Wildfires in 2021 emitted a record-breaking amount of carbon dioxide
2023-03-03
Irvine, Calif., March 2, 2023 — Carbon dioxide emissions from wildfires, which have been gradually increasing since 2000, spiked drastically to a record high in 2021, according to an international team of researchers led by Earth system scientists at the University of California, Irvine.
Nearly half a gigaton of carbon (or 1.76 billion tons of CO2) was released from burning boreal forests in North America and Eurasia in 2021, 150 percent higher than annual mean CO2 emissions between 2000 and 2020, the scientists reported in a paper in Science.
“According to our measurements, boreal fires in 2021 shattered previous ...
In his new book, Julian Mcclements explains why he is committed to eating ‘meat less’
2023-03-03
Distinguished Professor of Food Science and prolific author David Julian McClements has a new book out this month – Meat Less: The Next Food Revolution (Springer, 2023).
Meat Less describes McClements’ journey to vegetarianism, a shift inspired by his daughter and his ongoing research work on developing healthier and more sustainable foods.
“In writing this book I take the viewpoint that there are no easy answers and that everyone must make the decision to eat meat or not based ...
Illuminating the evolution of social parasite ants
2023-03-03
Ants are known as hard workers, tirelessly attending to their assigned tasks—foraging for food, nurturing larvae, digging tunnels, tidying the nest. But in truth, some are total layabouts. Called workerless social parasites, these rare species exist only as queens, and they die without workers to tend to them. To survive, parastic ants infiltrate a colony of closely related ants, where, as long as they keep their numbers relatively low, they and their offspring become the leisure class of the colony.
It’s long been thought that ...
Parasitic infections common in kids in low-resource US communities, study finds
2023-03-03
Most Americans view parasitic infections as a problem of the past or one that only impacts low-income countries. However, new research from Washington University in St. Louis finds evidence that the problem is likely widespread in low-resource communities throughout southern United States where environmental conditions combined with infrastructural neglect and inadequate access to health care create the perfect breeding ground for these infections.
In a small, preliminary study published on March 2 in American Journal of Human Biology, 38% of children sampled from a rural Mississippi Delta community were found to have either ...
Study finds ‘classic triad’ of meningitis symptoms rare in both children and adults
2023-03-03
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
**Note – the press release is available in Spanish and Portuguese, see links below**
Embargo – 2301H UK time Thursday 2 March
Prompt recognition of symptoms and treatment is vital for good outcomes in cases of meningitis. However, new research to be presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April) shows both adults ...
NFL players who experienced concussion symptoms during careers show reduced cognitive performance decades after retirement
2023-03-03
Former professional football players who reported experiencing concussion symptoms during their playing careers were found to perform worse on a battery of cognitive tests than non-players, according to a study led by Mass General Brigham investigators from McLean Hospital and Spaulding Rehabilitation Network. Results of the study are published March 2nd in Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology.[JR1]
Of the more than 350 former National Football League (NFL) players who were studied an average of 29 years after their playing career ended, those who reported experiencing concussion symptoms during their careers ...
Gene editing technique highlighted as possible ‘savior’ for climate change threatened rice crops
2023-03-03
A review of gene editing techniques suggests that the CRISPR/Cas (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/Cas) method could be a possible ‘saviour’ for rice crops threatened by climate change and high food demand.
The study, published in CABI Reviews, highlights that while rice is one of the most consumed cereals worldwide and feeds about three billion people, climate-induced abiotic and biotic stresses have affected the production and quality of rice crops.
Dr Antonio Costa de Oliveira, lead author of the Federal University of Pelotas, Brazil, and a team of fellow ...
Scientists find that people use emojis to hide, as well as show, their feelings
2023-03-03
Have you ever received an unwanted gift and still said ‘thank you’? This choice to hide a negative emotion is a display rule — one of many which define socially appropriate responses to emotions. Although display rules can promote interpersonal harmony, they can also have negative consequences for the person choosing to change how they express emotions. As more social interaction goes online, scientists are investigating how emojis are used to reflect our emotions in different contexts. Are there display rules that apply to emojis, and how do those affect people’s wellbeing?
“As online socializing becomes more prevalent, ...
AI used to predict future flares of ulcerative colitis activity
2023-03-03
Ulcerative colitis assessment could be improved after new research shows that an artificial intelligence model could predict flare-ups and complications after reading biopsies.
In a new paper published in Gastroenterology today (Friday 3 March), researchers supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre have trialled an AI diagnostic tool that can read digitised biopsies taken during colonoscopy.
The Computer-Aided Diagnostic model was able to predict the risk of flare-ups for ulcerative colitis, which is a relapsing-remitting ...
