Study finds residual inflammation after statin therapy strongly predicted cardiovascular events, death
2023-03-06
New evidence released today from a study of 31,245 patients already taking statin therapy indicates that inflammation may be a more powerful predictor of risk of future cardiovascular events—such as heart attack and stroke — than “bad” cholesterol. Treatments that aggressively lower vascular inflammation need to be incorporated into daily practice if doctors are to maximize patient outcomes, according to the study’s corresponding author, Paul Ridker, MD, a preventive cardiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General ...
Study finds exhaled breath could enhance detection, diagnosis of COVID-19 and variants
2023-03-06
The emergence of new COVID-19 variants has led to reduced accuracy across current rapid testing methods, but a recent University of Michigan study suggests that a patient’s breath might hold the key to a more precise diagnosis.
Investigators from the University of Michigan’s Max Harry Weil Institute for Critical Care Research and Innovation, including faculty and students from the College of Engineering and Michigan Medicine, used portable gas chromatography to examine breath samples collected during the pandemic’s Delta ...
Some ‘allies’ don’t want gay neighbors
2023-03-06
In a survey of 545,531 people, 8.5% of those who said they were ‘fully accepting’ of gay people did not want gay neighbors.
First study to explore stigmatizing behaviors expressed by avid supporters of sexual minorities
‘Simple legal inclusion can help mobilize the accepting population to their fullest potential’
CHICAGO --- When legal systems choose to offer no protections to sexual minorities, even avid LGBTQ supporters would reject their gay neighbors, reports a new Northwestern Medicine study.
The study examined ...
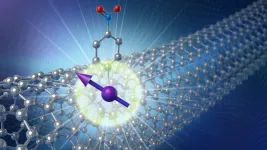
An innovative twist on quantum bits: Tubular nanomaterial of carbon makes ideal home for spinning quantum bits
2023-03-06
Scientists find that a tubular nanomaterial of carbon makes for ideal host to keep quantum bits spinning in place for use in quantum information technologies.
Scientists are vigorously competing to transform the counterintuitive discoveries about the quantum realm from a century past into technologies of the future. The building block in these technologies is the quantum bit, or qubit. Several different kinds are under development, including ones that use defects within the symmetrical structures of diamond and silicon. They may one day transform computing, accelerate drug discovery, generate unhackable networks and more.
Working with researchers from several universities, scientists ...
LOINC continues facilitating health data interoperability with biannual issuance of new concepts
2023-03-06
INDIANAPOLIS -- LOINC® from Regenstrief Institute is issuing its semi-annual release, which contains 608 new concepts to help health systems, laboratories and other health organizations accurately exchange medical data. Some of the new information has been released in coordination with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Association of Public Health Laboratories.
“Aligning the release of LOINC with emerging healthcare trends is an important component of our mission and critical in promoting effective health information exchange among providers, patients and health systems,” said Marjorie Rallins, ...
New study uncovers key culprit behind pediatric brain cancer metastasis
2023-03-06
New research pinpoints a key cause of metastasis from an aggressive form of brain cancer in children and provides a potential new therapy for treating these tumors in the future.
In a paper, published in Nature Cell Biology, physician-scientists from the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh discovered that medulloblastomas hijack a skill that normal brain cells use during their early development and then manipulate it to help tumors spread.
“Children with medulloblastomas that have not yet metastasized may have a high likelihood of long-term survival, but if ...
Can artificial intelligence help find life on Mars or icy worlds?
2023-03-06
March 6, 2023, Mountain View, CA – Wouldn’t finding life on other worlds be easier if we knew exactly where to look? Researchers have limited opportunities to collect samples on Mars or elsewhere or access remote sensing instruments when hunting for life beyond Earth. In a paper published in Nature Astronomy, an interdisciplinary study led by SETI Institute Senior Research Scientist Kim Warren-Rhodes, mapped the sparse life hidden away in salt domes, rocks and crystals at Salar de Pajonales at the boundary of the Chilean Atacama Desert and Altiplano. Then they trained a machine learning model to recognize the patterns and rules associated with their distributions ...
Geosciences at the Crossroads of America
2023-03-06
Boulder, Colo., USA: Oklahoma State University is hosting the 57th annual meeting of the Geological Society of America’s South-Central Section on 13–14 March. The meeting will have a diverse program of workshops, technical sessions, short courses, and field trips that covers a spectrum of geologic disciplines.
The list below highlights a selection of environmental-related session topics you might like:
· Tar Creek Superfund Site Field Trip (Field Trip)
Managed Aquifer Recharge in the Arbuckle Simpson Aquifer (Field Trip)
Geoscience Career Workshop: Career Planning and Networking
· Hydrogeologic Challenges and Roles ...
