Pandemic shift to telemedicine helped maintain quality of care for depression
2023-03-10
March 10, 2023 – The rapid transition from in-person to care to telemedicine visits at the start of the COVID‑19 pandemic did not adversely affect the quality of care – and even improved some aspects of care – for patients with major depression in a major integrated health system, according to a new report. The study appears as part of a special "Virtual Visits" supplement to Medical Care, published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"A rapid shift to virtual behavioral health care was possible without compromising health care-related practices," according to the new research, led by Nancy ...
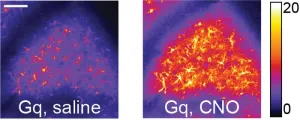
Astrocyte cells critical for learning skilled movements
2023-03-10
From steering a car to swinging a tennis racket, we learn to execute all kinds of skilled movements during our lives. You might think this learning is only implemented by neurons, but a new study by researchers at The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory at MIT shows the essential role of another brain cell type: astrocytes.
Just as teams of elite athletes train alongside staffs of coaches, ensembles of neurons in the brain’s motor cortex depend on nearby astrocytes to help them learn to encode when and how to move, and the ...
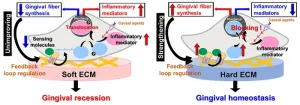
Study reveals that soft gums are more prone to inflammation
2023-03-10
The tissue area that surrounds our teeth is known as the gingiva, and healthy teeth will nestle firmly into the gums thanks to the many gingival fibers that connect the tooth to the gingiva. The gingiva is home to fibroblasts - cells that contribute to the formation of connective tissue. A group of scientists from Tohoku University have discovered that the gingiva stiffness influences the properties of gingival fibroblasts, which in turn affects whether inflammation is likely to occur and make gingival fibers difficult to form.
Their findings were published in the journal Scientific ...
HKU Marine Scientist contributes to research assessing the potential risks of ocean-based climate intervention technologies on deep-sea ecosystems
2023-03-10
The deep sea is one of the least well-known areas on Earth, comprising multiple vulnerable ecosystems that play critical roles in the carbon cycle. However, the deep sea is directly exposed to the effects of human-induced climate change and may now face additional challenges arising from efforts to counteract climate change artificially. These efforts have evolved into geoengineering solutions that could operate on vast spatial scales.
Ocean-based climate interventions (OBCIs) are increasingly claimed as promising solutions to mitigate climate change. These interventions use different technologies to remove carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and sequester the carbon ...
The future of dentistry is digital
2023-03-10
Digitalisation, one of the megatrends of the future, has arrived in the world of dentistry. Modern technologies underpin precision applications while also making treatments less invasive for patients. At the beginning of June 2023, an international congress will bring dentistry experts from all over Europe to Vienna to discuss the broad range of application options opened up by the latest breakthroughs.
The University Clinic of Dentistry Vienna is a renowned international innovation driver, especially ...
The perils of bacteria’s secret weapons
2023-03-10
Did you know that bacteria can hide their antimicrobial resistance? Much like storing military defence equipment without revealing it to the enemy, bacteria can mask their ability to resist antimicrobials. This hidden antimicrobial resistance can pass under the radar and cause treatment failure in patients.
A recent study published by researchers at UiT The Arctic University of Norway sheds light on this “hidden resistance”. The researchers describe that this phenomenon is often so rare that you cannot detect it through traditional testing methods, ...
April meeting of the American Physical Society to be held in Minneapolis and online
2023-03-10
Physicists from around the world will meet to present new research that spans from quarks to the cosmos at the American Physical Society’s (APS) April Meeting. The conference will be held in person in Minneapolis April 15-18 and online everywhere April 24-26.
Scientific Program
The scientific program includes more than 1,400 presentations on astrophysics, cosmology, particle physics, gravitation, nuclear physics and more. For more information, search the scientific program. All times are in U.S. Central time.
Hybrid Format
The April Meeting will have ...
Earth Map works in tandem with its users to achieve a more conscious, climate-aware and environmental-friendly world
2023-03-10
Rapid access to information is one of the largest barriers we have to deal with as a group of people in the Internet Age. Earth Map is a free application designed to be easily used and accessible to anyone with an internet connection and the desire to observe any environment at any time, with zero expertise (or travel) required.
This new tool features an intuitive point-and-click way of interfacing with the program, lending further to its ease of use.
The researchers published their results on January 12th in the Journal of Remote Sensing.
The authors underline the importance of ...
Northern and southern resident orcas hunt differently, which may help explain the decline of southern orcas
2023-03-10
Link to Google Drive folder containing images with caption and credit information:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Ye7QXkoTHfq7L4qEcJ33r6I6w7aB2-Mn?usp=share_link
In the Pacific Northwest and British Columbia, scientists have been sounding the alarm about the plight of southern resident orcas. Annual counts show that population numbers, already precarious, have fallen back to mid-1970s levels. Most pregnancies end in miscarriage or death of the newborn. They may not be catching enough food. And many elderly orcas — ...
