C-reactive protein reduces the immune response in inflammatory disease
2023-03-09
The biological function of the C-reactive protein, CRP, has long been unknown. Researchers at Linköping University in Sweden now show that this protein has a beneficial function in systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE, an inflammatory disease. But this is true only for one of CRP’s two forms, according to the study published in Journal of Autoimmunity.
Most of us have had a CRP blood test on more than one occasion. This is a very common routine health care test used to detect infection or systemic inflammation in the body. What is measured is the level of C-reactive protein, or CRP for short.
“CRP ...
Study: Higher fracture risk after total hip replacement when cementless implant used to treat femoral neck fracture
2023-03-09
A study by Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) and other centers found that total hip replacement performed with a cementless prosthesis for a femoral neck fracture led to a higher rate of a second fracture and subsequent revision surgery. The research was presented today at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) Annual Meeting in Las Vegas. The results were also published online in The Journal of Arthroplasty in October 2022.
Treatments for a femoral neck fracture range from nonoperative management to total hip replacement. When hip replacement is the best treatment option, it can be performed with or without bone cement to secure the prosthesis.
“Femoral ...
Mass General researchers discover the role of intestinal fibrosis in inflammatory bowel disease
2023-03-09
Intestinal fibrosis is a common feature of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and the primary cause of end-stage organ failure. Traditionally considered a bystander of inflammation, with negligible involvement in disease pathogenesis, new research published in Gastroenterology now shows that fibrosis has a direct bearing on disease progression in IBD.
The investigation was spearheaded by Nima Saeidi, PhD, Associate Professor of Surgery at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and Harvard Medical School, along with co-first authors, Shijie He, PhD, and Peng Lei, PhD.
The critical question posed by the investigators ...
Digital rectal examination is not useful to early detect prostate cancers
2023-03-09
A common method of detecting prostate cancer may not be accurate enough as a reliable screening tool by itself, scientists have warned.
The digital rectal exam (DRE) is widely used by medical professionals to check the prostate gland with a finger for unusual swelling or lumps in the rectum as an initial check for the signs of prostate cancer in men.
In some countries, such as Germany, it is the sole method used in a national screening programme for the disease.
But new research by scientists of the PROBASE trial coordinated at the German Cancer Research Center (Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, DKFZ) ...
Long Covid is much less likely after omicron than after variant circulating at start of COVID-19 pandemic
2023-03-09
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Wednesday 8 March
The omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 is much less likely to lead to long Covid than the variant circulating at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, new research being presented at this year's European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April) suggests.
The Swiss study found that healthcare ...
World’s most comprehensive study on COVID-19 mental health
2023-03-09
COVID-19 has taken a relatively limited toll on the mental health of most people around the globe, according to a paper published today in the BMJ by a McGill University-led research team involving collaborators from McMaster University, the University of Toronto, and other institutions.
The team reviewed data from 137 studies in various languages involving 134 cohorts of people from around the world. Most of the studies were from high or middle-income countries, and about 75% of participants were adults and 25% were children and adolescents between the ages of 10-19.
To their surprise, the researchers found that despite the dramatic stories to the contrary, where ...
Low dose radiation linked to increased lifetime risk of heart disease
2023-03-09
Exposure to low doses of ionising radiation is associated with a modestly increased excess risk of heart disease, finds an analysis of the latest evidence published by The BMJ today.
The researchers say these findings “have implications for patients who undergo radiation exposure as part of their medical care, as well as policy makers involved in managing radiation risks to radiation workers and the public.”
And a linked editorial suggests that these risks “should now be carefully considered in protection ...
Study suggests little deterioration in mental health linked to the pandemic
2023-03-09
Mental health among the general population has not changed by large amounts during the covid-19 pandemic compared with pre-pandemic levels, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
Some specific groups, particularly women, appear to have been more negatively affected, but changes have been minimal to small, say the researchers.
Many studies and media reports suggest that covid-19 has led to widespread decline in mental health, but inconsistencies in study quality and misinterpretation of cross-sectional data may ...
Can children map read at the age of four?
2023-03-09
Children start to develop the basic skills that underlie map reading from the age of four – according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today reveals that they become able to use a scale model to find things in the real world.
The study involved 175 two to five-year-olds and is the largest of its kind.
The team say that this new spatial ability potentially lays the foundations for maths and science skills.
Lead researcher Dr Martin Doherty, from UEA’s School of Psychology, said: “We wanted to find out when children can use scale models or maps ...
