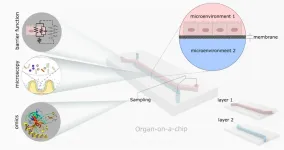
Your gut’s microbiome, on a chip
2023-02-28
WASHINGTON, Feb. 28, 2023 – The gut is one of the most complex organs in the body. Inside, it teems with a diverse microbial population that interacts and cooperates with intestinal cells to digest food and drugs. Disruptions in this microbiome have strong links to a wide spectrum of diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, asthma, and even psychological and behavioral disorders.
Valid models of the gut are therefore immensely useful for understanding its function and associated ailments. In APL Bioengineering, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of California, Berkeley and Lawrence Berkeley National ...
Portable breath-based volatile organic compound monitoring for detection of COVID-19
2023-02-28
About The Study: The findings of this diagnostic study with 167 participants suggest that breath analysis has promise for COVID-19 detection. However, similar to rapid antigen testing, the emergence of new variants poses diagnostic challenges. The results of this study warrant additional evaluation on how to overcome these challenges to use breath analysis to improve the diagnosis and care of patients.
Authors: Xudong Fan, Ph.D., and Kevin R. Ward, M.D., of the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, are the corresponding authors.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Gender, racial, ethnic Inequities among recipients of multiple NIH research project grants
2023-02-28
About The Study: In this study of National Institutes of Health (NIH) investigators from 1991 to 2020, researchers found a growing gap among NIH investigators that created a cohort of highly funded NIH investigators. Importantly, there were persistent gender, ethnic, and racial inequities among this elite class of super principal investigators (investigators receiving three or more research project grants). As the NIH develops critical initiatives and reforms to promote equity among its investigators, consideration of the persistent gender and ethnic and racial gaps in this elite class ...
Study finds 1-in-5 patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease refuse statin therapy
2023-02-28
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, killing someone in the United States every 34 seconds, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A new study by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, conducted the first population-based study on patients’ nonacceptance of statin therapy recommendations.
The study found that in patients at high risk of developing cardiovascular disease, over 20 percent refused to take statin medications. They were particularly ...
Digital twin opens way to effective treatment of inflammatory diseases
2023-02-28
Inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis have complex disease mechanisms that can differ from patient to patient with the same diagnosis. This means that currently available drugs have little effect on many patients. Using so-called digital twins, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have now obtained a deeper understanding of the “off and on” proteins that control these diseases. The study, which is published in Cell Reports Medicine, can lead to more personalised drug therapies.
Many patients with inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, never feel fully healthy despite being on medication. ...
Super-fast insect urination powered by the physics of superpropulsion
2023-02-28
Saad Bhamla was in his backyard when he noticed something he had never seen before: an insect urinating. Although nearly impossible to see, the insect formed an almost perfectly round droplet on its tail and then launched it away so quickly that it seemed to disappear. The tiny insect relieved itself repeatedly for hours.
It’s generally taken for granted that what goes in must come out, so when it comes to fluid dynamics in animals, the research is largely focused on feeding rather than excretion. But Bhamla, an assistant professor in the School ...
Ultrasound device may offer new treatment option for hypertension
2023-02-28
NEW YORK, NY (Feb. 28, 2023)—A device that uses ultrasound to calm overactive nerves in the kidneys may be able to help some people get their blood pressure under control.
A new study led by researchers at Columbia University and Université de Paris, France, has found that the device consistently reduced daytime ambulatory blood pressure by an average of 8.5 points among middle-aged people with hypertension.
Doctors usually prescribe lifestyle changes, such as reducing salt intake or losing weight, and medications to lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Yet about one-third of hypertensive ...
Identifying the inflammatory cells behind chemo brain
2023-02-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Immune cells that keep the brain free of debris but also contribute to inflammation are the likely culprits behind the concentration and memory problems that sometimes follow one type of chemotherapy, a new study in mice suggests.
Researchers previously showed that female mice given paclitaxel, a drug commonly used to treat breast, ovarian and other cancers, developed memory problems that were linked to inflammation in the brain. Mice receiving a placebo did not develop the “mental fog” phenomenon known as chemo brain.
In this study, the team used a technique to delete immune cells called microglia from the brains ...
Targeting wealth managers would cripple Russia's oligarchs
2023-02-28
From astronomical sums of money to opulent superyachts and lavish villas, the assets of the oligarchs providing the political and financial backing for Russian president Vladimir Putin's military ambitions have been publicly and fervently seized by Western nations since Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
Yet, the invasion—now in its second year—remains largely unabated as Russia's moneyed elite challenge sanctions in court or simply dodge them.
