Marine mammal reproduction rests on a precarious tipping point of ocean resources
2023-03-08
Changing environmental conditions may threaten marine mammal populations by making it harder to find prey, and a new study shows how small, gradual reductions in prey could have profound implications for animal populations.
The reproductive success of female elephant seals depends on their ability to find prey and put on weight during their months-long foraging migrations. Researchers at UC Santa Cruz studied the relationships between elephant seal behavioral strategies in the open ocean, weight gain, and lifetime success at producing pups.
Their findings, published March 8 in Ecology Letters, reveal a sharp threshold in the relationship between ...
UCF researcher creates world’s first energy-saving paint – inspired by butterflies
2023-03-08
–EMBARGOED:
NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL 2:00 p.m. EST, WEDNESDAY, 08 MARCH 2023–
UNIVERSITY OF CENTRAL FLORIDA
UCF Researcher Creates World’s First Energy-saving Paint – Inspired by Butterflies
Instead of pigment-based colored paint, which requires artificially synthesized molecules, a UCF researcher has developed an alternative way to produce colored paint that is more natural, environmentally friendly and light weight.
ORLANDO, March 8, 2023 — University of Central Florida researcher Debashis Chanda, a professor in UCF’s NanoScience Technology Center, has drawn inspiration from butterflies to create the first environmentally ...
Researchers discover how too much oxygen damages cells and tissues
2023-03-08
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—March 8, 2023—When it comes to oxygen, you can have too much of a good thing. Breathing air that contains higher levels of oxygen than the usual 21 percent found in Earth’s atmosphere can cause organ damage, seizures, and even death in people and animals, particularly if it’s in excess of the body’s oxygen needs. Until now, however, scientists have mostly speculated about the mechanisms behind this phenomenon, known as oxygen toxicity, or hyperoxia.
Now, researchers at Gladstone Institutes have discovered how excess oxygen changes a handful of proteins in our cells that ...
Colorectal cancer research
2023-03-08
Excessive iron absorption by tumor cells in the digestive tract is known to play a major role in driving colorectal cancer – the third most prevalent and third leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S.
In a new study published in the journal Advanced Science, University of New Mexico researchers describe the part played by the transferrin receptor (TFRC) gene in the growth of colorectal cancer tumors.
Iron is absorbed into intestinal cells both from the bloodstream and from iron-rich foods, such as red meat, said Xiang Xue, PhD, assistant professor ...
A pool at Yellowstone is a thumping thermometer
2023-03-08
While the crowds swarm around Old Faithful to wait for its next eruption, a little pool just north of Yellowstone National Park’s most famous geyser is quietly showing off its own unique activity, also at more-or-less regular showtimes. Instead of erupting in a towering geyser, though, Doublet Pool cranks up the bass every 20 to 30 minutes by thumping. The water vibrates and the ground shakes.
Doublet Pool’s regular thumping is more than just an interesting tourist attraction. A new study led by University of Utah researchers shows that the ...
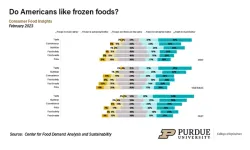
Americans planning frugal uses for their 2023 tax refunds
2023-03-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Americans likely are receiving smaller tax refunds than they have in recent years, and most people will not be going out to spend this money, according to the February 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report. This month’s report also looks more closely at religious demographics and includes new data on frozen food preferences.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, ...
Unprecedented increase in ocean plastic since 2005 revealed by four decades of global analysis
2023-03-08
A global dataset of ocean plastic pollution between 1979 and 2019 reveals a rapid and unprecedented increase in ocean plastics since 2005, according to a study published March 8, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Marcus Eriksen from The 5 Gyres Institute, USA, and colleagues.
Understanding plastic accumulation in the oceans to date could provide a critical baseline to help address this form of pollution. Previous studies have focused primarily on northern-hemisphere oceans near the world’s most industrialized nations, ...
Places of worship linked with more neighborhood crime in Washington, D.C.
2023-03-08
A new analysis of crime statistics near hundreds of places of worship in Washington, D.C., shows that these sites are associated with higher levels of violent and property crime—even after accounting for other factors commonly linked with crime. James Wo of the University of Iowa, U.S., presents these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 8, 2023.
Prior research has established that places of worship foster social ties and community actions for the common good, suggesting that these sites would reduce crime in their neighborhoods. However, few studies have addressed the hypothesized ...
For educational attainment, it's more helpful to grow up in an affluent neighborhood than it is harmful to grow up in a poor one, per 23-year large Netherlands cohort study
2023-03-08
For educational attainment, it's more helpful to grow up in an affluent neighborhood than it is harmful to grow up in a poor one, per 23-year large Netherlands cohort study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281928
Article Title: Neighbourhood effects on educational attainment. What matters more: Exposure to poverty or exposure to affluence?
