Senior researcher at Illinois VA Hospital named 2023 VA Magnuson Award winner
2023-03-03
Dr. Richard L. Lieber, a senior research career scientist at the Edward Hines, Jr., VA Hospital in Hines, Ill., has received the 2023 Paul B. Magnuson Award for his work to return functional capacity, mobility, and quality of life to Veterans with physical disabilities. The Magnuson Award recognizes outstanding achievement in VA rehabilitation research.
Lieber is also a professor in the departments of physiology, biomedical engineering, and physical medicine and rehabilitation at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., and the chief scientific officer and senior vice president at the Shirley Ryan Ability ...
One-year adverse outcomes among adults with long COVID vs those without COVID-19
2023-03-03
About The Study: This case-control study leveraged a large commercial insurance database and found increased rates of adverse outcomes over a 1-year period for a post–COVID-19 condition (long COVID) cohort surviving the acute phase of illness. The results indicate a need for continued monitoring for at-risk individuals, particularly in the area of cardiovascular and pulmonary management.
Authors: Andrea DeVries, Ph.D., of Elevance Health, Inc., in Indianapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed ...
Association of structural fires in New York City with inequities in safe heating for immigrant communities
2023-03-03
About The Study: This study found that the frequency of heating complaints was significantly associated with the frequency of structural fires in New York City. Importantly, this association varied across community districts, with more fires occurring in districts with greater proportions of Black and Latinx residents.
Authors: Clifford C. Sheckter, M.D., of the Santa Clara Valley Medical Center in San Jose, California, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.1575)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
Skilled nursing facilities continued to provide high quality care for those hospitalized during the pandemic
2023-03-03
Older adults who entered skilled nursing facilities (SNF) for care after hospitalizations after the pandemic received rehabilitation care comparable to the levels of care that were provided pre-pandemic, according to research published in the JAMA Health Forum.
Despite exceptional challenges during the pandemic, SNFs provided post-acute rehabilitation with only a modest decline in intensity, said the researchers. This suggests that SNFs were largely able to adapt and provide post-acute care ...
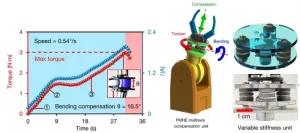
Scientists develop self-tunable electro-mechano responsive elastomers
2023-03-03
Recently, a team led by Prof. ZHANG Shiwu from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) and their collaborators from UK and Australia developed a new electro-mechano responsive elastomer that autonomously adjust stiffness, conductivity and strain sensitivity in response to changes in external mechanical loads and electrical signals. Their research was published in Science Advances.
Nowadays, more and more application scenarios like soft robotics and medical surgical equipment call for self-tunable intelligent materials. A widely adopted solution is composite material composed of low melting ...
Additive to make slurry more climate-friendly
2023-03-03
Greenhouse gases act like a layer of window glass in the atmosphere: They prevent heat from being radiated from the Earth's surface into space. Methane does that 28 times as effectively as carbon dioxide - it is (to stay in the picture) a kind of invisible double glazing.
Over the past 200 years, the concentration of methane in the atmosphere has more than doubled. This is mainly due to human meat consumption: For one thing, cows and other ruminants produce methane during digestion. Another important source is the excrement of the animals. "One-third ...
Case study of rare, endangered tortoise highlights conservation priorities for present, future World Wildlife Days
2023-03-03
Though wildlife trafficking has been effectively disrupted since the first World Wildlife Day—established 50 years ago today via the 1973 Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) of Wild Fauna and Flora—a newly published case study on one of the world’s rarest tortoise species, the ploughshare tortoise, highlights how much room for improvement still exists.
In a new paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academies of the Sciences, University of Maryland Associate Professor Meredith Gore and her coauthors—Babson College’s Emily Griffin, ...
Fluorescent protein sheds light on bee brains
2023-03-03
An international team of bee researchers involving Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) has integrated a calcium sensor into honey bees to enable the study of neural information processing including response to odours. This also provides insights into how social behaviour is located in the brain, as the researchers now report in the scientific journal PLOS Biology.
Insects are important so-called model organisms for research. Despite more than 600 million years of independent evolution, insects share more than 60% of their DNA with humans. For several decades it was mainly the fruit fly ...
Researchers identify gene mutation capable of regulating pain
2023-03-03
Pain afflicts at least 1.5 billion people worldwide, and despite the availability of various painkilling drugs, not all forms of pain are treatable. Moreover, pain medications can have side-effects such as dependence and tolerance, especially in the case of morphine and other opioids.