Gene and cell therapies to combat pancreatic cancer
2023-03-06
Pancreatic cancer is an incurable form of cancer, and gene therapies are currently in clinical testing to treat this deadly disease. A comprehensive review of the gene and cell biotherapies in development to combat pancreatic cancer is published in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the article now
The article titled “Pancreatic Cancer Cell and Gene Biotherapies: Past, Present and Future,” contributed by corresponding author Pierre Cordelier, from the University of Toulouse, and coauthors, ...
Oncotarget | HALP score: Prognostic ability in cancers - a literature review
2023-03-06
“In the last several years, the Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte, Platelet Score (HALP) has emerged in the literature as a new prognostic biomarker [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- March 6, 2023 – A new review paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on February 25, 2023, entitled, “What is hemoglobin, albumin, lymphocyte, platelet (HALP) score? A comprehensive literature review of HALP’s prognostic ability in different cancer types.”
Since its inception, the Hemoglobin, Albumin, Lymphocyte, Platelet (HALP) Score has gained attention as a new prognostic biomarker to predict several clinical outcomes in a multitude ...
Nationwide study finds that women have greater risk of mortality than men after coronary artery bypass surgery
2023-03-06
Compared with men, women continue to have a roughly 30-40 percent higher risk of dying following coronary artery bypass surgery, according to a large study led by investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine and NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center. The analysis showed that, without adjusting for differences in age and other health factors that influence risk, the female bypass patients had a 2.8 percent rate of death during or soon after surgery, compared with 1.7 percent for male patients, a nearly 50 percent difference that only dropped 10-20 percent after accounting for these factors.
The study, which appears Mar. 1 in JAMA Surgery, was based on ...
Assessing the risk of excess folic acid intake
2023-03-06
It is well established that folic acid supplementation can significantly reduce the risk of birth defects, including neural tube defects like spina bifida, the most common birth defect of the central nervous system and the second most common of all structural birth defects. More than 80 nations, including the U.S. 25 years ago, have established mandated folic acid food fortification programs, which have been successful.
“However, there is a lack of research on whether excessive folic acid intake has the potential ...
Geisinger study supports genetic testing for people with cerebral palsy
2023-03-06
DANVILLE, Pa. – A Geisinger meta-analysis of recent research on the genetics of cerebral palsy (CP) provides evidence that genetic testing should be offered as the standard of care for people with the disorder, similar to current recommendations for individuals with other neurodevelopmental disorders (NDD). The findings were published Tuesday in JAMA Pediatrics.
Individual cases of CP—a condition that affects movement, balance and posture—have often been attributed to birth asphyxia, although recent studies show that asphyxia accounts for less than 10% of cases. A growing body of evidence suggests that a significant proportion of CP is caused by genetic changes, ...
New Geology articles published online ahead of print
2023-03-06
Boulder, Colo., USA: Article topics and locations include the Red Lake greenstone belt, Canada; Anak Krakatau volcano, Indonesia; martian soil; Glacial Lake Missoula, Montana, USA; and findings from IODP Expedition 385. These Geology articles are online at https://geology.geoscienceworld.org/content/early/recent .
Crustal conductivity footprint of the orogenic gold district in the Red Lake greenstone belt, western Superior craton, Canada
Ademola Q. Adetunji; Gaetan Launay; Ian J. Ferguson; Jack M. Simmons; Chong Ma ...
A magnetotelluric (MT) study across the Red Lake greenstone belt of the ...
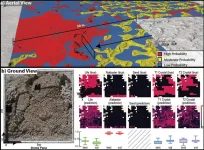
Mississippi River Delta study reveals which human actions contribute to land loss
2023-03-06
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. — Research from scientists at Indiana University and Louisiana State University reveals new information about the role humans have played in large-scale land loss in the Mississippi River Delta — crucial information in determining solutions to the crisis.
Published in Nature Sustainability, the study compares the impacts of different human actions on land loss and explains historical trends. Until now, scientists have been unsure about which human-related factors are the most consequential, and why ...
High-dose anticoagulation can reduce intubations and improve survival for hospitalized COVID-19 patients
2023-03-06
High-dose anticoagulation can reduce deaths by 30 percent and intubations by 25 percent in hospitalized COVID-19 patients who are not critically ill when compared to the standard treatment, which is low-dose anticoagulation. These are the significant findings from the large-scale international “FREEDOM” trial, led by Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, President of Mount Sinai Heart and Physician-in-Chief of The Mount Sinai Hospital, and General Director of the Spanish National Center for Cardiovascular Research (CNIC).
The study results were announced Monday, March 6, ...
