Existing chest scans offer new opportunities for predicting surgical risks
2023-03-02
Instead of special heart scans, physicians can use images of the chest captured months earlier, and for other reasons, to estimate patients’ risk of heart attack or death during several kinds of major surgeries, a new study shows.
Researchers at NYU Grossman School of Medicine analyzed existing computed tomography (CT) scans to estimate levels of hardened (calcified) fatty plaque deposits in the heart’s three largest blood vessels. They found that patients with greater buildup of this plaque had higher chances of developing serious health issues following surgery.
Major surgeries, which usually ...
Using radar to predict Alzheimer’s disease and fall accidents
2023-03-02
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden have developed a method for predicting fall accidents and cognitive illnesses such as Alzheimer’s disease by reading a person’s walking pattern with the aid of a radar sensor. The small sensor can be attached to furniture, walls and ceilings, both in the home and in a healthcare setting.
“Our method is both precise and easy to use. It can help healthcare staff to carry out a more reliable risk analysis and tailor interventions to achieve a significant effect early on. Hopefully it can ...
2023 GOLD Report proposes a new definition of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
2023-03-02
New York, NY – March 02, 2023 – Despite COPD’s pervasiveness, it is generally assumed that the main instigator in its development is tobacco smoking. The 2023 Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease or GOLD report is proposing a new definition of COPD, one that acknowledges the key pathogenic role of tobacco smoking but accounts for other factors that also contribute to COPD. The report is now available online in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
The GOLD 2023 report ...
Physicians should screen youth for cyberbullying, social media use
2023-03-02
Most adolescents and young adults have experienced bullying in some form, with about one-third of them experiencing cyberbullying, contributing to mental health concerns. Cyberbullying involves electronic communication such as texts, emails, online videos and social media, which has become increasingly problematic over the last few decades. Several reasons include the anonymity it allows, the fact that it is not as easily monitored, and that adolescents and young adults have easier access to devices.
In an article published in the journal Primary Care Clinical ...
Skin samples reveal where southern right whales feed
2023-03-02
Scientists have analysed chemicals in the skin of southern right whales to give new insights into the animals’ distribution, as well as long-term environmental changes in the Southern Ocean.
The research was published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). [https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2214035120]
The scientists from the US, Australia, Argentina, Brazil, South Africa, Europe, UK, and Aotearoa New Zealand measured the amounts of various carbon and nitrogen isotopes ...
Socioeconomic factors play a role in detection, transmission and treatment of HIV
2023-03-02
Those living in unstable housing conditions, such as hostels or informal dwellings and those who had not completed post-secondary studies were more likely to contract HIV in South Africa, according to a new study from McGill University. A team of researchers based at the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) has reported survey results that show socioeconomic factors play a critical role in the detection, transmission, and treatment of HIV in regions of South Africa. “We found that factors such as education and dwelling situations still impact ...
U.S. birds’ Eastern, Western behavior patterns are polar opposites
2023-03-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio – There is much more to avian biodiversity in the United States than the number of different species living in a given region or community, but the diversity of birds’ ecosystem contributions – assessed through measures of their diet, body structure and foraging methods – are much tougher to study.
And with hundreds of species migrating south for the winter and north for summer breeding, birds’ ecosystem function patterns change over space and time – creating a serious analytical challenge.
But two scientists from The Ohio State University have ...
Adaptability to climate change and resilience
2023-03-02
To fill the two Chairholders positions, ÉTS is seeking researchers who are experts in the field of buildings and infrastructure and whose work focuses on resilience capacity and adaptability to climate change.
Canada Research Chair (Tier 1)
This Research Chair will receive CAN$ 200,000 in funding per year over a period of seven years, and is open to researchers whose achievements have had a significant impact on their field of expertise.
Candidates who wish to submit an application must be capable of proposing an original, innovative research program related to the adaptability of infrastructure and buildings ...
Small differences in mom’s behavior may show up in child’s epigenome
2023-03-02
PULLMAN, Wash. – Adding evidence to the importance of early development, a new study links neutral maternal behavior toward infants with an epigenetic change in children related to stress response.
Epigenetics are molecular processes independent of DNA that influence gene behavior. In this study, researchers found that neutral or awkward behavior of mothers with their babies at 12 months correlated with an epigenetic change called methylation, or the addition of methane and carbon molecules, on a gene called NR3C1 when the children were 7 years ...