In search of novel painkillers, researchers at Butantan Institute’s Special Pain and Signaling Laboratory (LEDS) in São Paulo, Brazil, studied TRPV1, a sensory neuron receptor that captures noxious stimuli, including heat and the burning sensation conveyed by chili peppers, and ...
Chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer cells protect their neighbors
2023-03-03
Certain chemotherapy-resistant ovarian cancer cells protect neighboring cancer cells by sending signals that induce resistance, according to a new study from University of Pittsburgh and UPMC researchers that may help explain why ovarian cancer patients respond poorly to chemotherapy or relapse after treatment.
Published in Clinical Cancer Research, the study investigated chemotherapy-resistant cancer cells called quiescent cells. As chemotherapy primarily targets rapidly dividing cells, quiescent cells are resistant because they divide ...
When ‘good genes’ go bad: how sexual conflict can cause population collapse
2023-03-03
Males of a species evolving traits for sexual conflict can cause problems for females, and, ultimately, the whole population.
A new model by Imperial College London and University of Lausanne researchers, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, shows how so-called ‘good genes’ can sometimes cause a population to collapse.
Males of any species may compete for females, either by fighting other males for access or impressing females to win their approval. In both cases, ...
UC Davis study uncovers age-related brain differences in autistic individuals
2023-03-03
A new study led by UC Davis MIND Institute researchers confirms that brain development in people with autism differs from those with typical neurodevelopment. According to the study published in PNAS, these differences are linked to genes involved in inflammation, immunity response and neural transmissions. They begin in childhood and evolve across the lifespan.
About one in 44 children in the U.S. has autism. Autistic individuals may behave, communicate and learn in ways that are different from neurotypical people. As they age, they often have challenges with social communication ...
An interdisciplinary solution for enhanced high-resolution imaging in electron and optical microscopy
2023-03-03
Although electron microscopy can already reveal details as small as one nanometer, ongoing research seeks to break through barriers limiting image quality and reducing the optical dose on the samples. Aberration is a common problem in electron microscopy that can reduce the resolution and quality of the images produced. Additional complex phase and amplitude controls are needed in these microscopes. An international team of researchers led by Akhil Kallepalli (Kallepalli Lab) working within the Optics Group at the University of Glasgow set out to address the problem. Working from an optics perspective, they developed and tested a new ghost ...
Tree rings and strontium point researchers to the provenance of 400-year-old timber
2023-03-03
Tree-ring analysis – so-called dendrochronological analysis – has been part of archaeology for many years and has made it possible for archaeologists to date old wooden objects with great precision. And in many cases, they have also been able to determine the provenance of the wood.
But it has proven difficult for researchers to determine timber’s place of origin when the historic timber was imported into Denmark from further afield to serve as building material.
In a new study in the journal PLOS ONE, Associate Professor Aoife Daly and Dr Alicia Van Ham-Meert from the University of Copenhagen show that combining analyses of ...
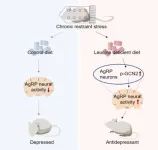
Chinese scientists discovered roles of hypothalamic amino acid sensing in antidepressant effects
2023-03-03
Depression is a leading cause of disability around the world and contributes greatly to the global burden of disease. Nutrition is essential for the maintenance of normal emotional states. Nutritional therapy is rising up in many disease treatments, but little is known in the depression field. Unbalanced nutrition is implicated in the etiology of depression, potentially hindering treatment. For example, many essential amino acids (EAAs) in serum are changed in patients with depression, such as tryptophan, threonine, leucine, isoleucine, and valine. However, whether EAA contributes to depression ...
Health policy experts call for confronting anti-vaccine activism with life-saving counter narratives
2023-03-03
Public and private sector health officials and public policymakers should team up immediately with community leaders to more effectively disseminate accurate narratives regarding the life-saving benefits of vaccines to counter widespread, harmful misinformation from anti-vaccine activists.
Such is the message of a UC Riverside-led viewpoint piece published Thursday, March 2, in the leading international medical journal, The Lancet.
“We need to consistently amplify the best science and find the best ways of communicating so that people are hearing it through multiple channels instead of through one or two sources,” ...
Inspirational women from UK Synchrotron launch major recruitment campaign to promote STEM careers at AAAS international science conference
2023-03-03
Today, at the prestigious AAAS science conference in Washington DC, Diamond Light Source, the UK’s synchrotron science facility, will unveil plans for its biggest recruitment campaign since its inception 20 years ago. Dozens of new roles will be available in the coming year and some examples of the variety of STEM careers will be showcased and celebrated by an all-women line up from the Diamond team. This recruitment drive aims to ensure the facility has the knowledge and expertise required to help plan and deliver world leading science for the next decade and beyond
In the lead up to ...
