Immune system drug shows promise in treating alcohol use disorder, a Scripps Research clinical trial reports
2023-02-28
LA JOLLA, CA—A clinical trial carried out at Scripps Research has shown that apremilast, approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of psoriasis, cuts alcohol intake by more than half in people with severe alcohol use disorder (AUD). Collaborators at Oregon Health and Science University (OHSU) and other institutions also showed that, in mice, apremilast boosts activity in an area of the brain known to be involved in AUD.
The research was published online ahead of ...
$10 million grant funds Scripps Research Alcohol Research Center through its 50th year
2023-02-28
LA JOLLA, CA—The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) has awarded scientists at Scripps Research a $10 million grant to study the cellular and molecular changes in the brain that underlie alcohol use disorder (AUD). The grant will fund the Scripps Research Alcohol Research Center (TSRI-ARC) for five years, carrying the research into its 50th year of consecutive NIAAA funding—first beginning in 1977.
“A lot of exciting things have happened in the AUD field over the last 45 years, and the center has been at the forefront of many of them,” ...
First study to show childhood obesity is linked to increased risk of four of the five newly proposed subtypes of adult-onset diabetes
2023-02-28
New research published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [EASD]) is the first study to show that childhood obesity is associated with an increased risk of four of the five recently proposed subtypes of adult-onset diabetes. The study is by Yuxia Wei, Institute of Environmental Medicine, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, and colleagues.
In 2018, a ground-breaking study identified five novel subtypes of adult-onset diabetes: severe autoimmune diabetes (SAID, including type 1 diabetes and latent autoimmune diabetes in adults [LADA]) and four ...
Pakistan streamflow timing will become three times faster by end of century
2023-02-28
Nature has remained in balance for a long time, but climate change due to modern human activities is disrupting the balance of the natural system. The disruption makes it more difficult for humans – who must work with nature to survive – to predict the future. Moreover, developing countries with limited understanding and preparation for climate change are more vulnerable to climate change-driven social and economic damage. Recently, a research team from POSTECH corrected the biases of future regional climate model projection data to ...
Forgoing one food treats eosinophilic esophagitis as well as excluding six
2023-02-28
Eliminating animal milk alone from the diet of adults with eosinophilic esophagitis, or EoE, is as effective at treating the disease as eliminating animal milk plus five other common foods, a clinical trial funded by the National Institutes of Health has found. For people with EoE whose disease remains active after they forgo animal milk, a more restrictive diet may help them achieve remission, according to the researchers. These findings were published today in the journal The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology.
“Diet-based therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis will be much ...
Are our pets leaking information about us?
2023-02-28
Are our pets leaking information about us?
Pet and animal-related apps are creating cybersecurity risks to their owners, new research has shown.
While being able to trace your cat and dog may be an attractive benefit to many pet owners as it can provide peace of mind, allowing a third party to track your movements may be much less attractive.
Computer scientists at Newcastle University and Royal Holloway, University of London have exposed multiple security and privacy issues by evaluating 40 popular Android apps for pets and other companion animals as well as farm animals. The results show that several of these apps ...
Experts demand fire safety policy change over health impact of widely used flame retardants
2023-02-28
Leading environmental health experts have called for a comprehensive review of the UK's fire safety regulations, with a focus on the environmental and health risks of current chemical flame retardants.
The health dangers of substances meant to improve fire safety have prompted experts to demand a range of new measures to reduce risk.
Flame retardants are widely used to slow down or stop the spread of fire. They are used regularly in a range of products – from sofas and textiles, to building materials. However, hundreds of studies have reported on the adverse effects of these chemicals, many of which are bioaccumulative and have been linked ...
Loneliness is central to perinatal depression
2023-02-28
Loneliness can often contribute to depression in expectant and new mothers, finds a new review of evidence led by UCL researchers.
The researchers say people working with expectant mothers, such as in antenatal classes or consultations, should be aware of the importance of loneliness and the value of encouraging new mothers to develop and maintain good social connections. The findings suggest that increased support from family and healthcare professionals can be helpful in reducing the mental health impacts of loneliness.
Published in BMC Psychiatry, the meta-synthesis (an evidence review using a systematic ...
Obesity in pregnant women could alter the structure and function of the placenta increasing the risk of poor health outcomes for both mother and baby
2023-02-28
Maternal obesity alters the structure of the placenta (a vital organ that nourishes the baby during pregnancy) more than gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM; a condition is diagnosed by poor glucose control in pregnancy). The new insight, published in The Journal of Physiology, enhances understanding about the mechanisms underlying poor pregnancy outcomes and the subsequent greater risk of poor neonatal and offspring health. The identification of specific changes in the placenta could lead to the potential development ...