Dim lights before bedtime to reduce risk of gestational diabetes
2023-03-10
Gestational diabetes mellitus is a common pregnancy complication with significant health risks for both mother and offspring
Gestational diabetes is rising fast and is now 7.8% of all births in U.S.
Mother with gestational diabetes has increased risk of diabetes, heart disease and dementia; offspring more likely to have obesity and hypertensio
CHICAGO --- Pregnant persons should dim the lights in their home and turn off or at least dim their screens (computer monitors and smartphones) a few hours before ...
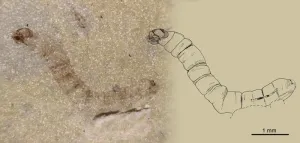
Discovery of oldest known fossil gnat shows how insects adapted to a postapocalyptic world
2023-03-10
Near the small harbour of Estellencs at the northeast of Mallorca (Balearic Islands, Spain), a pebbly beach can be found at the base of an impressive scarp that threatens rockfall. Remains of plants, crustaceans, insects, and fish have been discovered in the grey-blue rock layers formed from sediments deposited 247 million years ago. Fossils in these rocks are of great interest since they offer a window into the time where the planet was recovering from the greatest mass extinction.
A few years ago, Mallorcan ...
Sea temperatures control the distributions of European marine fish
2023-03-10
An analysis extending from southern Portugal to northern Norway highlights the importance of temperature in determining where fish species are found.
By confirming temperature as a key driver of large-scale spatial variation in fish assemblages the study was able to use future climate projections to predict where species will be most common by 2050 and 2100. The results show that overall, the greatest community-level changes are predicted at locations with greater warming, with the most pronounced effects further north - at higher latitudes.
The study was the first of its ...
McMaster researcher crafting post-COVID-19 condition guidelines, commonly known as long COVID
2023-03-10
Hamilton, ON (March 9, 2023) - McMaster University clinician-researcher Holger Schünemann is receiving $9 million in federal funding to develop official guidelines for post-COVID-19 Condition (PCC), commonly known as long COVID.
Schünemann’s project, titled McMaster Development and Dissemination of Post COVID-19 Condition (PCC) Guidelines and Knowledge Translation Products, is being developed by McMaster in collaboration with the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC).
Schünemann said that Cochrane Canada and ...
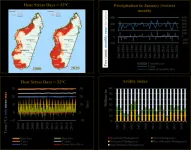
USC research identifies existential threats to the iconic Nile River Delta
2023-03-10
Large-scale heavy metal pollution, coastal erosion and seawater intrusion pose an existential threat to the Nile River Delta and endanger 60 million people (about twice the population of Texas) in Egypt who depend on its resources for every facet of life, according to new research from the USC Viterbi School of Engineering. Furthermore, the Nile River Delta is a critical stopover for migrating birds across their journey along the East African flyway.
The study, led by Essam Heggy from the USC Viterbi Innovation Fund Arid Climates ...
Researchers unveil new AI-driven method for improving additive manufacturing
2023-03-10
Many industries rely on metal additive manufacturing to rapidly build parts and components. Rocket engine nozzles, pistons for high performance cars, and custom orthopedic implants are all made using additive manufacturing, a process that involves building parts layer-by-layer using a 3D printer.
Additive manufacturing allows users to build complex parts quickly, but structural defects that form during the building process is one of the reasons that have prevented this approach from being widely adopted. Researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne ...
Advanced imaging may help in clinical treatment of prostate cancer
2023-03-10
An advanced imaging method is showing promise as a way to improve the diagnosis of prostate cancer by giving clinicians a clearer view of suspected tumours during biopsy.
A trial conducted at the University Hospital Bonn, in Germany, has been testing the benefit of a scanning method known as PSMA-PET/CT to help target where to take biopsy samples.
Interim results reveal that when used alongside standard imaging techniques, the additional scans might help clinicians make improved decisions about subsequent courses of treatment.
Compared to the standard scans alone, when PSMA-PET/CT was used clinicians changed ...
UK study reveals ethnic differences in obstetric anesthesia care
2023-03-10
Black Caribbean-British women in the UK are 58% more likely than white women to be given general anaesthesia for elective caesarean births; for Black African-British women, they are 35% more likely to have general anaesthesia
For emergency Caesarean births, Black Caribbean-British women are 10% more likely than white women to be given general anaesthesia
For vaginal births, Bangladeshi-British (by 24%), Pakistani-British (by 15%) and Black Caribbean-British (by 8%) women less likely than white women to receive an epidural
Black women are approximately 40% less likely to have an assisted vaginal birth (forceps/ventouse [suction] delivery) compared to white women but instead are more likely ...
