Whistleblowers losing faith in media impact
2023-03-07
The whistleblowers who once trusted journalism are losing faith in the institution.
A new study from the University of Georgia found that many whistleblowers who reached out to journalists in the past no longer believe media has the same ability to motivate change, and they feel let down by a system they once trusted.
“If you don’t believe that an outlet or journalist can carry you across the finish line—meaning can affect change, attract enough attention and attract the attention of the right people—then you’re losing faith,” said Karin Assmann, study lead and assistant professor in UGA’s Grady College of Journalism ...
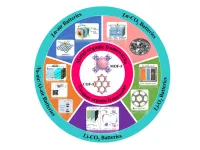
STEP Demo pilot plant achieves supercritical CO2 fluid conditions
2023-03-07
SAN ANTONIO — March 7, 2023 —The Supercritical Transformational Electric Power (STEP) Demo pilot plant, a $155 million, 10-megawatt supercritical carbon dioxide (sCO2) test facility at Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) in San Antonio, developed in partnership with GTI Energy and GE Research and sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy, has successfully achieved its first operation with CO2 at supercritical fluid conditions in its compressor section. This accomplishment represents significant progress toward ...
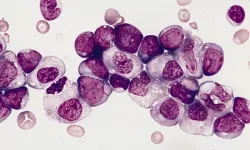
Splicing deregulation detected and targeted in type of childhood leukemia
2023-03-07
Pediatric acute myeloid leukemia or pAML is a childhood blood cancer, one that has proved confounding to clinicians and researchers, with a high relapse rate and relatively few identified genetic mutations (compared to the adult version) that might explain its cause.
In a new study, published in the March 7, 2023 issue of Cell Reports, an international team led by scientists and physicians at University of California San Diego School of Medicine deployed an array of analytical and gene-splicing tools to parse more deeply the mysteries of mutation in pAML.
“Compared to adult AML, pediatric AML is associated with relatively ...
Synchronizing to a beat predicts how well you get ‘in sync’ with others
2023-03-07
How well you synchronize to a simple beat predicts how well you synchronize with another mind, according to a new Dartmouth study published in Scientific Reports.
Previous work has demonstrated that the pupil dilation patterns of speakers and listeners synchronize spontaneously, illustrating shared attention. The team set out to understand how the tendency to synchronize in this way may vary at the individual level and generalize across contexts, as it has been widely debated whether one form of synchrony bears any relationship to another.
“We were ...
How high altitude changes your body’s metabolism
2023-03-07
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—March 7, 2023—Compared to those of us who live at sea level, the 2 million people worldwide who live above 4,500 meters (or 14,764 feet) of elevation—about the height of Mount Rainier, Mount Whitney, and many Colorado and Alaska peaks—have lower rates of metabolic diseases such as diabetes, coronary artery disease, hypercholesterolemia, and obesity.
Now, researchers at Gladstone Institutes have shed light on this phenomenon. They showed how chronically low oxygen levels, such as those experienced at high elevation, rewire how mice burn sugars ...
Endocrine Society elects Newell-Price as 2024-2025 President
2023-03-07
Endocrine Society members elected John Newell-Price, M.D., Ph.D., F.R.C.P., as its 2024-2025 President. He will serve as President-Elect for a year beginning in June 2023 before becoming President in June 2024.
Newell-Price is Professor of Endocrinology at the University of Sheffield in Sheffield, United Kingdom. He also is head of the endocrinology service at the Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and of the European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society at the hospital.
Newell-Price’s clinical expertise ...
Genetic and socioeconomic factors interact to affect risk of type 2 diabetes and obesity
2023-03-07
BOSTON – New research led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), indicates that socioeconomic and genetic factors likely interact in an additive way to affect people’s risks of developing obesity and type 2 diabetes. The findings, which are published in Diabetes Care, suggest that interventions to improve socioeconomic deprivation may decrease metabolic diseases at the individual and community levels, especially among people with concomitant high genetic risk.
Genetic and socioeconomic factors—one intrinsic and unmodifiable and ...
Heart tissue heads to space to aid research on aging and impact of long spaceflights
2023-03-07
Note: Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers Deok-Ho Kim and Devin Mair will participate in a NASA teleconference for journalists on Tuesday, March 14, at 11 a.m. ET.
Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers are collaborating with NASA to send human heart “tissue-on-a-chip” specimens into space as early as March. The project is designed to monitor the tissue for changes in heart muscle cells’ mitochondria (their power supply) and ability to contract in low-gravity conditions.
The tissue samples will ...