But a new study led by Dartmouth College researchers exposes a massive vulnerability for the Kremlin's critical cadre of billionaires—the small, secretive network of financial experts ...
The highlight advances in planetary science over the past 20 years
2023-02-28
With the development of human space technology, planetary exploration has become one of the most important space exploration activities of mankind. As of December 2021, a total of 252 planetary probes have been launched around the world. The missions reveal the deep space to humankind. In the new paper published in the journal Space: Science & Technology, Yixin Sun et al review some advances in planetary science made by these missions in the past years.
1.Research Advances in Terrestrial Planets
1. ...
Galactic explosion offers astrophysicists new insight into the cosmos
2023-02-28
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Using data from the James Webb Space Telescope’s first year of interstellar observation, an international team of researchers was able to serendipitously view an exploding supernova in a faraway spiral galaxy.
The study, published recently in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, provides new infrared measurements of one of the brightest galaxies in our cosmic neighborhood, NGC 1566, also known as the Spanish Dancer. Located about 40 million miles away from Earth, the galaxy’s extremely active center has led it to become especially popular with scientists aiming to learn more about how star-forming nebulae form and evolve.
In this case, ...
Internet treatment program to prevent child sexual abuse launched in several languages
2023-02-28
Following a successful pilot study, an online anonymous treatment program aimed at reducing child sexual abuse by providing treatment to individuals who exhibit sexual urges towards children is being launched across the EU. It is now available in Swedish, German, and Portuguese as well as in an updated English version. The treatment program, which has been developed by researchers and psychologists at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden, will be evaluated within the framework of an international research collaboration funded by the EU.
"Sexual exploitation of children is a major problem within ...
Liquid nitrogen spray could clean up stubborn moon dust
2023-02-28
PULLMAN, Wash – A liquid nitrogen spray developed by Washington State University researchers can remove almost all of the simulated moon dust from a space suit, potentially solving what is a significant challenge for future moon-landing astronauts.
The sprayer removed more than 98% of moon dust simulant in a vacuum environment with minimal damage to spacesuits, performing better than any techniques that have been investigated previously. The researchers report on their work in the journal, Acta Astronautica.
While people have managed ...
Annals HRSA Special Supplement February 2023 Media Tip Sheet
2023-02-28
LEAWOOD, Kansas—Articles appearing in an Annals of Family Medicine special supplement published yesterday contain observations, insights, and ideas for advancing health care equity, promoting interprofessional collaboration, transforming education, and improving primary care practices.
The supplement, titled, “Advancing Primary Care through Research, Education and Practice: Work of the Health Resources and Services Administration–Supported Academic Units for Primary Care Training and Enhancement,” highlights activities of six HRSA-funded academic units for primary care training enhancement. ...
Breathing is going to get tougher
2023-02-28
Not all pollution comes from people. When global temperatures increase by 4 degrees Celsius, harmful plant emissions and dust will also increase by as much as 14 percent, according to new UC Riverside research.
The research does not account for a simultaneous increase in human-made sources of air pollution, which has already been predicted by other studies.
“We are not looking at human emissions of air pollution, because we can change what we emit,” said James Gomez, UCR doctoral student and lead author of the study. “We can ...
Scientists unveil plan to create biocomputers powered by human brain cells
2023-02-28
Artificial intelligence (AI) has long been inspired by the human brain. This approach proved highly successful: AI boasts impressive achievements – from diagnosing medical conditions to composing poetry. Still, the original model continues to outperform machines in many ways. This is why, for example, we can ‘prove our humanity’ with trivial image tests online. What if instead of trying to make AI more brain-like, we went straight to the source?
Scientists across multiple disciplines ...
From anti-antibiotics to extinction therapy: how evolutionary thinking can transform medicine
2023-02-28
The word ‘evolution’ may bring to mind dusty dinosaur bones, but it impacts our health every day. For example, even though antibiotics were invented only a century ago, the evolution of antibiotic resistance is already a major concern. The rise in modern health problems such as obesity can also be traced back to evolutionary principles.
An article published in Frontiers in Science demonstrates how applying an evolutionary perspective to medicine can inspire new ways of preventing and treating disease.
“Evolutionary medicine holds promise to transform our understanding of why we get sick ...
Researchers from the Institute of Botany discovered a new type of coexistence between algae and fungi
2023-02-28
Researchers from the Institute of Botany, Czech Academy of Sciences, described the symbiotic relationship between fungi and algae which science has largely overlooked until now. The coexistence of algae and corticioid basidiomycetes, which are common in temperate forests, has been given a new name: alcobiosis.