Emergency department visits for attempted suicides rose globally among youth during pandemic
2023-03-10
EMBARGOED UNTIL 4:30 PM MST, MARCH 9
Calgary, AB – Even though pediatric emergency department visits decreased greatly overall during the COVID-19 pandemic, a newly published study led out of the University of Calgary shows there was also a sharp increase in emergency department visits for attempted suicide and suicide ideation among children and adolescents in that same period of social isolation.
Dr. Sheri Madigan, a clinical psychologist in the Department of Psychology, is the lead author on the study, published today (March 9) in Lancet Psychiatry, which ...
Reducing trip hazards and decluttering can prevent falls among older people living at home
2023-03-10
Eliminating hazards around the home, such as clutter, stairs without railings and poor lighting, can reduce the risk of falls for older people by around a quarter, according to a new Cochrane review.
The review did not find any compelling evidence for other measures to reduce falls, such as making sure older people have the correct prescription glasses, special footwear, or education on avoiding falls.
It also found that decluttering and reducing hazards had the most benefit for older people who are at risk of falls, ...
Online ‘personal brands’ key to job success for Gen Z
2023-03-10
New research reveals how Generation Z perceive online ‘personal brands’ as a crucial tool to gain more advantage in job markets.
The study, led by the University of East Anglia in collaboration with the University of Greenwich, demonstrates the importance of authentically building online personal branding strategies and tactics to bridge the gap between Gen Z’s desired and perceived images on social media when job seeking.
Gen Z - the generation of people born between the late 1990s and early 2010s - are also in favour of a more dynamic, interactive, work-in-progress style of authentic personal brands, which may not necessarily show them as “perfect”, ...
Ozone pollution is linked with increased hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease
2023-03-10
Sophia Antipolis, 10 March 2023: The first evidence that exceeding the World Health Organization (WHO) ozone limit is associated with substantial increases in hospital admissions for heart attack, heart failure and stroke is published today in European Heart Journal, a journal of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1 Even ozone levels below the WHO maximum were linked with worsened health.
“During this three-year study, ozone was responsible for an increasing proportion of admissions ...
Development of a photonic dispersion solver
2023-03-10
An exponential increase in the amount of information required in society is making the development of new optoelectronic devices increasingly important. Recently, photonic crystals have emerged as an alternative to overcome the limitations of conventional photonic devices thanks to their ability to control photons freely in microscopic space to introduce the next generation of highly integrated devices. A research team at POSTECH has developed a photonic dispersion solver that may act as the foundation of studies on photonic crystals.
Professor Junsuk Rho (Department of Mechanical Engineering and Department of Chemical Engineering) at POSTECH along with a team from Gwangju Institute ...
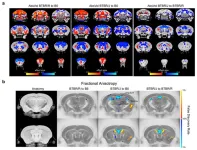
Ancient virus genome drives autism?
2023-03-10
Although autism is a common neurodevelopmental disorder, the multiple factors behind its onset are still not fully understood. Animal models of idiopathic autism*1, especially mice, are often used to help researchers understand the complicated mechanisms behind the disorder, with BTBR/J being the most commonly used mouse model in the world.
Now, an international research collaboration including Kobe University’s Professor TAKUMI Toru and Researcher Chia-wen Lin et al. have made new discoveries regarding autism onset in mouse models.
In their detailed series of experiments and analyses of BTBR/J mice and the other subspecies BTBR/R, they revealed that endogenous ...
If you think you understand how incentives work, think again
2023-03-09
How can people be incentivized to drive more fuel-efficient cars, be more innovative at work, and get to the gym on a regular basis? Uri Gneezy, professor of economics and strategy at the Rady School of Management at UC San Diego explains this in his new book “Mixed Signals: How Incentives Really Work.”
In the book, Gneezy, a pioneering behavioral economist, reveals how we can create reward systems that minimize unintended consequences and maximize happiness, health, wealth and success. “Mixed Signals” was recently included in Adam Grant’s ...
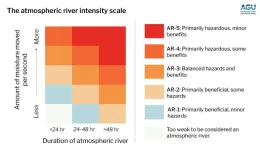
The world’s atmospheric rivers now have an intensity ranking like hurricanes
2023-03-09
American Geophysical Union
9 March 2023
AGU Release No. 23-10
For Immediate Release
This press release and accompanying multimedia are available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/the-worlds-atmospheric-rivers-now-have-an-intensity-ranking-like-hurricanes/
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, +1 (202) 777-7492, news@agu.org (UTC-5 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Bin Guan, University of California Los Angeles and California Institute of Technology, bin.guan@jpl.nasa.gov (UTC-8 hours)
WASHINGTON — Atmospheric rivers, which are long, narrow bands of water vapor, are becoming more intense and frequent with climate ...
[1] ... [2067]
[2068]
[2069]
[2070]
[2071]
[2072]
[2073]
[2074]
2075
[2076]
[2077]
[2078]
[2079]
[2080]
[2081]
[2082]
[2083]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.