Author Countries: The Netherlands, UK
Funding: The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Research Council (https://erc.europa.eu/) ...
After 6 months of disrupted schooling during COVID-19, German students scored substantially lower on intelligence tests than comparative earlier cohorts, with the gap persisting after 16 months.
2023-03-08
After 6 months of disrupted schooling during COVID-19, German students scored substantially lower on intelligence tests than comparative earlier cohorts, with the gap persisting after 16 months
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281779
Article Title: Students’ intelligence test results after six and sixteen months of irregular schooling due to the COVID-19 pandemic
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The study was supported by a grant awarded to M.B. by the Research Fund of ...
Participants in psychology studies are more likely than average to exhibit symptoms of personality disorders, potentially skewing the findings of such research
2023-03-08
Participants in psychology studies are more likely than average to exhibit symptoms of personality disorders, potentially skewing the findings of such research
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281046
Article Title: Self-selection biases in psychological studies: Personality and affective disorders are prevalent among participants
Author Countries: Poland, Spain, Italy
Funding: To conduct Face-to-Face Studies IK was supported by grants 2017/01/X/HS6/02022 from the National Center of Science ...
A surprising way to trap a microparticle
2023-03-08
New study finds obstacles can trap rolling microparticles in fluid
Through simulations and experiments, physicists attribute the trapping effect to stagnant pockets of fluid, created by hydrodynamics
Random motions of the molecules within the fluid then ‘kick’ the microroller into a stagnant pocket, effectively trapping it
Size of the obstacle also controls how easy it is to trap a microroller and how long it remains trapped
EVANSTON, Ill. — When physicists steered a tiny microparticle toward a cylindrical obstacle, they expected one of two outcomes to occur. The particle would either collide into the ...
Fresh understanding of ageing in the brain offers hope for treating neurological diseases
2023-03-08
Scientists from the Trinity Biomedical Sciences Institute (TBSI) have shed new light on ageing processes in the brain. By linking the increased presence of specialised immune cells to conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and traumatic brain injury for the first time, they have unearthed a possible new target for therapies aimed at treating age-related neurological diseases.
The research, which benefited from a collaboration with experts at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and focused ...
Cyborg technology analyzes the functional maturation of stem-cell derived heart tissue
2023-03-08
Research in animal models has demonstrated that stem-cell derived heart tissues have promising potential for therapeutic applications to treat cardiac disease. But before such therapies are viable and safe for use in humans, scientists must first precisely understand on the cellular and molecular levels which factors are necessary for implanted stem-cell derived heart cells to properly grow and integrate in three dimensions within surrounding tissue.
New findings from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) make it possible ...
Anthropogenic climate change poses systemic risk to coffee cultivation
2023-03-08
Coffee is important to the economies of coffee producing regions. A study published in PLOS Climate by Doug Richardson at CSIRO Oceans & Atmosphere, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia and colleagues suggests that climate change may significantly affect land where coffee is cultivated.
Coffee plants are sensitive to climate variability and change. However, the impact of synchronous climate hazards occurring in multiple areas important for coffee production is unknown. In order to better understand how large-scale climate modes such as El Niño ...
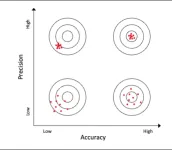
Celebrity sightings have a built-in contradiction
2023-03-08
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Their popularity makes celebrities easy to spot. Strangers, however, can also get mistaken for celebrities, resulting in cases of false “celebrity sightings.” In attempting to explain the contradiction, a University of California, Riverside, study reports that celebrity faces are remembered more precisely but less accurately.
Precision, in this context, refers to how memories for a particular face resemble each other over repeated memory retrievals, which can be likened to the clustering of arrows on a target in archery. Accuracy measures ...
A new class of drugs could prevent resistant COVID-19 variants, study finds
2023-03-08
New Haven, Conn. — The constant evolution of new COVID-19 variants makes it critical for clinicians to have multiple therapies in their arsenal for treating drug-resistant infections. Researchers have now discovered that a new class of oral drugs that acts directly on human cells can inhibit a diverse range of pathogenic SARS-CoV-2 strains.
In their newly published study, the team found a novel mechanism through which the gene that expresses angiotensin converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2)—the cellular receptor to which SARS-CoV-2 ...
