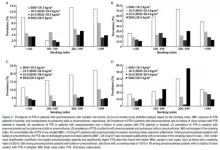
New study could help pinpoint hidden helium gas fields – and avert a global supply crisis
2023-03-01
Helium – essential for many medical and industrial processes – is in critically short supply worldwide. Production is also associated with significant carbon emissions, contributing to climate change.
This study provides a new concept in gas field formation to explain why, in rare places, helium accumulates naturally in high concentrations just beneath the Earth’s surface.
The findings could help locate new reservoirs of carbon-free helium – and potentially also hydrogen.
Research led by the University of Oxford could help overturn the current supply crisis of helium, ...
Unique alcohol avoidance program is associated with lower death rates
2023-03-01
A statewide alcohol-monitoring program that requires people arrested for drunk driving and other alcohol-involved offenses to be tested frequently for alcohol use can reduce the likelihood that participants die for several years after their involvement with the program, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Analyzing results from South Dakota’s 24/7 Sobriety Program, researchers found that those arrested for drunk driving who participated in 24/7 Sobriety had on the order of a 50% lower risk of dying during the study period compared to those arrested for drunk driving who did not participate in the program..
The results are published in the latest edition of the ...
Outcomes of women undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery
2023-03-01
About The Study: The results of this study of more than 1.2 million patients indicate that women remain at significantly higher risk for adverse outcomes following coronary artery bypass grafting and no significant improvement has been seen over the course of the last decade. Further investigation into the determinants of operative outcomes in women is urgently needed.
Authors: Mario Gaudino, M.D., Ph.D., M.S.C.E., of Weill Cornell Medicine in New York, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2022.8156)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Reexamining time from breast cancer diagnosis to surgery
2023-03-01
About The Study: This case series study using the data of 373,000 patients from the National Cancer Database found that time from breast cancer diagnosis to surgery of greater than eight weeks was associated with worse overall survival. Time to surgery of greater than eight weeks may partly be associated with disadvantageous social determinants of health.
Authors: Heather B. Neuman, M.D., of the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health in Madison, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2022.8388)
Editor’s ...
Oldest human genome from southern Spain
2023-03-01
An international team of researchers has analysed ancient human DNA from several archaeological sites in Andalucía in southern Spain. The study reports on the oldest genome to date from Cueva del Malalmuerzo in southern Spain, as well as the 7,000 to 5,000-year-old genomes of early farmers from other well-known sites, such as Cueva de Ardales.
The Iberian Peninsula plays an important role in the reconstruction of human population history. As a geographic cul-de-sac in the southwest of Europe, it is on one hand considered a refuge during the last Ice Age with its drastic temperature fluctuations. On the other hand, it may have been one of the starting points for the recolonisation ...
The counting of nine billion trees could help manage climate credits and nature restoration
2023-03-01
Researchers from the University of Copenhagen and NASA have developed a method that has now mapped several billion trees and their carbon uptake in Africa’s Sahel region. In the future, the method could be used to monitor whether climate credit purchases have a positive effect on the number of trees and whether nature restoration is working.
The purchase of indulgences for CO2 emissions is gaining steam among global corporations. Carbon offset credits allow companies to emit a given amount of CO2 in exchange for the greenhouse gas being neutralized elsewhere, in the form of trees planted or left unfelled.
But with billions upon billions of trees across the planet, keeping track ...
New study unveils epigenetic ‘traffic lights’ controlling stop and go for gene activity
2023-03-01
A major new study in the journal Nature reveals a ‘traffic light’ mechanism controlling genetic activity within cells – a system which could potentially be targeted by cancer drugs already in development.
The research describes how ‘epigenetic’ changes to the structure of DNA can act as a stop-go signal in determining whether a gene should be read.
Unlike our genetic make-up, which is well understood, the world of epigenetics is still largely unexplored and referred to as the ‘dark matter’ of the genome.
But the new findings answer a fundamental and longstanding question – how epigenetic proteins regulate the ...
New NASA DART data prove viability of asteroid deflection as planetary defense strategy
2023-03-01
NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART) was Earth’s first attempt at launching a spacecraft to intentionally collide with and deflect an asteroid as a planetary defense technique. On September 26, 2022, the DART spacecraft collided with a small asteroid moon called Dimorphos, which orbits a larger asteroid called Didymos. Neither asteroid posed a threat to Earth, but they represented similar celestial bodies that could one day approach and endanger the planet.
In four papers published in the journal Nature on ...
Insilico Medicine’s Generative AI Pioneer Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD at Lab of the Future March 9
2023-03-01
Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, a pioneer of generative artificial intelligence (AI) for biology and chemistry, and founder and CEO of Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”) will present at the Lab of the Future Congress at the Renaissance Boston Waterfront Hotel on March 9, 2pm ET.
