Study of immune ‘neighborhoods’ highlights macrophages as key players in invasive breast cancers
2023-03-16
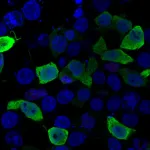
Most immunotherapies, which aim to boost T cell activity, work poorly in treating estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer. Targeting a different type of immune cell called macrophages could be a more effective approach, suggests a comprehensive new analysis of invasive ER+ breast cancers led by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists.
Published today in Nature Cancer, the study found that macrophages were the dominant immune cell infiltrating ER+ invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) and invasive ductal carcinoma ...
Genetic causes of three previously unexplained rare diseases identified
2023-03-16
New York, NY (March 16, 2023) – Using a new computational approach they developed to analyze large genetic datasets from rare disease cohorts, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and colleagues have discovered previously unknown genetic causes of three rare conditions: primary lymphedema (characterized by tissue swelling), thoracic aortic aneurysm disease, and congenital deafness. The work was done in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Bristol, UK; KU Leuven, Belgium; the University of Tokyo; the University of Maryland; Imperial College London, and others from around the world.
An enhanced understanding of the functions ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers discover a new approach to harvesting aerial humidity with organic crystals
2023-03-16
Fast facts:
The global shortage of fresh water currently affects hundreds of millions of people around the world, and it is estimated that by 2025, 1.8 billion people will experience severe water scarcity and hunger due to loss of fertile farming lands caused by droughts.
The discovery of alternative water-harvesting technologies holds the potential to alleviate the foreseeable socioeconomic impacts of severe water scarcity.
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 16 2023: Researchers of the Smart Materials Lab (SML) and the Center for Smart Engineering Materials (CSEM) at NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) have reported a novel method of harvesting water from ...
Dual immunotherapy plus chemotherapy before surgery improves patient outcomes in operable lung cancer
2023-03-16
HOUSTON ― In a Phase II trial led by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, adding ipilimumab to a neoadjuvant, or pre-surgical, combination of nivolumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy, resulted in a major pathologic response (MPR) in half of all treated patients with early-stage, resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
New findings from the NEOSTAR trial, published today in Nature Medicine, provide further support for neoadjuvant immunotherapy-based treatment as an approach to reduce viable tumor at surgery and to improve outcomes in NSCLC. The combination also was associated with an increase in immune cell infiltration and a favorable gut microbiome ...
How fishermen benefit from reversing evolution of cod
2023-03-16
Leipzig. Intense fishing and overexploitation have led to evolutionary changes in fish stocks like cod, reducing both their productivity and value on the market. These changes can be reversed by more sustainable and far-sighted fisheries management. The new study by researchers from the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), Leipzig University and the Institute of Marine Research in Tromsø, which was published in Nature Sustainability, shows that reversal of evolutionary change would only slightly reduce the profit of fishing, but would help regain and conserve natural genetic diversity.
The impact of global fisheries on marine ecosystems ...
Displays with more brilliant colors through a fundamental physical concept
2023-03-16
A research team from the University of Cologne (Germany) and the University of St Andrews (Scotland) has shown in a new study how a fundamental physical concept can be used to boost the colour brilliance of smartphone, computer or TV screens without cutbacks in energy efficiency. The results have been published in Nature Photonics.
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) have conquered the market for displays in recent years – from high-resolution smartphone to wall-sized television screens. However, industry and science face several challenges in creating the next generation of devices ...
Hot topic – how heat flow affects the Earth’s magnetic field
2023-03-16
Hot topic – how heat flow affects the Earth’s magnetic field
Compass readings that do not show the direction of true north and interference with the operations of satellites are a few of the problems caused by peculiarities of the Earth’s magnetic field.
The magnetic field radiates around the world and far into space, but it is set by processes that happen deep within the Earth’s core, where temperatures exceed 5,000-degress C.
New research from geophysicists at the University of Leeds suggests that ...
Case report of first mixed race woman possibly cured of HIV published in Cell
2023-03-16
A new method to cure HIV—by transplanting HIV-resistant stem cells from umbilical cord blood—has yielded long-term successful results, say scientists. The approach was successfully used to treat the “New York patient,” a middle-aged woman with leukemia and HIV who self-identifies as mixed race, who has been without HIV since 2017. Using stem cells from cord blood rather than from compatible adult donors, as has been done previously, increases the potential to cure HIV via stem cell transplantation ...
Genomic analysis shows the Amazon’s Ashaninka people are made up of two subgroups with distinct histories
2023-03-16
The Ashaninka are the most numerous Indigenous people living in the rainforests of Peru and Brazil where they inhabit a crucial area between the Andes and sources of the Amazon River. And yet, despite the size of the population and their importance in the past and present, their genetic history has remained understudied.