Heart toggles between maintenance and energy-boost mode using ribosomes
2023-03-07
Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona have discovered a mechanism involving ribosomes which helps the heart toggle between a ‘regular maintenance mode’ for day-to-day function and an ‘energy-boost mode’ which aids recovery for high-demand situations including heart attacks. The findings are published in a ‘Breakthrough Article’ in the journal Nucleic Acids Research, a distinction awarded to studies that answer long-standing questions in the field.
Ribosomes are the molecular factories that manufacture proteins in all living cells. Historically, they have been ...
NYU Langone orthopedic surgeons present latest clinical findings & research at AAOS 2023
2023-03-07
Experts from NYU Langone Orthopedics will present their latest clinical findings and research discoveries at the 2023 American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Annual Meeting, March 7 to 11, in Las Vegas.
Topics being presented include the following:
minimally invasive in-office needle arthroscopy to diagnosis and treat a common cause of chronic ankle pain
improving postoperative pain with intraoperative injections during hip fracture surgery
using an additional dose of dexamethasone to reduce postoperative opioid use for pain after knee replacement
“Our clinical teams continue to innovate and investigate how we can provide our patients with the best possible outcomes. ...
Teacher supports, guidance for elementary social studies education vary widely across U.S., report finds
2023-03-07
A new RAND Corporation report finds that the basic infrastructure to support elementary (grades K-5) social studies instruction – academic standards, accountability requirements, assessment programs – is inadequate in many states. Even where state-level infrastructure to guide teachers’ instruction is in place, its comprehensiveness and quality vary greatly.
Support and guidance at the district and school level to underpin social studies instruction are also lacking compared to other core academic ...
Electric vehicle batteries could get big boost with new polymer coating
2023-03-07
Scientists at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have developed a conductive polymer coating – called HOS-PFM – that could enable longer lasting, more powerful lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles.
“The advance opens up a new approach to developing EV batteries that are more affordable and easy to manufacture,“ said Gao Liu, a senior scientist in Berkeley Lab’s Energy Technologies Area.
The HOS-PFM coating conducts both electrons and ions at the same time. This ensures battery stability and high charge/discharge rates while enhancing battery life. The coating ...
Researchers identify key protein that promotes DNA repair and prevent cancer
2023-03-07
A research team, affiliated with UNIST has unveiled a key factor involved in the DNA damage response (DDR), homologous recombination (HR) and DNA interstrand crosslink (ICL) repair. According to the research team, their findings are expected to establish an effective control environment for chromosome instability (CIN), a major factor in cancer evolution, and further help combat malignant tumors .
Published in the January 2023 issue of Nucleic Acids Research, this breakthrough ...
FDA mandate to limit acetaminophen in acetaminophen-opioid medications is associated with reduced serious liver injury
2023-03-07
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – A United States Food and Drug Administration mandate to limit the dosage of acetaminophen in pills that combine acetaminophen and opioid medications is significantly associated with subsequent reductions in serious liver injury, researchers report in the medical journal JAMA. The federal mandate was announced in 2011 and implemented in 2014.
“The FDA mandate that limits acetaminophen dosage to 325 milligrams per tablet in combination acetaminophen-opioid medications was associated with a significant and persistent decline in the yearly rate of hospitalizations and proportion per year of acute liver failure ...
Elegantly modeling earth’s abrupt glacial transitions
2023-03-07
WASHINGTON, March 7, 2023 – Proxy data – indirect records of the Earth’s climate found in unlikely places like coral, pollen, trees, and sediments – show interesting oscillations approximately every 100,000 years starting about 1 million years ago. Strong changes in global ice volume, sea level, carbon dioxide concentration, and surface temperature indicate cycles of a long, slow transition to a glacial period and an abrupt switch to a warm and short interglacial period.
Milutin Milankovitch hypothesized that the timing of these cycles was controlled by the orbital parameters of the Earth, including the shape of its path around ...
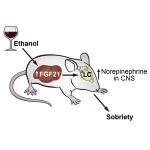
Drunk mice sober up after a hormone shot
2023-03-07
A hormone called fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) protects mice against ethanol-induced loss of balance and righting reflex, according to a study publishing on March 7 in the journal Cell Metabolism.
“We’ve discovered that the liver is not only involved in metabolizing alcohol but that it also sends a hormonal signal to the brain to protect against the harmful effects of intoxication, including both loss of consciousness and coordination,” says co-senior study author Steven Kliewer of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
“We’ve further shown that by increasing FGF21 concentrations even higher by injection, we can dramatically ...
The case for female mice in neuroscience research
2023-03-07
At a glance:
New research suggests female mice show more stable exploratory behavior than male mice, despite hormone cycles
The results challenge a long-held assumption that hormones have a broad effect on behavior in female mice, making them less suitable for research
The findings make a strong scientific case for increasing the inclusion of female mice in neuroscience and other experiments
Mice have long been a central part of neuroscience research, providing a flexible model that scientists ...