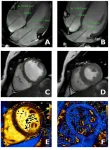
Imaging the adolescent heart
2023-03-03
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has allowed scientists at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC) to produce an accurate picture of the healthy heart in adolescence. Using this advanced technology, the research team was able to determine reference values for anatomical and functional parameters in the heart during adolescence. This information, pubished in eClinicalMedicine, has direct implications for clinical practice.
“Magnetic resonance imaging has become a very important method for studying the heart because it avoids exposing patients to radiation ...
Archaeological study of 24 ancient Mexican cities reveals that collective forms of governance, infrastructural investments, and collaboration all help societies last longer
2023-03-03
Some cities only last a century or two, while others last for a thousand years or more. Often, there aren’t clear records left behind to explain why. Instead, archaeologists piece together clues from the cities’ remains to search for patterns that help account for why certain places retained their importance longer than others. In a new study published in the journal Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, researchers examined 24 ancient cities in what’s now Mexico and found that the cities that lasted the longest showed indications of collective forms of governance, infrastructural investments, and cooperation between households.
“For years, my colleagues and I have ...
50 leading national organizations unite to curb infodemic of health and science misinformation and disinformation
2023-03-03
The Coalition for Trust in Health & Science today announced its formation and public launch during the 2023 American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) Annual Meeting in Washington, D.C. The alliance was formed to unite leading organizations from across the entire health ecosystem to advance trust and factual science-based decision-making. The partnership aims to achieve a measurable increase in the public’s willingness – and ability – to access evidence-based information necessary to make the best personally appropriate health decisions for themselves, their ...
DART impact provided real-time data on evolution of asteroid's debris
2023-03-03
When asteroids suffer natural impacts in space, debris flies off from the point of impact. The tail of particles that form can help determine the physical characteristics of the asteroid. NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Test mission in September 2022 gave a team of scientists including Rahil Makadia, a Ph.D. student in the Department of Aerospace Engineering at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, a unique opportunity—to observe the evolution of an asteroid’s ejecta as it happened for the first time.
“My work on this mission ...
Artifical intelligence approach may help detect Alzheimer's disease from routine brain imaging tests
2023-03-03
BOSTON – Although investigators have made strides in detecting signs of Alzheimer’s disease using high-quality brain imaging tests collected as part of research studies, a team at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) recently developed an accurate method for detection that relies on routinely collected clinical brain images. The advance could lead to more accurate diagnoses.
For the study, which is published in PLOS ONE, Matthew Leming, PhD, a research fellow at MGH’s Center for Systems Biology and an investigator at the Massachusetts Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, and his colleagues used deep learning—a type of machine learning ...
Wildfires in 2021 emitted a record-breaking amount of carbon dioxide
2023-03-03
Irvine, Calif., March 2, 2023 — Carbon dioxide emissions from wildfires, which have been gradually increasing since 2000, spiked drastically to a record high in 2021, according to an international team of researchers led by Earth system scientists at the University of California, Irvine.
Nearly half a gigaton of carbon (or 1.76 billion tons of CO2) was released from burning boreal forests in North America and Eurasia in 2021, 150 percent higher than annual mean CO2 emissions between 2000 and 2020, the scientists reported in a paper in Science.
“According to our measurements, boreal fires in 2021 shattered previous ...
In his new book, Julian Mcclements explains why he is committed to eating ‘meat less’
2023-03-03
Distinguished Professor of Food Science and prolific author David Julian McClements has a new book out this month – Meat Less: The Next Food Revolution (Springer, 2023).
Meat Less describes McClements’ journey to vegetarianism, a shift inspired by his daughter and his ongoing research work on developing healthier and more sustainable foods.
“In writing this book I take the viewpoint that there are no easy answers and that everyone must make the decision to eat meat or not based ...
Illuminating the evolution of social parasite ants
2023-03-03
Ants are known as hard workers, tirelessly attending to their assigned tasks—foraging for food, nurturing larvae, digging tunnels, tidying the nest. But in truth, some are total layabouts. Called workerless social parasites, these rare species exist only as queens, and they die without workers to tend to them. To survive, parastic ants infiltrate a colony of closely related ants, where, as long as they keep their numbers relatively low, they and their offspring become the leisure class of the colony.
It’s long been thought that ...
[1] ... [2068]
[2069]
[2070]
[2071]
[2072]
[2073]
[2074]
[2075]
2076
[2077]
[2078]
[2079]
[2080]
[2081]
[2082]
[2083]
[2084]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.