Now a team of researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on March 16 has analyzed the genomes of more than 50 individuals to clarify the group’s interactions with nearby South American regions, including Central America and the Caribbean. ...
Indigenous Ashaninka DNA helps geneticists write new chapters of pre-colonial history in South America
2023-03-16
Geneticists have written new chapters in the reconstruction of pre-colonial Americas history after using DNA from the indigenous Ashaninka people from Amazonian Peru. They have discovered previously unexpected levels of genetic variation in this group and uncovered a strong hint that these people were involved in a South-to-North migration that led to the transition from an archaic to ceramic culture in the Caribbean islands.
The dramatic impact of European colonisation during the second half of the last millennium has strongly influenced the genetic history of the Americas, making the reconstruction ...
Financial hardship and employment loss among adults with disabilities during COVID-19
2023-03-16
About The Study: This survey study found that people with disabilities were more likely to report household employment loss and financial hardship during the initial COVID-19 pandemic, which are especially pronounced among racial and ethnic minority respondents. These findings suggest people with disabilities may be disproportionately affected by the initial pandemic and may require additional resources and policy strategies (e.g., training programs, workplace accommodations) as several labor markets adapt to the pandemic (e.g., shifting to remote working).
Authors: Kea Turner, Ph.D., M.P.H., M.A., of the H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center ...
Readmission rates, episode costs for Alzheimer disease and related dementias
2023-03-16
About The Study: In this study of 722,000 hospitalization episodes, patients with Alzheimer disease and related dementias (ADRD) had higher readmission rates and overall readmission and episode costs than their counterparts without ADRD. Hospitals may need to be better equipped to care for patients with ADRD, especially in the post-discharge period. Considering that any type of hospitalization may put patients with ADRD at a high risk of 30-day readmission, judicious preoperative assessment, postoperative discharge, and ...
Preterm babies do not habituate to repeated pain
2023-03-16
Preterm infants do not get used to repeated pain in the way that full-term infants, children and adults do habituate to pain, finds a study led by UCL (University College London) researchers.
The authors of the new Current Biology paper say that if preterm infants have not yet developed the mechanism that enables people to get used to moderate pain, medical procedures in their first few weeks of life could potentially impact their development.
Lead author Dr Lorenzo Fabrizi (UCL Neuroscience, Physiology & Pharmacology) said: “The way that we can get used to things can be seen as the simplest example of behavioural and brain plasticity, and it is ...
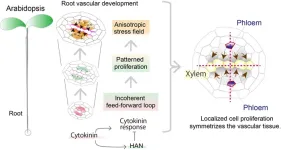
Compressive stress shapes the symmetry of Arabidopsis root vascular tissue
2023-03-16
Ikoma, Japan – The generation and maintenance of tissue boundaries are fundamental to the development of functional organs in both plants and animals. In general, tissue boundaries are initially set among primordial cells, and their shapes and arrangements are refined during subsequent organ growth. In this process, cell migration plays a curtail role for boundary refinement in animal systems, however, plant tissue lacks such cell fluidity due to its cell walls. Despite significant progress in understanding the initial patterning of tissue boundaries in several ...
How countries can benefit from linking data
2023-03-16
A recent study makes it clear: Countries like Sweden that can link data from different areas - such as the labor market and health care - have a decisive advantage when it comes to setting targeted actions.
A research team from the Complexity Science Hub, together with scientists from Sweden, Denmark and the Netherlands, investigated the extent to which mental and somatic illnesses influence integration into the labor market and whether there is a difference here between refugee and Swedish-born young adults. "In total, we analyzed ...
Pusan National University researchers examine combined effects of two combustion technologies on the emission of coal-fired boilers
2023-03-16
Coal-fired power plants have been in place for a long time to meet the global demands for power generation. Needless to say, there are environmental and human health concerns to be addressed on this front. While there are ongoing efforts to transition to renewable energy resources, coal-fired power plants may not become obsolete just yet. Against this backdrop, it is pertinent to explore how the efficiency of these coal-fired boilers can be improved while mitigating their harmful effects on the environment, namely greenhouse gas emissions, acid rain, and photochemical smog generation, and the human health.
To this end, various ...
Bottled water masks world’s failure to supply safe water for all, can slow sustainable development: UN
2023-03-16
The rapidly-growing bottled water industry can undermine progress towards a key sustainable development goal: safe water for all, says a new United Nations report.
Based on an analysis of literature and data from 109 countries, the report says that in just five decades bottled water has developed into “a major and essentially standalone economic sector,” experiencing 73% growth from 2010 to 2020. And sales are expected to almost double by 2030, from US$ 270 billion to $500 billion.
Released ...