In a talk titled “Novel Target Discovery and Molecular Design Using AI,” Dr. Zhavoronkov will share the breakthroughs and discoveries that have made Insilico Medicine a leader in generative AI drug discovery. This includes ...
Review of studies finds disparity in presumptive chlamydia and gonorrhea treatment rates despite CDC guidelines
2023-03-01
INDIANAPOLIS – A Regenstrief Institute-led review of studies on proactive health services for chlamydia and gonorrhea has found that rates of presumptive treatment -- antibiotics prior to laboratory test confirmation -- varies widely.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends presumptive treatment of individuals with symptoms of or known contact with these infections to decrease likelihood of secondary infections as well as poor outcomes.
The healthcare settings of all 18 of the studies reviewed were within the U.S. and patients were age 14 and older. Presumptive treatment rates were found to ...
Chinese Medical Journal study identifies major risk factors of pulmonary tuberculosis in patients with pneumoconiosis in China
2023-03-01
Pneumoconiosis comprises a group of heterogeneous lung diseases resulting from the inhalation of mineral dust. It is an occupational hazard with significant economic and social implications. Notably, patients with pneumoconiosis have an elevated risk of contracting pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB). Unfortunately, pneumoconiosis has a strong presence in China. However, extensive population-based studies on the prevalence of PTB in patients with pneumoconiosis have not been conducted in China since almost three decades.
To bridge this gap, a team of ...
National Comprehensive Cancer Network updates annual conference with new in-person venue, hybrid format, expert-led sessions, highlighted research perspectives, and small-group conversations
2023-03-01
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [March 1, 2023] — The National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) today announced the NCCN 2023 Annual Conference will debut a new hybrid format, including in-person events at a new venue. This marks the first time in three years that this premier oncology meeting will be held in-person, and the first-ever time at the Orlando World Center Marriott, starting on March 31.
“We’ve heard from many people who learn better by being in the ‘room where it happens,’” said Robert W. ...
Moose can play a big role in global warming
2023-03-01
One of the biggest potential single sources of carbon emissions from wooded parts of Norway has four legs, weighs as much as 400-550 kg and has antlers.
That’s right — moose can reduce carbon storage in clearcut sites equivalent to as much as 60 per cent of the annual fossil fuel carbon emissions from a region, a new study shows.
“Moose are an ecosystem engineer in the forest ecosystem, and strongly impact everything from the species composition and nutrient availability in the forest,” said Gunnar Austrheim, an ecologist at the NTNU University Museum who was one of the study’s co-authors. “A grown animal can eat 50 kilograms ...
America on the move: How urban travel has changed over a decade
2023-03-01
A new Florida Atlantic University study on America’s urban travel trends shows important variations in travel behaviors across income, home ownership, ethnicity, gender, age, and life-cycle stages. The sixth in a series of studies compared changes in travel modes, trip frequency, trip distance and vehicle ownership among a range of socioeconomic groups using nationwide travel survey data since 1977.
The most notable trend, published in the journal Transportation Research Part D, reveals that although private automobiles continue to be the dominant travel mode in American cities, the share of car trips has slightly and steadily decreased ...
JAMA Network names new editor in chief of JAMA Internal Medicine
2023-03-01
Chicago, March 1, 2023 — Sharon K. Inouye, M.D., M.P.H., Professor of Medicine at Harvard Medical School and the Milton and Shirley F. Levy Family Chair and Director of the Aging Brain Center, Marcus Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife has been named the editor in chief of JAMA Internal Medicine.
An internationally recognized leader in internal medicine, geriatrics, and aging research, Dr. Inouye’s research focuses on delirium and functional decline in hospitalized older patients. She is currently the overall principal investigator of the Successful Aging after ...
Chemotherapy alters immune cell landscape in pancreatic cancer
2023-03-01
Chemotherapy affects the ability of a patient’s immune system to attack pancreatic tumors, a new study shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, the work revolves around the immune system, which includes T cells designed to attack foreign organisms like viruses. To spare normal cells, the system uses “checkpoint” molecules like PD1 on T cell surfaces to turn off their attack when they receive the right signals. The body also recognizes tumors as abnormal, but cancer cells ...
Dutch healthcare system isn't prepared for pregnant transgender men
2023-03-01
Transgender men can, and often wish to, become pregnant. However, they do need extra guidance and care providers often lack the necessary knowledge and skills. Amsterdam UMC is the first to conduct qualitative research into the experiences of Dutch transgender people with maternity care. This research is now avaliable as a pre-print in Midwifery.
