Technology uses 'single' approach to develop electronics, acoustics
2021-03-25
(Press-News.org) WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - A Purdue University innovator has developed a new approach to creating popular thin films used for devices across a broad range of fields, including optics, acoustics and electronics.
Epitaxial lithium niobate (LNO) thin films are an attractive material for electronics and other devices. These films offer flexibility and other properties that are important to manufacturers.
The challenge is that these devices demand high-quality thin films that can be difficult to grow and produce. Haiyan Wang, a Purdue materials engineer, developed a new approach to creating these films. The work is published in Advanced Photonics Research.
"We created an approach that makes these films easier to produce," said Wang, the Basil S. Turner Professor of Engineering in Purdue's College of Engineering. "We developed a versatile nanocomposite-seeded approach that allows us to create single-layer films. Typically, engineers have used a double-layer approach, which adds to the complicated production process."
This work is supported by Sandia National Laboratories through its Academic Alliance initiative. This technology work also is supported through Sandia's Diversity Initiative.
"Our approach offers an efficient new option for optics, acoustics and electronics," said Robynne Paldi, a Ph.D. candidate at Purdue who helped lead the research. "Our films are grown through a pulsed laser deposition method and growth conditions are optimized to achieve high-quality films that can be easily integrated into devices."
The innovators worked with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization to patent their technology.
INFORMATION:
The innovators and OTC are looking for partners to continue developing their technology. For more information on licensing and other opportunities, contact Will Buchanan of OTC at wdbuchanan@prf.org and mention track code 2021-WANG-69382.
About Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization
The Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization operates one of the most comprehensive technology transfer programs among leading research universities in the U.S. Services provided by this office support the economic development initiatives of Purdue University and benefit the university's academic activities through commercializing, licensing and protecting Purdue intellectual property. The office is located in the Convergence Center for Innovation and Collaboration in Discovery Park District, adjacent to the Purdue campus. In fiscal year 2020, the office reported 148 deals finalized with 225 technologies signed, 408 disclosures received and 180 issued U.S. patents. The office is managed by the Purdue Research Foundation, which received the 2019 Innovation and Economic Prosperity Universities Award for Place from the Association of Public and Land-grant Universities. In 2020, IPWatchdog Institute ranked Purdue third nationally in startup creation and in the top 20 for patents. The Purdue Research Foundation is a private, nonprofit foundation created to advance the mission of Purdue University. Contact otcip@prf.org for more information.
About Purdue University
Purdue University is a top public research institution developing practical solutions to today's toughest challenges. Ranked the No. 5 Most Innovative University in the United States by U.S. News & World Report, Purdue delivers world-changing research and out-of-this-world discovery. Committed to hands-on and online, real-world learning, Purdue offers a transformative education to all. Committed to affordability and accessibility, Purdue has frozen tuition and most fees at 2012-13 levels, enabling more students than ever to graduate debt-free. See how Purdue never stops in the persistent pursuit of the next giant leap at purdue.edu.
About Sandia Labs
Sandia National Laboratories is a multimission laboratory operated by National Technology and Engineering Solutions of Sandia LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Honeywell International Inc., for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration. Sandia Labs has major research and development responsibilities in nuclear deterrence, global security, defense, energy technologies and economic competitiveness, with main facilities in Albuquerque, New Mexico, and Livermore, California.
Writer: Chris Adam, cladam@prf.org
Source: Haiyan Wang, hwang00@purdue.edu
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-03-25
PLYMOUTH MEETING, PA [March 25, 2021] -- New recommendations to advance racial equity, ways to mitigate the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer care, and ongoing strategies for preventing and controlling HPV-associated cancers led the conversation at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network® (NCCN®) 2021 Virtual Annual Conference March 18-20. More than 1,300 attendees from across the United States and more than 40 countries met online to learn about updates to the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®) and new research in the field. Sessions explored supportive care and ways to help survivors return to work, updates on best ...
2021-03-25
For the first time, scientists have succeeded in continuous monitoring of a subglacial discharge plume, providing a deeper understanding of the glacier-fjord environment.
As marine-terminating glaciers melt, the fresh water from the glacier interacts with the seawater to form subglacial discharge plumes, or convective water flows. These turbulent plumes are known to accelerate the melting and breakup (calving) of glaciers, drive fjord-scale circulation and mixing, and create foraging hotspots for birds. Currently, the scientific understanding of the dynamics of subglacial plumes based on direct measurements is limited to isolated instances.
A team of scientists consisting of Hokkaido University's Assistant Professor Evgeny A. Podolskiy and Professor Shin Sugiyama, and the ...