Quantifying the life expectancy gap for people living with sickle cell disease
2023-03-16
(WASHINGTON, March 16, 2023) – While research has long established disparities in health outcomes among individuals living with sickle cell disease (SCD), few studies have quantified these gaps. A new study published in Blood Advances finds that the average life expectancy of publicly insured patients living with SCD is roughly 52.6 years. In contrast, the CDC reports that the average life expectancy in the United States is 73.5 years for men and 79.3 years for women, demonstrating the considerable ...
Genetics as conservation tool for endangered chimpanzees
2023-03-16
The western chimpanzees of Guinea are threatened by mining activities. Using a novel genetic approach, UZH researchers and an international team have collected information on population size and community structure of the endangered species. These data provide an important baseline to assess the impact of mining.
The western chimpanzee is listed as “Critically Endangered” on the Red List of the International Union for the Conservation of Nature. The Mount Nimba Strict Nature Reserve, a UNESCO World Heritage site, located on the borders of Guinea, Liberia and Côte ...
CityU scientists develop energy-saving, tunable meta-devices for high-precision, secure 6G communications
2023-03-16
The future of wireless communications is set to take a giant leap with the advent of sixth-generation (6G) wireless technology. A research team at City University of Hong Kong (CityU) invented a groundbreaking tunable terahertz (THz) meta-device that can control the radiation direction and coverage area of THz beams. By rotating its metasurface, the device can promptly direct the 6G signal only to a designated recipient, minimizing power leakage and enhancing privacy. It is expected to provide a highly adjustable, directional and secure means for future 6G communications systems.
The potential of THz band technology ...
Ochsner Health advances precision medicine, becomes national leader in universal genomic testing for chemotherapy
2023-03-16
New Orleans, Louisiana – Ochsner Health is leading the way for precision medicine nationwide by becoming one of the first hospital systems to standardize genomic testing, significantly advancing ways in which care teams can treat cancer patients. This change helps providers determine individualized treatment by understanding how patients will react to certain drugs, thereby lowering risk of adverse side effects, improving patient experience, and bettering patient outcomes.
Pharmacogenomics, or PGx, testing guides physicians how patients metabolize certain drugs and warns of possible side effects so they may ...
Bigger flowers, greater rewards: Plants adapt to climate disruptions to lure pollinators
2023-03-16
Photos
There's been a well-documented shift toward earlier springtime flowering in many plants as the world warms. The trend alarms biologists because it has the potential to disrupt carefully choreographed interactions between plants and the creatures—butterflies, bees, birds, bats and others—that pollinate them.
But much less attention has been paid to changes in other floral traits, such as flower size, that can also affect plant-pollinator interactions, at a time when many insect pollinators are in global decline.
In ...
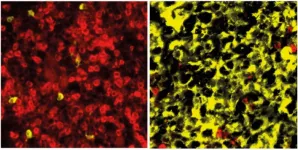
Novel disease models for multiple myeloma
2023-03-16
B lymphocytes – also known simply as B cells – play a central role in the immune system. If pathogens enter the body, B cells are activated and develop into plasma cells, which then release antibodies. One important step in this process is the germinal center reaction. If the B cells’ maturation into plasma cells is disrupted, multiple myeloma can develop – one of the most common blood cancers. This disease has a variety of subtypes and is not yet curable.
Multiple myelomas develop very slowly and in several stages. The process is initiated by spontaneous genetic aberrations that occur ...
Scientists identify 100 important questions facing plant science
2023-03-16
What are the key research priorities that will help tackle the global challenges of climate change, the biodiversity crises and feed a growing population in a sustainable way? Ten years after these priorities were first debated and summarised by a panel of scientists and published in New Phytologist, the panel reflects on the changes to plant science and the progress made to address these research areas, published on 16 March in a Letter in New Phytologist.
To re-evaluate research priorities, a new panel was formed in 2022 to provide an international perspective on the important areas for plant science research. This project, ...
Clinical trial investigating innovative way to control Type 2 diabetes
2023-03-16
LOS ANGELES — More than 37 million Americans have diabetes, and approximately 90-95% have Type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body does not produce or effectively use insulin. A lack of insulin leads to raised blood glucose (sugar) levels, which can cause heart disease and stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage and other severe complications.
Keck Medicine of USC has launched a Phase 2 clinical trial investigating the effectiveness of a new outpatient, nonsurgical endoscopic procedure in stabilizing blood glucose levels for patients.
“Currently, the only treatment for diabetes ...
[1] ... [2055]
[2056]
[2057]
[2058]
[2059]
[2060]
[2061]
[2062]
2063
[2064]
[2065]
[2066]
[2067]
[2068]
[2069]
[2070]
[2071]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.