Swan Hellenic and SETI Institute announce lecturers for Explore Space at Sea Series
2023-03-08
March 8, 2023, Mountain View, CA – The SETI Institute and Swan Hellenic announce SETI Institute guest lecturers who will offer cruise guests expert insights into the history and latest discoveries in astronomy, astrophysics, astrobiology and planetary science, and the quest to find other forms of life within and beyond our solar system. This quest takes SETI Institute researchers to the planet’s most remote and inhospitable corners to explore life, including Antarctica, where the Swan Hellenic fleet is present for several months every year.
Outlining ...
New articles for Geosphere posted early online
2023-03-08
Boulder, Colo., USA: GSA’s dynamic online journal, Geosphere, posts articles online regularly. Topics this month include an analysis of geoscience job applications; Uturuncu volcano, Bolivia; Picture Gorge Basalt; and the Red Bluff Granite Suite. You can find these articles at https://geosphere.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent .
Critical workforce skills for bachelor-level geoscientists: An analysis of geoscience job advertisements
G.W. Shafer; K. Viskupic; A.E. Egger
Understanding the skills ...
Human Brain Project: spin-off receives EIC grant to develop energy-efficient AI technology
2023-03-08
The European Innovation Council (EIC) has recently announced that it will award a Transition grant to SpiNNcloud Systems GmbH, a deep-tech startup based in Saxony, Germany.
The team from SpiNNcloud Systems GmbH, a spin-off from Professor Christian Mayr’s research group at Technische Universität Dresden, is receiving a grant of 2.5 million euros for their groundbreaking project, “SpiNNode: SpiNNaker2 on the edge.”
“SpiNNaker2 is a bio-inspired supercomputer which was developed at my Chair in collaboration with Prof. Steve Furber’s research group at the University of Manchester as part ...
New GSA Bulletin articles published online ahead of print
2023-03-08
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Geological Society of America regularly publishes articles online ahead of print. GSA Bulletin topics studied this month include the nature and dynamics of China and Tibet; the Lower Mississippi Valley, USA; and the polarity of Mesozoic arcs along the western margin of North America. You can find these articles at https://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent .
Magmatic-hydrothermal evolution of long-lived Nb-Ta-(Sn) mineralization in Lianyunshan, NE Hunan, South China
Nuerkanati Madayipu; Huan Li; Safiyanu Muhammad Elatikpo; Michael W. Förster; Hou-Xiang Zhou ...
The ...
Group exercise program for older adults led to more independent exercise despite pandemic restrictions, MU study finds
2023-03-08
COLUMBIA, Mo. -- Sticking with an exercise program can be tough, even during the best of times. But what about during a pandemic?
A new study by the University of Missouri and Oklahoma State University found that even when gyms were closed and there were other COVID-19 restrictions limiting face-to-face meetings, older adults who completed the Stay Strong, Stay Healthy exercise program — created at MU in 2005 — continued to maintain long-term exercise habits independently, which resulted in improved lifestyle changes and an increase in both physical energy and self-confidence.
“We ...
Incident atrial fibrillation appears to heighten dementia risk
2023-03-08
People with a recent diagnosis of atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common irregular heart rhythm, have a modestly higher risk of developing dementia than people without the condition, according to research published today.
“Previous studies that have examined the link between atrial fibrillation and dementia have yielded conflicting results, and we hope that our study’s large sample size helps to establish confidence in our findings,” said Dr. Nisha Bansal, a professor of medicine at the University of Washington School of Medicine. “The study also included a community based, diverse population, which may increase the generalizability ...
Lunar telescope will search for ancient radio waves
2023-03-08
UPTON, NY—Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory are leading a new effort to land a radio telescope on the moon. If successful, the project will mark the first step towards exploring the Dark Ages of the universe.
The Dark Ages are an early era of cosmological history starting about 380,000 years after the Big Bang. There were no stars or planets in the Dark Ages. It’s a point in time that scientists have never been able to observe. Though radio waves from the Dark Ages still linger in space, the abundance of radio interference on Earth has masked these signals from scientists seeking to study them.
If ...
How a metabolite causes inflammation and disease
2023-03-08
A new study shows for the first time a connection between a mitochondrial metabolite and the activation of an inflammatory response. Mitochondria are functional units of our cells that fulfil important tasks, i.e. chemical reactions, for the functioning of the cell. One of these tasks is the production of energy that is necessary for cell growth and reproduction. If certain chemical reactions in the mitochondrion change, diseases occur. For example, deficiencies in fumarate hydratase (FH) in the Krebs cycle, one of the most important metabolic pathways in mitochondria, ...
[1] ... [2058]
[2059]
[2060]
[2061]
[2062]
[2063]
[2064]
[2065]
2066
[2067]
[2068]
[2069]
[2070]
[2071]
[2072]
[2073]
[2074]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.