Employees tend to avoid taking breaks despite high levels of stress
2023-03-16
Heavy workloads make employees feel a greater need for a break, but new research finds they may actually discourage employees from taking breaks at work despite causing high levels of stress, fatigue, and poor performance.
Researchers from the University of Waterloo found employees often kept working despite wanting to pause. One potential reason is employees may have felt pressure to continue working to get everything done on time.
“Our research provides a comprehensive account of the processes involved in the decision to take a break and provides insights into how employees and managers can make more effective use of breaks at work, ...
Aging | AAV1.NT-3 gene therapy prevents age-related sarcopenia
2023-03-15
“Considering the cost and quality of life to the individual, we believe our study has important implications for management of age-related sarcopenia.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 15, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 5, entitled, “AAV1.NT-3 gene therapy prevents age-related sarcopenia.”
Sarcopenia is progressive loss of muscle mass and strength occurring during normal aging with significant consequences on the quality of life for elderly. Neurotrophin 3 (NT-3) is an important autocrine factor supporting ...
Where the sidewalk ends
2023-03-15
It’s easier than ever to view maps of any place you’d like to go — by car, that is. By foot is another matter. Most cities and towns in the U.S. do not have sidewalk maps, and pedestrians are usually left to fend for themselves: Can you walk from your hotel to the restaurants on the other side of the highway? Is there a shortcut from downtown to the sports arena? And how do you get to that bus stop, anyway?
Now MIT researchers, along with colleagues from multiple other universities, have developed an open-source tool that uses aerial imagery and image-recognition to create complete maps of sidewalks and crosswalks. The tool can help planners, policymakers, ...
HSE researchers examine wellbeing of Russian social media users and rank public holidays by popularity
2023-03-15
Researchers of the HSE Graduate School of Business trained a machine-learning (ML) model to infer users' subjective wellbeing from social media posts. Having processed 10 million tweets, the researchers compiled a rating of holidays celebrated in Russia based on their popularity. The New Year tops the list, but Russian-speaking users of Twitter are also happy to celebrate Defender of the Fatherland Day, International Women's Day, Victory Day and Halloween. The study findings have been published in PeerJ Computer Science.
As one of the most popular methods for ...
Good news for those with MS—fertility treatments not linked to increase in relapses
2023-03-15
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 15, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – There’s good news for those with multiple sclerosis (MS). A new study has found that female participants were no more likely to have a flare-up of the disease after receiving fertility treatments than they were before their treatments. The study is published in the March 15, 2023, online issue of Neurology® Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation, an official journal of the American Academy of Neurology. Earlier studies had shown conflicting results. The study also found a link between the use of MS medications and a lack of increase in relapses during fertility ...
UTA team to measure pollutants in DC sewer pipe project
2023-03-15
A University of Texas at Arlington civil engineering researcher received a one-year, $300,000 competitive grant from the Water Research Foundation to evaluate a trenchless process to renew sanitary sewer pipes in Soapstone Valley Park, a popular Washington, D.C., attraction.
Mohammad Najafi, associate professor in the Department of Civil Engineering, is leading the project.
Najafi said the project will use a trenchless cured-in-place-pipe (CIPP) method that relines the old sewer pipe with new plastic material. That material then is cured in place with hot water.
“We will ...
Tak W. Mak, PhD, FAACR, selected for 2023 Pezcoller Foundation-AACR International Award for Extraordinary Achievement in Cancer Research
2023-03-15
PHILADELPHIA – The Pezcoller Foundation–American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) International Award for Extraordinary Achievement in Cancer Research will be presented to Tak W. Mak, PhD, Fellow of the AACR Academy, during the AACR Annual Meeting 2023, April 14-19 at the Orange County Convention Center in Orlando, Florida.
Mak is a senior scientist at the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, University Health Network, as well as a university professor in the departments of medical biophysics and immunology at the Temerty Faculty of Medicine ...
Kermanshachi receives 40 Under 40 award
2023-03-15
Sharareh “Sherri” Kermanshachi, a University of Texas at Arlington associate professor of civil engineering, has received the 40 Under 40 Award from Mass Transit magazine, which recognizes individuals who have shown a capacity for innovation and demonstrated leadership and a commitment to making an impact in transit.
“I am honored and humbled to receive this award and be named to the 40 Under 40 Mass Transit award list,” said Kermanshachi, who is also director of the Resilient Infrastructures and Sustainable Environment ...
Nobel Laureate Carolyn R. Bertozzi, PhD, to receive 2023 AACR Award for Outstanding Achievement in Chemistry in Cancer Research
2023-03-15
PHILADELPHIA – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) will honor Nobel Laureate Carolyn R. Bertozzi, PhD, with the 2023 AACR Award for Outstanding Achievement in Chemistry in Cancer Research during the AACR Annual Meeting 2023, April 14-19 in Orlando, Florida.
Bertozzi is the Anne T. and Robert M. Bass Professor of Chemistry in the School of Humanities and Sciences and a professor (by courtesy) of chemical and systems biology and of radiology at Stanford University, an investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and the Baker Family Director of Sarafan ChEM-H. Bertozzi is being recognized for advancing basic ...
Study offers a potential strategy to improve T cell therapy in solid tumors
2023-03-15
PHILADELPHIA – A new approach that delivers a “one-two punch” to help T cells attack solid tumors is the focus of a preclinical study by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The findings, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), showed that targeting two regulators that control gene functions related to inflammation led to at least 10 times greater T cell expansion in models, resulting in increased antitumor immune activity and durability.
CAR T cell therapy was pioneered at Penn Medicine by ...
