperiaris, or the larva of the moth Comadia redtenbacheri, the latter which is thought to be declining in numbers in recent years? Or is the worm the larva of a weevil, or another unidentified insect species? Researchers used DNA-based identification analysis of larvae inside 21 commercially ...
New device for lower extremity rehabilitation receives FDA approval!
2023-03-08
COTRAS Co., Ltd. (hereon referred to as COTRAS), an innovative medical-device firm focused on rehabilitation products, has secured approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for MOBILISE, a medical device to help degenerative knee arthritis patients.
MOBILISE has been promoted among UNIST (Professor Sang Hoon Kang), COTRAS Co., Ltd. (hereon referred to as COTRAS), Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), and Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (SNUH). The aim is to further develop the original technology created by UNIST ...
First nasal monoclonal antibody treatment for COVID-19 shows promise for treating virus, other diseases
2023-03-08
In a pilot trial and clinical sample-based investigations, the drug Foralumab decreased inflammatory markers in patients with COVID-19
Similar reduction in inflammatory markers were seen when given to patients with multiple sclerosis
A pilot trial by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, tested the nasal administration of the drug Foralumab, an anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody. Investigators found evidence that the drug dampened the inflammatory T cell response and decreased lung inflammation in patients with COVID-19. Further analysis showed the same gene expression modulation in patients ...
Scientists show how gene expression controls synaptic plasticity in the aging human brain
2023-03-08
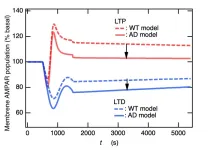
Scientific evidence shows how the cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is caused by the buildup of amyloid beta proteins, which promote synaptic malfunction. One of the neuropathological features in the brains of patients with AD is the degeneration of the basal forebrain cholinergic neurons, leading to a decrease in the number of cholinergic projections to the hippocampus. As a symptomatic treatment of AD, cholinergic neurotransmission is enhanced by the use of certain drugs, known as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. For better prevention and treatment of cognitive disorders like AD and schizophrenia, it is necessary to understand how acetylcholine regulates synaptic transmissions.
Higher ...
UTSA ScooterLab receives $1.7M NSF award to deploy a fleet of data collecting e-scooters
2023-03-08
When a speedy campus scooter nearly collided with Murtuza Jadliwala, he had an epiphany. The micro-mobility form of transportation could be a vehicle for change.
Scooters carry people as well as sensors—sensors that can collect a wealth of data. This data is key to improving the quality of life. With that in mind, Jadliwala, an associate professor in the UTSA Department of Computer Science, created the ScooterLab, which has received a $1.7M grant from the National Science Foundation.
“This funding is critical for ScooterLab as it enables us to take this community research infrastructure from vision to reality,” Jadliwala said. “We are hoping that our new research ...
Two-year mission to study human impact on Europe’s seas and coastal regions
2023-03-08
Europe’s coastlines are environments rich in biodiversity that also represent important sites of industry, culture, and heritage. Forty per cent of Europe’s population live within a coastal region, and many European societies have been, and still are, defined by their relationships with the sea.
Our seas and coasts represent key ecosystems that host an extremely rich diversity of life and play critical roles in the stability and sustainability of wider ecosystems. However, anthropogenic interferences such as pollution, farming, and building ...
Do school shootings increase stress-related emergency department visits in local communities?
2023-03-08
New research in Contemporary Economic Policy reveals that school shootings may worsen mental health in surrounding communities and increase health system costs.
For the study, investigators compared the number of stress-related emergency department visits by California residents in zip-codes within 5 miles of school shootings and by California residents in zip-codes 10–15 miles from school shootings, both before and after these violent events.
Compared with before school shootings, exposure to school shootings and to fatal school shootings was associated with increases of 0.7 and 1.5 ...
Blocking gene that inhibits root growth may enhance drought resistance in crops
2023-03-08
A strong root system allows crops to absorb water and nutrients from the soil, but scientists have little information about the genes that control root development. Recent research published in New Phytologist reveals that blocking a negative regulator gene of root development leads to enhanced root growth in plants.