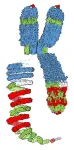
Researchers provide proof of the helical coiling of condensed chromosomes
2023-03-02
The iconic X-shaped organization of metaphase chromosomes is frequently presented in textbooks and other media. The drawings explain in captivating manner that the majority of genetic information is stored in chromosomes, which transmit it to the next generation. “These presentations suggest that the chromosome ultrastructure is well-understood. However, this is not the case”, says Dr. Veit Schubert from IPK’s research group “Chromosome structure and function”.
Several models have been proposed to describe the higher-order structure of metaphase chromosomes based on data obtained using a range of molecular and microscopy methods. These models ...
Importance of early-life factors identified in new lung health study
2023-03-02
New insights into the importance of early-life factors on lung health have been unveiled in the most comprehensive study of its kind, led by the Universities of Essex and Bristol.
The researchers hope the findings, published today in the European Respiratory Journal, will pave the way to developing predictive tools for respiratory health and reduce healthcare inequality by targeting early-life interventions for people at higher risk.
The study analysed data collected from 7,545 participants of Bristol’s Children of the 90s ...
Academic freedom deteriorates in 22 countries
2023-03-02
Today, the Academic Freedom Index (AFI) project presents its Update 2023, providing an overview of the state of academic freedom in 179 countries. The decline in academic freedom affects over 50% of the world's population, approximately 4 billion people. The Index identifies 22 countries where universities and scholars experience significantly less academic freedom today than they did ten years ago. This includes democratic systems as well as autocratic countries. During the same period, academic freedom levels have only ...
Study finds political campaigns may change the choices of voters – but not their policy views
2023-03-02
A new paper in The Quarterly Journal of Economics, published by Oxford University Press, measures the overall impact of electoral campaigns and finds that televised debates have little effect on the formation of voter choice. Information received from other sources such as the media, political activists, and other citizens, matters more.
Researchers and pundits have long debated the impact of political campaigns. One view is that the weeks immediately preceding elections are a crucial period. Campaign information can help voters assess the performance of incumbent politicians, compare the qualities and positions of all candidates, and perhaps even reconsider their policy preferences. But ...
Older Black men are likelier to die after surgery than others, particularly following elective procedures, new UCLA research suggests
2023-03-02
Embargoed for Use Until:
3:30 p.m. PT/6:30 p.m. ET on Wednesday, March 1, 2023
Older Black men are likelier to die after surgery than others, particularly following elective procedures, new UCLA research suggests
Older Black men have a higher chance of dying within 30 days of surgery than do Black women and white men and women – with their odds of death 50% higher after elective surgery compared with white men.
The researchers suspect that the “especially high cumulative amounts of stress and allostatic load” that Black men face the U.S. may significantly contribute to declines in their physical health, they write.
“While ...
Black men more likely to die after surgery than White men, or women of either race
2023-03-02
Black men have a higher death rate within 30 days of surgery compared with any other subgroup of race and sex, finds a study of adults in the United States published in The BMJ.
This inequality in death rate was mainly observed for elective, or planned, surgeries, where the death rate for Black men was 50% higher than that of White men.
The researchers say further research is needed to understand better the “factors contributing to this higher mortality rate among Black men after elective surgery.”
In previous studies, racial inequities in surgical care and outcomes, including a higher death rate following surgery for Black patients, have been well documented.
However, ...
US government catalyzed and substantially invested in mRNA covid-19 vaccine development over decades
2023-03-02
In the 35 years before the covid-19 pandemic, the US government invested at least $337 million into critical research that led to the mRNA covid-19 vaccines, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
The US government also paid $31.6 billion during the pandemic to support vaccine research, production, and to purchase vaccines for all Americans and for global donation.
These public investments saved millions of lives - and mRNA vaccine technology also has the potential to address future pandemics and treat other diseases. But the researchers ...
Public investment in critical research contributed to the success of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines
2023-03-02
Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech have recently announced plans to increase the price of their respective mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, thrusting them into the spotlight of debates around drug price hikes. A new study, led by investigators from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system, analyzed the role of public funding in the development of mRNA vaccines. In a systematic assessment, the team found that over the last 35 years, three federal agencies—the National Institutes of Health, the Department ...
Only two in five British businesses have introduced support to help staff with the rising cost of living as many see operating costs rise
2023-03-02
New research from the Work Foundation at Lancaster University reveals that while two thirds of senior business leaders (66%) agree that employers have a ‘substantial role’ to play in supporting staff through the rising cost of living, only 40% have introduced new support measures since the start of 2022.