Eiphosoma laphygmae likely to be best classical biological control against devastating fall armyworm pest
2023-03-09
A review, conducted by CABI scientist Dr Marc Kenis suggests that the parasitoid Eiphosoma laphygmae is likely to be the best classical biological control from the Americas against the devastating fall armyworm pest.
Dr Kenis, Head of Risk Analysis and Invasion Ecology based at CABI’s Swiss centre in Delémont, evaluated the prospects and constraints of a classical biological control programme to fight the fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) using larval parasitoids which are considered the most suitable natural enemies ...
Ultra-soft and highly stretchable hydrogel-based sensor for monitoring overactive bladder
2023-03-09
Modern living seems to have exacerbated the conditions of our gut. There is an escalating prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome and overactive bladder syndrome among individuals who do not exhibit signs of infectious maladies or other established ailments, but rather report experiencing sudden symptoms. Recently, a team of researchers from POSTECH and Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have proposed a sensor to monitor overactive bladders.
The research team consisting of Professor Sung-Min Park and Young-Soo ...
Toxic Twitter abuse could skew UK wildlife law
2023-03-09
Wildlife conservation efforts could suffer because toxic online rows about trophy hunting are becoming increasingly abusive, ecologists have warned.
Scientists analysed hundreds of tweets about trophy hunting and found that 7% were abusive. This is a similar proportion to content on partisan topics on social media platforms known to highlight extreme viewpoints.
The findings, by conservation scientists at the University of Reading and the University of Sheffield, are published today (9 March) in the journal ...
Racial bias in artificial intelligence restricts vital access to healthcare and financial services, says data scientist
2023-03-09
These are just some examples given by a leading data science expert who has analyzed the depths of systemic racism in AI and suggested the ways in which the biases can be confronted.
A pervasive threat
Artificial intelligence is a pervasive part of modern-day life and is used by vital institutions from banks to police forces.
But a growing mountain of evidence suggests that the AI used by these organizations can entrench systemic racism.
This can negatively impact Black and ethnic minority groups when applying ...
Aston University and the British Council to help boost global number of female photonics experts
2023-03-08
Aston University to support more women carve out a career in photonics
Three new grants available for women from eligible countries across east Asia
Scholarships will be based in the College of Engineering and Physical Sciences.
Aston University and the British Council are aiming to support more women carve out a career in photonics.
The British Council is funding three grants for women who have recently completed a PhD or equivalent and are from eligible countries across east Asia.
This scholarship programme aims to increase opportunities in science, technology, engineering and maths (STEM) for women.
According ...
Marine mammal reproduction rests on a precarious tipping point of ocean resources
2023-03-08
Changing environmental conditions may threaten marine mammal populations by making it harder to find prey, and a new study shows how small, gradual reductions in prey could have profound implications for animal populations.
The reproductive success of female elephant seals depends on their ability to find prey and put on weight during their months-long foraging migrations. Researchers at UC Santa Cruz studied the relationships between elephant seal behavioral strategies in the open ocean, weight gain, and lifetime success at producing pups.
Their findings, published March 8 in Ecology Letters, reveal a sharp threshold in the relationship between ...
UCF researcher creates world’s first energy-saving paint – inspired by butterflies
2023-03-08
–EMBARGOED:
NOT FOR RELEASE UNTIL 2:00 p.m. EST, WEDNESDAY, 08 MARCH 2023–
UNIVERSITY OF CENTRAL FLORIDA
UCF Researcher Creates World’s First Energy-saving Paint – Inspired by Butterflies
Instead of pigment-based colored paint, which requires artificially synthesized molecules, a UCF researcher has developed an alternative way to produce colored paint that is more natural, environmentally friendly and light weight.
ORLANDO, March 8, 2023 — University of Central Florida researcher Debashis Chanda, a professor in UCF’s NanoScience Technology Center, has drawn inspiration from butterflies to create the first environmentally ...
Researchers discover how too much oxygen damages cells and tissues
2023-03-08
SAN FRANCISCO, CA—March 8, 2023—When it comes to oxygen, you can have too much of a good thing. Breathing air that contains higher levels of oxygen than the usual 21 percent found in Earth’s atmosphere can cause organ damage, seizures, and even death in people and animals, particularly if it’s in excess of the body’s oxygen needs. Until now, however, scientists have mostly speculated about the mechanisms behind this phenomenon, known as oxygen toxicity, or hyperoxia.
Now, researchers at Gladstone Institutes have discovered how excess oxygen changes a handful of proteins in our cells that ...