The gene, called RRS1 (Robust Root System 1), encodes an R2R3-type MYB family transcription factor that activates the expression of another gene (OsIAA3) that inhibits root growth. Knocking out RRS1 in plants led to longer root length, longer lateral root length, and larger lateral root density. Also, a natural variant of RRS1 ...
Could having an irregular heart rhythm affect a person’s risk of developing dementia?
2023-03-08
In a large study of diverse adults in California, individuals with newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation, or an irregular heart rhythm, had a modestly elevated risk of developing dementia. The Journal of the American Heart Association study found that this risk was higher in younger adults and those without chronic kidney disease, but did not substantially vary across sex, race, or ethnicity.
In the study of nearly 200,000 adults, incidence rates for dementia over a median follow-up of 3.3 years were 2.79 versus 2.04 per ...
Can virtual reality tools help teach obstetrics and gynecology topics to medical students?
2023-03-08
Results from a trial published in the International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics support the benefit of 3D virtual reality lessons to improve medical students’ knowledge and understanding of complex topics in obstetrics and gynecology.
For the study, 21 students took part in a 15-minute virtual reality learning environment (VRLE) experience on the stages of fetal development, and 20 students received a PowerPoint tutorial on the same topic.
Knowledge increased after both learning experiences, but it was only retained in the VRLE group at one-week follow up. Questionnaires completed by participants reflected a high ...
Models predict nursing home residents’ risk of fall-related injuries
2023-03-08
In research published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, investigators developed and validated models that can predict the risk of fall-related injuries in nursing home residents based on routinely collected clinical data.
The prediction models achieved good discrimination and excellent calibration for accurately estimating individuals’ six-month and two-year risk of fall-related injuries. One short model that performed well included only five predictors: Activities of Daily Living Score, recent fall, hospitalization in the previous year, ability to walk in room, and history of non-hip fractures.
“These models ...
Protein derived from bone may help combat osteosarcoma
2023-03-08
A study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research has identified a bone matrix protein called Secreted phosphoprotein 24 kD (Spp24) that may help to treat osteosarcoma, the most common type of bone cancer.
In experiments conducted in cells and mice, investigators found that Spp24 inhibits the proliferation and invasiveness of osteosarcoma tumor cells and promotes their apoptosis, or death. Mechanistically, Spp24 binds to and neutralizes a protein called bone morphogenetic protein 2, which has tumor enhancing properties.
“Spp24 and ...
THE LANCET: Contracting a respiratory infection in early childhood associated with a higher risk of dying from respiratory disease as an adult, study finds
2023-03-08
Peer-reviewed / Observational study / People
Study of 3,589 people over 73 years suggests that children who had a lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI), such as bronchitis or pneumonia, by the age of two were almost twice as likely to die prematurely in adulthood from respiratory diseases, independent of socioeconomic factors and smoking status.
After adjusting for cofounders, analysis suggests a 2.1% rate of premature adult death from respiratory disease among those who had a LRTI in early childhood, compared to 1.1% among those who did not report a LRTI before the age of ...
Respiratory disease in early childhood linked to higher risk of death in adulthood
2023-03-08
Contracting a lower respiratory tract infection in early childhood is associated with a higher risk of dying from respiratory disease as an adult, according to new research.
A study, led by researchers from Imperial College London and published in The Lancet, has found that children who had a lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI), such as bronchitis or pneumonia, by the age of two were almost twice as likely to die prematurely in adulthood from respiratory diseases. The research showed the rate ...
Short-distance migration critical for climate change adaptation
2023-03-08
Short-distance migration, which accounts for the vast majority of migratory movements in the world, is crucial for climate change adaptation, according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA).
Contrary to common assumptions, most migratory movements are people moving short distances, largely due to economic, social and environmental factors, such as climate change.
A study of people living in the drylands of India and parts of Africa was carried out by UEA researchers in the School of International Development.
The paper, ‘Everyday mobility and changing livelihood trajectories: implications for vulnerability ...
[1] ... [2060]
[2061]
[2062]
[2063]
[2064]
[2065]
[2066]
[2067]
2068
[2069]
[2070]
[2071]
[2072]
[2073]
[2074]
[2075]
[2076]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.