Uncovering the voice of toothed whales: A distinct nasal structure helps produce diverse sounds
2023-03-02
Toothed whales like dolphins, orcas, and sperm whales produce their diverse repertoire of sounds through a distinct structure in the nasal passages, but in a way that is strikingly similar to the way terrestrial animals use the larynx or syrinx for vocalization. In a new study, researchers who employed four different techniques to get to the bottom of how these animals make the sounds they do describe this novel sound production system and show how it enables toothed whales to use different vocal registers for echolocation and communication. To date, vocal registers have been confirmed only in humans and crows. Odontocetes (toothed whales) navigate and hunt ...
Study reveals record-high carbon dioxide emissions from boreal fires in 2021
2023-03-02
Boreal fires, which typically account for 10% of global fire carbon dioxide emissions, contributed 23% in 2021, a new study reports. “Boreal forests could be a time bomb of carbon, and the recent increases in wildfire emissions we see make me worry the clock is ticking,” said study author Steven Davis, who will participate in an embargoed briefing on this study this week. Extreme wildfires – which impact the climate through the carbon dioxide they emit – have become more common. Wildfires in tropical forests ...
Largest-ever genetic analysis of grapevine varieties reveals how glacial cycles shaped grape domestication and the rise of wine
2023-03-02
In the largest ever genetic analysis of grapevine varieties, including samples from previously undocumented specimens in private collections, researchers provide new insights into how, when, and where wine and table grapevines were domesticated, which has been a longstanding question. “This work represents a major international collaborative effort, challenging to do in any circumstances but especially so given that we conducted it during the COVID-19 pandemic and associated lockdowns,” said author Wei Chen, who will also participate in an embargoed briefing ...
Ecological improvement of freshwater ecosystems benefits fish and people
2023-03-02
Biodiversity is declining rapidly. Many conservation actions focus on single species. An alternative approach is to comprehensively improve ecological processes and habitats, thereby supporting entire species communities. This so-called ecosystem-based management is however rarely implemented because it is costly. There is also a lack of evidence that ecosystem-based habitat management is more effective than obvious alternatives, such as releasing animals to enhance stocks.
Important lesson for fish conservation
A research team based in Berlin, in close cooperation with numerous angling clubs organized in ...
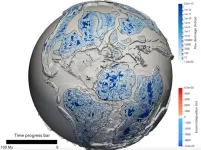
Most detailed geological model reveals Earth’s past 100 million years
2023-03-02
Climate, tectonics and time combine to create powerful forces that craft the face of our planet. Add the gradual sculpting of the Earth’s surface by rivers and what to us seems solid as rock is constantly changing.
However, our understanding of this dynamic process has at best been patchy.
Scientists today have published new research revealing a detailed and dynamic model of the Earth’s surface over the past 100 million years.
Working with scientists in France, University of Sydney geoscientists have published this new model in the prestigious journal Science.
For the first time, it ...
Animals best to supress personalities for group efficiency
2023-03-02
Social animals should limit individuality to conform with the behaviour of the group, a University of Bristol study has found.
Scientists at Bristol’s School of Biological Sciences observed that group safety was improved when animals paid attention to the behaviours of each other.
Their findings, published today in PLoS Computational Biology, reveal that simple social behavioural rules can drive conformity behaviour in groups, eroding consistent behavioural differences shown by individual animals.
Lead author Dr Sean Rands said: “Personality suppression may ...
Possible treatment strategy identified for bone marrow failure syndrome
2023-03-02
Bone marrow is the spongy tissue inside bone responsible for making red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Bone marrow failure syndromes lead to an increased risk of developing dangerous infections, anemia and an increased risk of blood cancers.
Research led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has identified a possible treatment strategy for a rare bone marrow failure syndrome that is named poikiloderma with neutropenia. The work also may have implications for treating other bone marrow failure syndromes with similar underlying dysfunctions.
The research is published March 3 in the journal ...
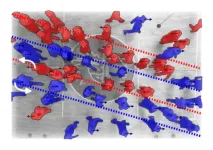
Stick to your lane: Hidden order in chaotic crowds
2023-03-02
Have you ever wondered how pedestrians ‘know’ to fall into lanes when they are moving through a crowd, without the matter being discussed or even given conscious thought?
A new theory developed by mathematicians at the University of Bath in the UK led by Professor Tim Rogers explains this phenomenon, and is able to predict when lanes will be curved as well as straight. The theory can even describe the tilt of a wonky lane when people are in the habit of passing on one side rather than the other (for instance, in a situation where they are often reminded to ‘pass on the right’).
This mathematical ...
Crowdsourced reports can quickly identify an earthquake’s impact
2023-03-02
Within minutes, a statistical model based on a global database of public reports of ground shaking can be used to identify an earthquake as a high- or low-impact event, according to a new study published in The Seismic Record.