ASBMB offers feedback on NIH’s proposed grant review framework
2023-03-06
After soliciting feedback from its members, the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent nine recommendations to the National Institutes of Health last week related to proposed changes to the research grant application peer-review process.
The society’s March 1 letter suggested:
Validating the proposed framework with a pilot study
Revamping the study section grant triage process
Conducting outreach before and during implementation
Using alternative criteria for certain types of projects
Moving forward with simplifying scored criteria and administrative document review
The NIH Office of Extramural Research ...
The marathon runners of the immune system
2023-03-06
When it comes to chronic infections and cancer, a particular type of immune cell plays a central role in our defenses. Researchers at the University of Basel have uncovered the key to the tenacity of these immune cells in coping with the marathon that is fighting a chronic infection. Their results lay the foundations for more effective therapies and vaccination strategies.
Infected and abnormal cells have to go. And as quickly as possible, before any more damage is done. This is the task of what are known as cytotoxic T cells. ...
A wholly sustainable plastics economy is feasible
2023-03-06
Plastic is everywhere. Our society cannot do without it: plastics have numerous advantages, are extremely versatile, and are also cost effective. Today, plastics are mainly produced from crude oil. When the products reach the end of their life, they often end up in a waste incineration plant. The energy-intensive production of plastics and their incineration release large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere, making plastic products a major contributor to climate change.
One way out would be to rely on sustainable production methods, such as the circular economy, in which as much plastic as possible is recycled. Then the main raw material for ...
Graphene quantum dots show promise as novel magnetic field sensors
2023-03-06
Trapped electrons traveling in circular loops at extreme speeds inside graphene quantum dots are highly sensitive to external magnetic fields and could be used as novel magnetic field sensors with unique capabilities, according to a new study.
Electrons in graphene (an atomically thin form of carbon) behave as if they were massless, like photons, which are massless particles of light. Although graphene electrons do not move at the speed of light, they exhibit the same energy-momentum relationship as photons and can be described as “ultra-relativistic.” ...
Parental nonadherence to recommendations for COVID-19 prevention among children
2023-03-06
About The Study: In this survey study of U.S. parents, one-quarter engaged in misrepresentation or nonadherence regarding public health measures for their children. The most common reason was to preserve parental autonomy. Additional reasons included wanting to resume a normal life for their child and the inability to miss work or other responsibilities, among other reasons.
Authors: Andrea Gurmankin Levy, Ph.D., M.B.E., of Middlesex Community College in Middletown, Connecticut, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our ...
Mineral particles and their role in oxygenating the Earth’s atmosphere
2023-03-06
Mineral particles played a key role in raising oxygen levels in the Earth’s atmosphere billions of years ago, with major implications for the way intelligent life later evolved, according to new research.
Up to now, scientists have argued that oxygen levels rose as the result of photosynthesis by algae and plants in the sea, where oxygen was produced as a by-product and released into the atmosphere.
But a research ...
Two-dimensional quantum freeze
2023-03-06
Glass nanoparticles trapped by lasers in extreme vacuum are considered a promising platform for exploring the limits of the quantum world. Since the advent of quantum theory, the question at which sizes an object starts being described by the laws of quantum physics rather than the rules of classical physics has remained unanswered.
A team formed by Lukas Novotny (Zurich), Markus Aspelmeyer (Vienna), Oriol Romero-Isart (Innsbruck), and Romain Quidant (Zurich) is attempting to answer precisely this question within the ERC-Synergy project Q-Xtreme. A crucial step ...
Scientists twist chemical bonds beyond their limits
2023-03-06
A group of scientists from Durham University and University of York have twisted molecules to their breaking point in order to challenge the understanding of chemical bonds.
The researchers explored how far the chemical bonding in an aromatic ring can be twisted before its aromatic bonding breaks.
They achieved this by making overcrowded aromatic rings. Rather than benzene, they used tropylium, which shares electrons around a ring of seven carbon atoms.
Each of these carbon atoms can be functionalised and having seven attachment points in the ring, rather than the six carbon atoms of benzene, allowed ...
Siblings should be screened in cases of suspected child physical abuse
2023-03-06
Siblings of a child suspected of experiencing physical abuse should also be screened for abusive injuries, according to a new international consensus statement led by researchers at UCL (University College London) and Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children (GOSH).
The team of 27 researchers, from six different continents, are calling for a policy change to stop inconspicuous injuries being missed in contact children (i.e. siblings, cohabiting children, or children who are under the same care), and to help prevent further ...
[1] ... [2064]
[2065]
[2066]
[2067]
[2068]
[2069]
[2070]
[2071]
2072
[2073]
[2074]
[2075]
[2076]
[2077]
[2078]
[2079]
[2080]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.