At the same time, four in ten business leaders (41%) also report increases in production costs in their organisation. Pressures that are likely to increase, the Work Foundation ...
Fishing for proteins: Scientists use new optical tweezer technology to study DNA repair
2023-03-02
Tucked away in a small, dark room at UPMC Hillman Cancer Center, Brittani Schnable is on a fishing expedition.
Wielding a joystick similar to those used by video gamers, she casts microscopic beads into an ocean of molecules, pushing and pulling the beads apart until they eventually catch a strand of DNA. After a few taps of the keyboard, a lightshow begins. A burst of colors flashes across the black screen like fireworks exploding in the night sky.
Although these colors seem random at first, a pattern starts to emerge. Lines of blue and red light streak across the screen: A DNA repair protein has bound to the site of damage.
Schnable, a Ph.D. student in Dr. Bennett ...
Can’t exercise a particular muscle? Strengthening the opposite side of your body can stop it wasting away
2023-03-02
Loss of muscle strength can be one of the most damaging outcomes when someone is unable to move a part of their body for a long period of time.
But a new Edith Cowan University (ECU) study may have found a way to offset or even protect against this — and it doesn’t even involve the affected body part at all.
Injury or illness may see a part of the body incapacitated for weeks or even months, causing unused muscles to weaken and lose their mass and strength, which can have ...
Physical activity can help mental health in pre-teen years
2023-03-02
Regular physical activity can improve adolescents’ mental health and help with behavioural difficulties, research suggests.
Engaging in regular moderate to vigorous physical activity at age 11 was associated with better mental health between the ages of 11 and 13, the study found.
Physical activity was also associated with reduced hyperactivity and behavioural problems, such as loss of temper, fighting with other children, lying, and stealing, in young people.
Researchers from the Universities of Edinburgh, Strathclyde, Bristol, and Georgia in the United States explored data from the Children of the 90s study (also known as the Avon Longitudinal Study of ...
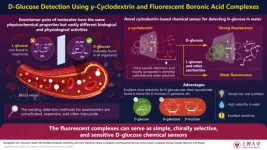
New fluorescent chiral-selective receptor system represents a breakthrough in molecular detection with potential for applications in diabetes management
2023-03-02
Diabetes mellitus, simply called diabetes, is a metabolic disorder characterized by the presence of abnormally high concentrations of glucose in blood. Existing methods for the diagnosis of diabetes rely on traditional techniques of detecting glucose in blood serum samples—a process that is typically tedious and expensive.
Molecular recognition is the science of accurately detecting specific compounds by exploiting their binding properties. Here, a receptor molecule–a kind of sensor–selectively binds to a target molecule. This process triggers some reaction, say, a change ...
Sleep too much or too little and you might get sick more, scientists find
2023-03-02
A good night’s sleep can solve all sorts of problems – but scientists have now discovered new evidence that sleeping well may make you less vulnerable to infection. Scientists at the University of Bergen recruited medical students working in doctors’ surgeries to hand out short questionnaires to patients, asking about sleep quality and recent infections. They found that patients who reported sleeping too little or too much were more likely also to report a recent infection, and patients ...
Study suggests EHR-focused interventions can significantly reduce unnecessary urine cultures among hospital patients
2023-03-02
Study Suggests EHR-Focused Interventions Can Significantly Reduce Unnecessary Urine Cultures Among Hospital Patients
Initiative highlighted in AJIC provides model for resource-limited institutions to decrease overdiagnosis and overtreatment of asymptomatic bacterial infections
Arlington, Va., March 2, 2023 – Physicians in the largest safety-net hospital system in the United States used two electronic health record (EHR)-focused interventions to significantly reduce inappropriate urine cultures among hospitalized patients. Findings from their study, published in the ...
Edible electronics: How a seaweed second skin could transform health and fitness sensor tech
2023-03-02
Scientists at the University of Sussex have successfully trialed new biodegradable health sensors that could change the way we experience personal healthcare and fitness monitoring technology.
The team at Sussex have developed the new health sensors – such as those worn by runners or patients to monitor heart rate and temperature – using natural elements like rock salt, water and seaweed, combined with graphene. Because they are solely made with ingredients found in nature, the sensors are fully biodegradable, making them more environmentally friendly than commonly used rubber and plastic-based alternatives. Their natural ...
[1] ... [2071]
[2072]
[2073]
[2074]
[2075]
[2076]
[2077]
[2078]
2079
[2080]
[2081]
[2082]
[2083]
[2084]
[2085]
[2086]
[2087]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.