Australia’s rarest bird of prey disappearing at alarming rate
2023-02-28
Australia’s rarest bird of prey - the red goshawk - is facing extinction, with Cape York Peninsula now the only place in Queensland known to support breeding populations.
PhD candidate Chris MacColl from The University of Queensland’s School of Earth and Environmental Sciences led the research project that made the discovery and was shocked by the hawk’s dwindling numbers.
“Over four decades the red goshawk has lost a third of its historical range, which ...
Local leaders announce plan to strengthen health services in Imperial County
2023-02-28
Representatives from the City of El Centro, El Centro Regional Medical Center (ECRMC), and UC San Diego Health today announced a strategic and operational plan to stabilize and financially bolster ECRMC, as well as the greater network of Imperial County hospitals.
Under the proposed 12- to 18-month plan, UC San Diego Health will assume full day-to-day operational, clinical and financial management of ECRMC while Preston Hollow Community Capital (PHCC), the majority bondholder for ECRMC, will provide financial and other resources to ECRMC for ...
Tiny worm plays a big role in learning whether Parkinson’s really starts in the gut
2023-02-28
AUGUSTA, Ga. (Feb. 28, 2023) – A tiny worm called the C. elegans is enabling scientists to explore the emerging theory that Parkinson’s disease starts in the gut.
Key to the condition known to produce uncontrollable shaking, but also characterized by cognitive problems and gastrointestinal distresses like constipation, is a sticky, toxic form of the protein alpha-synuclein, which literally gums up the works of our neurons and kills them.
Although it may seem counterintuitive, there is evidence from science labs like Neuroscientist Danielle Mor’s, PhD, that the toxic protein aggregates in the neurons ...
Gun violence spills into new neighborhoods as gentrification displaces drug crime, according to WVU study
2023-02-27
Gentrification doesn’t erase drug crime and gun violence. Instead, research from West Virginia University economist Zachary Porreca shows that when one urban block becomes upwardly mobile, organized criminal activity surges outward to surrounding blocks, escalating the violence in the process.
Porreca, a WVU doctoral student in the John Chambers College of Business and Economics, analyzed 2011-2020 data on shootings and real estate across various Philadelphia neighborhoods. His paper presenting the findings, published in the Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization, is one of the first of its kind to study the impact of gentrification ...
Astronomers discover metal-rich galaxies in early universe
2023-02-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – While analyzing data from the first images of a well-known early galaxy taken by NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), Cornell University astronomers discovered a companion galaxy previously hidden behind the light of the foreground galaxy — one that surprisingly seems to have already hosted multiple generations of stars despite its young age, estimated at 1.4 billion years old.
“We found this galaxy to be super-chemically abundant, something none of us expected,” said Bo Peng, a doctoral student in astronomy, ...
Climate trends in the west, today and 11,000 years ago
2023-02-27
People often say things like Phoenix has always been dry; Seattle has always been wet; and San Francisco has always been foggy. But “always” is a strong word.
A study from the University of California, Davis, synthesizes climate trends across the Western U.S. during a relatively young period of Earth’s history — the Holocene Era, which stretches from the present day to the past 11,000 years. This look at the really Old West shows that the hallmarks of California’s climate — the foggy coastlines ...
Mysteries of the Earth: FSU researchers predict how fast ancient magma ocean solidified
2023-02-27
Early in the formation of Earth, an ocean of magma covered the planet’s surface and stretched thousands of miles deep into its core. The rate at which that “magma ocean” cooled affected the formation of the distinct layering within the Earth and the chemical makeup of those layers.
Previous research estimated that it took hundreds of million years for that magma ocean to solidify, but new research from Florida State University published in Nature Communications narrows these large uncertainties down to less than just a couple of million years.
“This magma ocean has been an important part of Earth’s history, and this study helps us answer ...
The Texas Heart Institute delivers a new first in heart failure treatment using cell therapy
2023-02-27
Houston, TX – February 27, 2023 – Physician-scientists at The Texas Heart Institute announced today the results of the largest cell therapy trial to date in patients with chronic heart failure due to low ejection fraction. The therapy benefited patients by improving the heart’s pumping ability, as measured by ejection fraction, and reducing the risk of heart attack or stroke, especially in patients who have high levels of inflammation. Also, a strong signal was found in the reduction of cardiovascular death in patients treated with cells. The findings ...
Augmented reality headset enables users to see hidden objects
2023-02-27
MIT researchers have built an augmented reality headset that gives the wearer X-ray vision.
The headset combines computer vision and wireless perception to automatically locate a specific item that is hidden from view, perhaps inside a box or under a pile, and then guide the user to retrieve it.