Jan Vondrák of the Department of Taxonomy, Institute of Botany, and the first author of the study says “Years ago, during field trips, we were repeatedly puzzled to find a layer of green algae where some of the fungal coatings on wood or bark (so-called corticioid fungi) are disturbed. We discovered that this is a ...
The largest genomic study of rare cancer metastathic pheochromocytoma identifies patients at highest risk of metastasis and those who would respond to immunotherapy
2023-02-28
The new results will help to follow patients with a bad prognosis more closely, and to move towards more personalized treatments.
Mercedes Robledo, co-lead author, has been studying pheochromocytomas since 1996 and leads the CNIO group that has identified 5 of the 22 genes associated with these rare tumors.
The research analyzes an "exceptionally high" number of samples, something very difficult in rare diseases and achieved thanks to the collaboration of centers from countries all over the world.
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor, with an ...
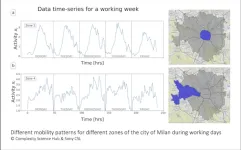
How to predict city traffic
2023-02-28
A new machine learning model can predict traffic activity in different zones of cities. To do so, a Complexity Science Hub researcher used data from a main car-sharing company in Italy as a proxy for overall city traffic. Understanding how different urban zones interact can help avoid traffic jams, for example, and enable targeted responses of policy makers - such as local expansion of public transportation.
Understanding people's mobility patterns will be central to improving urban traffic flow. “As populations grow in urban areas, this knowledge can help policymakers design and implement effective transportation ...
Parental support for LGBTQ youth is important, research shows
2023-02-28
Depression is more widespread among lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, or questioning (LGBTQ) youth than heterosexual, cisgender youth, making parental support more important for these adolescents. A new study released in Child Development by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin looks at parental social support and psychological control in relation to depressive symptoms for LGBTQ youth in the United States. Psychological control attempts to intrude into the psychological and emotional development of the child (e.g., thinking processes, self-expression, emotions, and attachment to parents). Although ...
SUTD to launch south-east Asia’s first O-RAN Open Testing and Integration Centre (OTIC)
2023-02-28
SUTD to Launch South-east Asia’s First O-RAN Open Testing and Integration Centre (OTIC)
Announced at the Mobile World Congress Barcelona (MWC) 2023, Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) will launch a new O-RAN[1] Asia & Pacific Open Testing and Integration Centre (OTIC) in Singapore. As part of Singapore’s S$70 million Future Communications R&D Programme (FCP) supported by Singapore’s Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) and the National Research Foundation, Singapore (NRF), the Asia & Pacific OTIC in Singapore ...
12 exotic bacteria found to passively collect rare earth elements from wastewater
2023-02-28
Rare earth elements (REEs) are a group of 17 chemically similar metals, which got their name because they typically occur at low concentrations (between 0.5 and 67 parts per million) within the Earth’s crust. Because they are indispensable in modern technology such as light emitting diodes, mobile phones, electromotors, wind turbines, hard disks, cameras, magnets, and low-energy lightbulbs, the demand for them has increased steadily over the past few decades, and is predicted to rise further by 2030.
As ...
Will future computers run on human brain cells?
2023-02-28
A “biocomputer” powered by human brain cells could be developed within our lifetime, according to Johns Hopkins University researchers who expect such technology to exponentially expand the capabilities of modern computing and create novel fields of study.
The team outlines their plan for “organoid intelligence” today in the journal Frontiers in Science.
“Computing and artificial intelligence have been driving the technology revolution but they are reaching a ceiling,” said Thomas Hartung, a professor of environmental health sciences at ...
Study reveals improvements in workplace support and leadership training will improve the mental health and potentially reduce burnout in healthcare professionals
2023-02-28
Amongst healthcare professionals, the feeling of being supported in the workplace can protect them against adverse mental health and burnout, according to a new study published in CMAJ Open by researchers at Queen Mary University of London and medical staff at various hospitals across the UK.
CoPE-HCP study was designed, during the early part of COVID-19 pandemic, when there was great concern for the mental health of healthcare professionals with no scientifically-proven mitigating strategies to reduce that impact. Funded by Barts Charity, this new longitudinal study found that feeling unsupported ...
[1] ... [2076]
[2077]
[2078]
[2079]
[2080]
[2081]
[2082]
[2083]
2084
[2085]
[2086]
[2087]
[2088]
[2089]
[2090]
[2091]
[2092]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.