Colorectal cancer research
2023-03-08
Excessive iron absorption by tumor cells in the digestive tract is known to play a major role in driving colorectal cancer – the third most prevalent and third leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S.
In a new study published in the journal Advanced Science, University of New Mexico researchers describe the part played by the transferrin receptor (TFRC) gene in the growth of colorectal cancer tumors.
Iron is absorbed into intestinal cells both from the bloodstream and from iron-rich foods, such as red meat, said Xiang Xue, PhD, assistant professor ...
A pool at Yellowstone is a thumping thermometer
2023-03-08
While the crowds swarm around Old Faithful to wait for its next eruption, a little pool just north of Yellowstone National Park’s most famous geyser is quietly showing off its own unique activity, also at more-or-less regular showtimes. Instead of erupting in a towering geyser, though, Doublet Pool cranks up the bass every 20 to 30 minutes by thumping. The water vibrates and the ground shakes.
Doublet Pool’s regular thumping is more than just an interesting tourist attraction. A new study led by University of Utah researchers shows that the ...
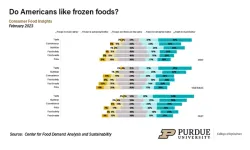
Americans planning frugal uses for their 2023 tax refunds
2023-03-08
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Americans likely are receiving smaller tax refunds than they have in recent years, and most people will not be going out to spend this money, according to the February 2023 Consumer Food Insights Report. This month’s report also looks more closely at religious demographics and includes new data on frozen food preferences.
The survey-based report out of Purdue University’s Center for Food Demand Analysis and Sustainability assesses food spending, ...
Unprecedented increase in ocean plastic since 2005 revealed by four decades of global analysis
2023-03-08
A global dataset of ocean plastic pollution between 1979 and 2019 reveals a rapid and unprecedented increase in ocean plastics since 2005, according to a study published March 8, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Marcus Eriksen from The 5 Gyres Institute, USA, and colleagues.
Understanding plastic accumulation in the oceans to date could provide a critical baseline to help address this form of pollution. Previous studies have focused primarily on northern-hemisphere oceans near the world’s most industrialized nations, ...
Places of worship linked with more neighborhood crime in Washington, D.C.
2023-03-08
A new analysis of crime statistics near hundreds of places of worship in Washington, D.C., shows that these sites are associated with higher levels of violent and property crime—even after accounting for other factors commonly linked with crime. James Wo of the University of Iowa, U.S., presents these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 8, 2023.
Prior research has established that places of worship foster social ties and community actions for the common good, suggesting that these sites would reduce crime in their neighborhoods. However, few studies have addressed the hypothesized ...
For educational attainment, it's more helpful to grow up in an affluent neighborhood than it is harmful to grow up in a poor one, per 23-year large Netherlands cohort study
2023-03-08
For educational attainment, it's more helpful to grow up in an affluent neighborhood than it is harmful to grow up in a poor one, per 23-year large Netherlands cohort study
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281928
Article Title: Neighbourhood effects on educational attainment. What matters more: Exposure to poverty or exposure to affluence?
Author Countries: The Netherlands, UK
Funding: The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Research Council (https://erc.europa.eu/) ...
After 6 months of disrupted schooling during COVID-19, German students scored substantially lower on intelligence tests than comparative earlier cohorts, with the gap persisting after 16 months.
2023-03-08
After 6 months of disrupted schooling during COVID-19, German students scored substantially lower on intelligence tests than comparative earlier cohorts, with the gap persisting after 16 months
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281779
Article Title: Students’ intelligence test results after six and sixteen months of irregular schooling due to the COVID-19 pandemic
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: The study was supported by a grant awarded to M.B. by the Research Fund of ...
Participants in psychology studies are more likely than average to exhibit symptoms of personality disorders, potentially skewing the findings of such research
2023-03-08
Participants in psychology studies are more likely than average to exhibit symptoms of personality disorders, potentially skewing the findings of such research
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281046
Article Title: Self-selection biases in psychological studies: Personality and affective disorders are prevalent among participants
Author Countries: Poland, Spain, Italy
Funding: To conduct Face-to-Face Studies IK was supported by grants 2017/01/X/HS6/02022 from the National Center of Science ...
[1] ... [2070]
[2071]
[2072]
[2073]
[2074]
[2075]
[2076]
[2077]
2078
[2079]
[2080]
[2081]
[2082]
[2083]
[2084]
[2085]
[2086]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.