2021-03-24
URBANA, Ill. - Pumpkin growers dread the tiny tan scabs that form on their fruit, each lesion a telltale sign of bacterial spot disease. The specks don't just mar the fruit's flesh, they provide entry points for rot-inducing fungus and other pathogens that can destroy pumpkins and other cucurbits from the inside out. Either way, farmers pay the price, with marketable yields reduced by as much as 90%.
Despite the disease's severity, scientists don't know much about the genetics of the pathogen that causes it; nearly all the molecular information required for accurate diagnostic testing and targeted treatments is lacking for the disease.
In a new study, University of Illinois scientists, with the help of two undergraduate students, have assembled the first complete ...
2021-03-24
Cambridge, MA - Astronomers have now obtained a new view of the supermassive black hole at the center of galaxy M87. Images released today by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration reveal how the black hole, some 55 million light-years away, appears in polarized light.
The image marks the first time astronomers have captured and mapped polarization, a sign of magnetic fields, so close to the edge of a black hole.
Scientists still don't understand how magnetic fields -- areas where magnetism affects how matter moves -- influence black hole activity. Do they help direct matter into the hungry mouths of black holes? Can ...
2021-03-24
When clinical trials were conducted to determine the immunogenicity -- the ability to elicit an immune response -- for the first two vaccines marshaled against SARS-CoV-2the virus that causes COVID-19, one group was not among those included: people who have received solid organ transplants and others (such as those with autoimmune disorders) who are immunocompromised.
Now, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers have tried to rectify that inequity, taking one of the first looks at how people who are immunocompromised respond to their first dose of one of the two mRNA vaccines -- Moderna and Pfizer-BioNTech -- currently being administered worldwide. Their findings, as published March 15, 2021, in a research letter in the END ...
2021-03-24
DANVILLE, Pa. - A survey of Geisinger employees conducted over two weeks in December 2020 found a steady increase in intent among healthcare workers to receive the COVID-19 vaccine.
On Dec. 4, 2020, an announcement about anticipated vaccine availability was emailed to all 23,784 Geisinger employees. Recipients were asked to indicate their intention to receive a vaccine when one was available to them and the reasons for any hesitation they might have. More than two-thirds of employees responded to the survey.
Of those who completed the survey before Dec. 10, when an independent FDA advisory committee ...
2021-03-24
News coverage of expert scientific evidence on vaccine safety is effective at increasing public acceptance of vaccines, but the positive effect is diminished when the expert message is juxtaposed with a personal narrative about real side effects, new research has found.
The study, by researchers affiliated with the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Illinois, tested the effects of messages about vaccination in televised news reports. These included video clips of Dr. Anthony Fauci, director of the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, talking about evidence supporting the value and safety of the MMR (measles, mumps and rubella) vaccine, and a mother who's refusing to vaccinate ...
2021-03-24
Scientists make pivotal discovery of method for wireless modulation of neurons with X-rays that could improve the lives of patients with brain disorders. The X-ray source only requires a machine like that found in a dentist's office.
Many people worldwide suffer from movement-related brain disorders. Epilepsy accounts for more than 50 million; essential tremor, 40 million; and Parkinson's disease, 10 million.
Relief for some brain disorder sufferers may one day be on the way in the form of a new treatment invented by researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory and ...
2021-03-24
Researchers Mario Guarracino the HSE Laboratory of Algorithms and Technologies for Networks Analysis in Nizhny Novgorod and Julius ?ilinskas and Algirdas Lančinskas from Vilnius University, have proposed a new method of testing for COVID-19. This group method allows results to be obtained 13 times faster as compared to individual testing of each sample. The research paper was published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The COVID-19 pandemic has already affected millions of people from over 200 countries. The rapid virus expansion demonstrated how fast such infections can spread in today's globalized world. At the beginning of the pandemic, when little was known about the virus and vaccines had not yet ...
2021-03-24
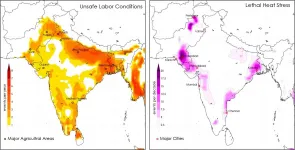
WASHINGTON--Residents of South Asia already periodically experience heat waves at the current level of warming. But a new study projecting the amount of heat stress residents of the region will experience in the future finds with 2 degrees Celsius of warming, the population's exposure to heat stress will nearly triple.
Limiting warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius will likely reduce that impact by half, but deadly heat stress will become commonplace across South Asia, according to the new study in Geophysical Research Letters, AGU's journal publishing high-impact, short-format reports with immediate implications spanning all Earth and space sciences.
With ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Technology uses 'single' approach to develop electronics, acoustics