Transgender men often undergo medical procedures to adjust their bodies to their male gender identity. These medical interventions can affect fertility. Some transgender men therefore choose not to undergo these treatments, postpone them or, even, to temporarily stop them. ...
Study shows those with a higher omega-3 index are more protected from severe COVID infection
2023-03-01
A study just published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (AJCN) explored the role of omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, and whether they might be protective against contracting and/or suffering adverse outcomes of COVID-19 infection.
The study compared the risk for three COVID-19 outcomes: 1-testing positive, 2-hospitalization, and 3-death as a function of baseline plasma DHA levels.
DHA levels (% of total fatty acids) were measured by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy but were converted to Omega-3 Index (red blood ...
Degrading modified proteins could treat Alzheimer’s, other ‘undruggable’ diseases
2023-03-01
Certain diseases, including Alzheimer’s, are currently considered “undruggable” because traditional small molecule drugs can’t interfere with the proteins responsible for the illnesses. But a new technique that specifically targets and breaks apart certain proteins — rather than just interfering with them — may offer a pathway toward treatment. Researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have, for the first time, designed a compound that targets and breaks down a posttranslationally modified protein closely associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Researchers have been exploring targeted protein degradation (TPD) as a way to get at ...
Toilet paper is an unexpected source of PFAS in wastewater, study says
2023-03-01
Wastewater can provide clues about a community’s infectious disease status, and even its prescription and illicit drug use. But looking at sewage also provides information on persistent and potentially harmful compounds, such as per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), that get released into the environment. Now, researchers in ACS’ Environmental Science & Technology Letters report an unexpected source of these substances in wastewater systems — toilet paper.
PFAS have been detected in many personal care products, such as cosmetics and cleansers, that people use every day and then wash down ...
Glacier National Park could provide climate haven for Canada Lynx
2023-03-01
PULLMAN, Wash – Glacier National Park is home to around 50 Canada lynx, more than expected, surprising scientists who recently conducted the first parkwide occupancy survey for the North American cat.
The Washington State University-led survey reveals the iconic predator resides across most of Glacier’s 1,600 square-mile landscape, although at lower densities than in the core of its range further north.
“The population in the park is still substantial and exceeded our expectations,” said Dan Thornton, WSU wildlife ecologist ...
Fraunhofer USA awarded patent for detecting air leakage in buildings using communicating thermostats
2023-03-01
The United States Patent and Trademark Office has awarded Fraunhofer USA with a patent for algorithms that detect and quantify air leakage from single-family homes using data from commercially available communicating, thermostats.
Outdoor air can infiltrate homes through many pathways, including windows and doors, poorly sealed connections between exterior walls and basements and attics, and unsealed wall, floor, and ceiling penetrations in occupied spaces. Prior field studies have found that most homes have appreciable air leakage, which accounts for approximately a quarter of space conditioning energy consumption. Not only can air leakage significantly increase home energy consumption, ...
New book warns of human extinction from climate change
2023-03-01
A new book, The Climate Pandemic: How Climate Disruption Threatens Human Survival, concludes that humans will not survive the unrelenting onslaught of climate disruption. The e-book is available free on Amazon March 1-5.
“As horrific as the COVID-19 pandemic has been, its effects pale in comparison to the coming catastrophe from climate disruption,” wrote author and veteran science writer Dennis Meredith. “In fact, the climate pandemic will steadily worsen, even bringing our species to extinction, unless we launch a global revolution to abandon our carbon-dependent energy system.
“Given the evidence in this book, I see only a vanishingly small possibility of ...
Book tackles myths about science of menstruation
2023-03-01
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new book from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign anthropology professor Kathryn Clancy takes an unflinching look at the many ways humans have struggled – and often failed – to understand one of the greatest mysteries of human biology: menstruation.
In “Period: The Real Story of Menstruation,” Clancy first focuses on the myriad ways human societies, their leaders, scientists and health practitioners have gotten it wrong – from myths and taboos about the purpose and health effects ...
Researchers uncover how gene that increases risk of genetic heart disease works, paving way for new treatments
2023-03-01
Researchers have discovered how a gene that increases the risk of developing genetic heart disease functions, paving the way for new treatments.
The study, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute and published in Nature Cardiovascular Research, has revealed a new pathway for how children and adults develop cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that affect the heart’s ability to pump blood around the body.
Heart disease is the leading cause of death worldwide. Patients with cardiomyopathy, a form of heart disease ...
[1] ... [2073]
[2074]
[2075]
[2076]
[2077]
[2078]
[2079]
[2080]
2081
[2082]
[2083]
[2084]
[2085]
[2086]
[2087]
[2088]
[2089]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.