High-impact earthquakes, as defined by the study, are those associated with at least one destroyed building, at least 50 damaged buildings, at least two deaths, or any documented financial losses.
The researchers were able to provide impact results for 393 global earthquake events from 2021 within 10 minutes. Their model was developed using more than 1.5 million globally collected felt ...
Ocean surface tipping point could accelerate climate change
2023-03-02
The oceans help to limit global warming by soaking up carbon dioxide emissions. But scientists have discovered that intense warming in the future could lessen that ability, leading to even more severe warming.
The discovery comes from a study led by The University of Texas at Austin in which researchers analyzed a climate simulation configured to a worst-case emissions scenario and found that the oceans’ ability to soak up carbon dioxide (CO2) would peak by 2100, becoming only half as efficient at absorbing the greenhouse gas by 2300.
The decline happens because of the emergence of a surface layer of low-alkalinity water ...
DRI announces space education trainings for Nevada teachers
2023-03-02
DRI is pleased to announce “Space Education Educator Professional Development Training,” available for 80 educators. The training will be conducted in Las Vegas and Reno by four Nevada educators who were selected to attend the NASA Space Exploration Educators Conference in Houston in February. In addition to touring NASA facilities, the conference provided hands-on training in lesson plans and activities, and these educators will use the knowledge they gained to teach Nevada teachers.
“DRI is pleased to offer NASA-approved space education training to ...
Stanford researchers develop a new way to identify bacteria in fluids
2023-03-02
Shine a laser on a drop of blood, mucus, or wastewater, and the light reflecting back can be used to positively identify bacteria in the sample.
“We can find out not just that bacteria are present, but specifically which bacteria are in the sample – E. coli, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Salmonella, anthrax, and more,” said Jennifer Dionne, an associate professor of materials science and engineering and, by courtesy, of radiology at Stanford University. “Every microbe has its own unique optical fingerprint. It’s like the genetic and proteomic code scribbled ...
Integrating humans with AI in structural design
2023-03-02
Modern fabrication tools such as 3D printers can make structural materials in shapes that would have been difficult or impossible using conventional tools. Meanwhile, new generative design systems can take great advantage of this flexibility to create innovative designs for parts of a new building, car, or virtually any other device.
But such “black box” automated systems often fall short of producing designs that are fully optimized for their purpose, such as providing the greatest strength in proportion to weight or minimizing the amount of ...
Foundation for anesthesia education and research establishes endowed NAM fellowship
2023-03-02
CHICAGO – The Foundation for Anesthesia Education and Research (FAER) announced it has established an endowed National Academy of Medicine (NAM) fellowship to provide early-career anesthesiology scholars with the opportunity to experience and participate in committee, workshop, and roundtable activities of NAM and the National Academy of Sciences (NAS).
Offering a robust catalogue of research grants and programs for early-career anesthesiology investigators, FAER – an American Society of Anesthesiologists’ foundation – is always exploring new avenues of support for up-and-coming researchers. The NAM Fellowship Program was recognized as one such ...
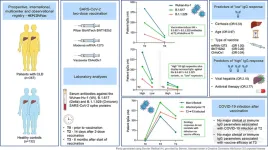
Liver cirrhosis is associated with a lower immune response to COVID-19 vaccines but not with reduced vaccine efficacy
2023-03-02
Amsterdam, March 2, 2023 – The overall responsiveness of patients with chronic liver disease (CLD) to COVID-19 vaccines has been shown to be decreased in patients with cirrhosis. A new prospective study in JHEP Reports, published by Elsevier, now shows that this lower response is observed up to six months following two-dose COVID-19 mRNA vaccination, but it does not reduce vaccine efficacy.
In this prospective study, more than 350 patients with CLD were recruited in clinical centers from Austria, Belgium, Italy, Portugal, Romania, and Spain. Cirrhosis, alongside age and vaccine ...
Human norovirus GII.4 exploits unexpected entry mechanism to cause gastroenteritis
2023-03-02
Human noroviruses are the leading cause of acute gastroenteritis worldwide, a major global health problem for which there are no specific treatments or vaccines. Understanding the first phase of infection – the process the virus follows to invade cells – is a decisive step in the development of effective preventive and therapeutic strategies. A team led by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine is making strides in that direction.
The researchers report in the journal Nature Communications that the globally dominant human norovirus GII.4 strain invades gastrointestinal cells via an unexpected mechanism. The viral strategy involves interactions ...
[1] ... [2069]
[2070]
[2071]
[2072]
[2073]
[2074]
[2075]
[2076]
2077
[2078]
[2079]
[2080]
[2081]
[2082]
[2083]
[2084]
[2085]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.