The system utilizes radio frequency (RF) signals, which can pass through common materials like cardboard boxes, plastic containers, or wooden dividers, to find hidden items that have been labeled with RFID tags, which reflect ...
How common is face blindness?
2023-02-27
How Common Is Face Blindness?
Study suggests condition affects more people than previously thought
For Immediate Release
Media Contacts:
Dennis Nealon
Dennis_Nealon@hms.harvard.edu
508-494-6117
Ekaterina Pesheva
Ekaterina_Pesheva@hms.harvard.edu
617-432-0441
At a Glance:
Study by researchers at Harvard Medical School/VA Boston Healthcare System suggests that face blindness lies on a continuum and may be more common than currently believed.
The study found similar face matching performance between prosopagnosics diagnosed with stricter vs. looser criteria, suggesting that the diagnostic criteria should be expanded.
As many as ...
Midwifery care safe for moderate- and high-risk pregnancies
2023-02-27
New UBC research shows that midwives in British Columbia are providing safe primary care for pregnancies of all medical risk levels, contrary to a popular belief that midwives mostly manage low-risk pregnancies.
The study, published in the Canadian Medical Association Journal, examined a decade of births in B.C. between 2008 and 2018. The researchers compared birth outcomes for people who had a midwife as their most responsible provider (MRP), with those who were cared for by a family physician or obstetrician.
The findings reveal that people who had a ...
Sustainable chemistry experts create blueprint for safer future
2023-02-27
Feb. 27, 2023
Media contacts:
Emily Gowdey-Backus, director of media relations, Emily_GowdeyBackus@uml.edu
Nancy Cicco, assistant director of media relations, Nancy_Cicco@uml.edu
Sustainable chemistry experts create blueprint for safer future
Group to share its work during free UMass Lowell webinar on March 1
Toxic chemicals – which pop up in everything from household cleaners and appliances to medical devices, paints, packaging and more – are all around. The February ...
Early-life stress can disrupt maturation of brain’s reward circuits, promoting disorders
2023-02-27
Irvine, Calif., Feb. 27, 2023 — A new brain connection discovered by University of California, Irvine researchers can explain how early-life stress and adversity trigger disrupted operation of the brain’s reward circuit, offering a new therapeutic target for treating mental illness. Impaired function of this circuit is thought to underlie several major disorders, such as depression, substance abuse and excessive risk-taking.
In an article recently published online in Nature Communications, Dr. Tallie Z. Baram, senior author and UCI Donald Bren Professor and Distinguished Professor in the Departments of Anatomy & Neurobiology, ...
Cedars-Sinai’s efforts to combat lower back pain get $2 million boost from CIRM
2023-02-27
Investigators at Cedars-Sinai have received a $2 million grant from the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM) to develop a new cell therapy that helps improve quality of life for patients with degenerated discs and chronic lower back pain.
Dmitriy Sheyn, PhD, assistant professor in the departments of Orthopaedics, Surgery and Biomedical Sciences at Cedars-Sinai leads this new project in collaboration with Debiao Li, PhD, director of the Biomedical Imaging Research Institute and professor of Biomedical Sciences and Imaging at Cedars-Sinai; and Hyun Bae, MD, professor of Orthopaedics and co-medical ...
Amazon develops algorithm to improve collaboration between robots and humans
2023-02-27
New Study Key Takeaways:
A new algorithm is identified to allow robots and humans to work together efficiently and profitably.
Robots bring shelves of inventory to associates to pick for customer orders.
The adoption of the algorithm cuts down on distance traveled by pods as well as the storage footprint for the company.
The fulfillment operation with the new algorithm results in a half a billion dollars in savings.
BALTIMORE, MD, February 27, 2023 – Amazon has identified a financially beneficial way for robots and humans to coexist, and it’s saving the online enterprise half a billion dollars per year. Using robots to bring ...
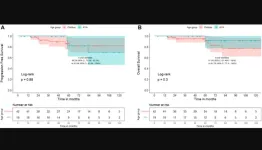
Oncotarget | WNT-pathway medulloblastoma: What constitutes low-risk and how low can one go?
2023-02-27
“The definition of low-risk WNT-pathway medulloblastoma may need to be refined in light of recent clinical data and newer biological information.”
BUFFALO, NY- February 27, 2023 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on February 7, 2023, entitled, “WNT-pathway medulloblastoma: what constitutes low-risk and how low can one go?”
Novel biological insights have established that medulloblastoma is a heterogenous disease comprising four broad molecular subgroups - WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 respectively, resulting in the incorporation of molecular/genetic information in 5th edition ...
[1] ... [2077]
[2078]
[2079]
[2080]
[2081]
[2082]
[2083]
[2084]
2085
[2086]
[2087]
[2088]
[2089]
[2090]
[2091]
[2092]
[2093]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.