Association of stress with cognitive function among older adults
2023-03-07
About The Study: This study of 24,000 participants age 45 or older found an independent association between perceived stress and both prevalent and incident cognitive impairment. The findings suggest the need for regular screening and targeted interventions for stress among older adults.
Authors: Ambar Kulshreshtha, M.D., Ph.D., of the Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.1860)
Editor’s ...
Telemedicine use by rural vs urban VA beneficiaries before, after onset COVID-19
2023-03-07
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that despite initial telemedicine gains at rural Veterans Affairs (VA) health care sites, the pandemic was associated with an increase in the rural-urban telemedicine divide across the VA health care system. To ensure equitable access to care, the VA health care system’s coordinated telemedicine response may benefit from addressing rural disparities in structural capacity (e.g., internet bandwidth) and from tailoring technology to encourage adoption among rural users.
Authors: Lucinda B. Leung, M.D., Ph.D., M.P.H., of the Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System in Los Angeles, is the corresponding ...
FDA rule lowering drug dose is associated with less liver injury
2023-03-07
A United States Food and Drug Administration mandate to limit the dosage of acetaminophen in pills that combine acetaminophen and opioid medications is significantly associated with subsequent reductions in serious liver injury, according to a study led by investigators at the University of Alabama and Weill Cornell Medicine. The federal mandate was announced in 2011 and implemented in 2014. The results were reported March 7 in the medical journal JAMA.
“After researchers found that more than 40 percent of acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure cases involved combination acetaminophen and opioid medications, and an FDA advisory ...
Counting heads: how deep learning can simplify tedious agricultural tasks
2023-03-07
The selective breeding of grain crops is one of the main reasons why domesticated plants produce such excellent yields. Selecting the best candidates for breeding is, however, a remarkably complex task. On one hand, it requires a skilled breeder with trained eyes to assess plant resistance to disease and pests, crop growth, and other factors. On the other hand, it also requires precise tool-assisted measurements such as grain size, mass, and quality.
Although all these standard measures are useful, none of them takes into account the number ...
Evidence for the health benefits of consuming more live microbes
2023-03-07
Safe live microorganisms are found in a variety of foods we eat every day, from yogurt and other fermented foods, to raw fruits and vegetables. Despite the widespread idea that these mixtures of live microbes contribute to health, convincing evidence linking live dietary microbes to health benefits has been lacking.
A new study provides some of the first real-world evidence that higher consumption of live microbes may promote health. A group of scientists led by the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) classified over 9,000 individual ...
IVI launches global study to determine the burden of HPV among girls and women
2023-03-07
The International Vaccine Institute (IVI), an international organization with a mission to discover, develop, and deliver safe, effective, and affordable vaccines for global health, announced the start of a multi-country study to better understand the burden of Human papillomavirus (HPV) among girls and women in low- and lower middle-income countries. This study received $14.99 million USD in funding from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation with $1 million USD co-funding from the Swedish government and will help inform intervention implementation and prioritization of research and development efforts that have the greatest potential public health ...
Novel porous materials are ideal for metal-air batteries, researchers report
2023-03-07
Sustainable energy solutions cannot be pulled out of thin air. However, combining air with metal and other frameworks may pave the way for environmentally friendly energy conversion and storage, according to a research team based in China.
They published their review of novel porous materials — called metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and covalent organic frameworks (COFs) — and their potential to advance metal-air batteries on 03 March in Nano Research Energy.
The porous crystal material frameworks comprise various arrangements of bonded materials that can induce desired properties, including the ability to accelerate reactions between oxygen and metals ...
Novel biomimetic polypeptides activate tumor-infiltrating macrophages, offering hope for cancer therapy
2023-03-07
Macrophages are highly specialized cells of the immune system that help the body detect and fight deadly pathogens. In particular, M1-like macrophages detect and destroy tumor cells, and release protective chemokines such as interleukin (IL)-6 and tumor-necrosis factor α (TNF α), thus shielding the body from life-threatening pathologies like cancer. However, not all macrophages show anti-tumor potential. Certain types of macrophages, i.e., M2-like macrophages, promote tumor growth. Luckily, the desired macrophage phenotype—a set of traits resulting from the genetic makeup of the macrophage—can be activated by modulating the ...
[1] ... [2074]
[2075]
[2076]
[2077]
[2078]
[2079]
[2080]
[2081]
2082
[2083]
[2084]
[2085]
[2086]
[2087]
[2088]
[2089]
[2090]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.