Uncovering the ritual past of an ancient stone monument in Saudi Arabia
2023-03-15
A comprehensive analysis of an archaeological site in Saudi Arabia sheds new light on mustatils—stone monuments from the Late Neolithic period thought to have been used for ritual purposes. Melissa Kennedy of the University of Western Australia, Perth, and colleagues, in conjunction with The Royal Commission for AlUla present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 15, 2023.
Built around 7,000 years ago, mustatils are rectangular, low-walled, stone structures that range from 20 to 600 meters in length. Researchers first discovered them in the 1970s, and more than 1,600 mustatils have now been discovered, primarily concentrated in northern ...
The WWII shipwreck of the SS Thistlegorm, now a popular Red Sea dive site, has formed an artificial coral reef for a diverse community of fish, according to data gathered by volunteer divers
2023-03-15
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282239
Article Title: Eight years of community structure monitoring through recreational citizen science at the “SS Thistlegorm” wreck (Red Sea)
Author Countries: Italy
Funding: STE project was funded by Project AWARE Foundation, ASTOI Association, Ministry of Tourism of the Arab Republic of Egypt, Settemari S.p.A Tour Operator, Scuba Nitrox Safety International, Viaggio nel Blu Diving Center. The funders had no role in study design, data collection ...
Analysis links specific skills taught by US undergraduate degree courses with graduate earnings
2023-03-15
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282323
Article Title: Connecting higher education to workplace activities and earnings
Author Countries: USA
Funding: This research is supported in part by the University of Pittsburgh Pitt Momentum Fund and the Center for Research Computing. This work has been supported (in part) by # 2109-33808 from the Russell Sage Foundation. Any opinions expressed are those of the principal investigator(s) alone and should not be construed as representing the opinions of the Foundation. The funders had no role in study design, data collection ...
Estrogen possible risk factor in disturbed heart rhythm
2023-03-15
The sex hormone estrogen has a negative impact on heartbeat regulation, according to an experimental study from Linköping University, Sweden, published in Science Advances. Estrogen impact seems to interact with hereditary changes causing a heart disease disturbing the heart’s rhythm, while other endogenous substances may have a protecting effect.
In a lifetime, the heart beats around 2.5 billion times. Each heartbeat is triggered by an electrical impulse that causes the heart muscle to contract in a very well-coordinated movement. ...
Radar images record potential volcanic activity on Venus
2023-03-15
Researchers have identified evidence they interpret as active volcanism on the surface of Venus, according to a new analysis of radar images from the Magellan spacecraft. The images reveal a vent that changed shape on Venus, which they believe points to ongoing volcanic activity there. Many volcanoes have been identified on the surface of Venus, but evidence of recent volcanic activity on the planet has been lacking. As a result, it was unknown whether the prominent volcanic features of Venus’ geologically young surface are a product of ongoing active volcanism ...
AJR on a decade of lung cancer screening in American newspapers
2023-03-15
Leesburg, VA, March 15, 2023—According to an accepted manuscript published in ARRS’ own American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), sentiment of U.S. newspaper articles covering lung cancer screening (LCS) from 2010 to 2022 was overall positive; however, certain key elements of LCS were infrequently mentioned.
“The findings highlight areas for potential improvement of LCS media coverage; radiologists have an opportunity to take a more active role in this coverage,” concluded first author Brent P. Little, MD, of Mayo Clinic Florida in Jacksonville.
Little et al. searched the ProQuest U.S. Newsstream ...
Resilient bug-sized robots keep flying even after wing damage
2023-03-15
Bumblebees are clumsy fliers. It is estimated that a foraging bee bumps into a flower about once per second, which damages its wings over time. Yet despite having many tiny rips or holes in their wings, bumblebees can still fly.
Aerial robots, on the other hand, are not so resilient. Poke holes in the robot’s wing motors or chop off part of its propellor, and odds are pretty good it will be grounded.
Inspired by the hardiness of bumblebees, MIT researchers have developed repair techniques that enable a bug-sized aerial robot to sustain severe damage to the actuators, or artificial muscles, that power its wings — but to still fly effectively.
They optimized these artificial muscles ...
Psychological intervention reduced stress during COVID lockdown
2023-03-15
Resilience and well-being in difficult times can be developed via online interventions in the workplace. An international team of researchers from France, the UK and Russia (with the participation of researchers from the HSE International Laboratory of Positive Psychology of Personality and Motivation) studied the effectiveness of SPARK Resilience, a programme for developing resilience, at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. The results of the study were published in the PLOS One journal.
By creating the SPARK Resilience programme, psychologists focused on helping people gain ...
Biotechnologies harnessing microbes might enable us to extract rare elements and minerals, chemicals and fuels from wastewater
2023-03-15
Biotechnologies harnessing microbes might enable us to extract rare elements and minerals, chemicals and fuels from wastewater.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/water/article?id=10.1371/journal.pwat.0000105
Article Title: Environmental biotechnologies can make water pollutants part of the path to mitigating climate change
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The author received no specific funding for this work.
END ...
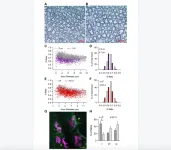
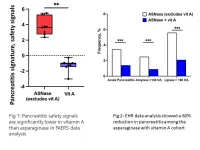
Vitamin A may reduce pancreatitis risk during ALL treatment
2023-03-15
Consuming a diet rich in vitamin A or its analogs may help prevent children and young adults with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) reduce their risk of developing painful pancreas inflammation during chemotherapy treatment.
Details about this potential dietary solution to prevent a potentially life-threatening adverse event were published March 15, 2023, in Science Translational Medicine. The research team was led by Sohail Husain, MD, chief of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition at Stanford University and Anil Goud Jegga, DVM, MRes, a computational ...
UAF scientist offers evidence that Venus is volcanically active
2023-03-15
Embargoed: Not for release until 2 p.m. U.S. Eastern time Wednesday, March 15, 2023
Venus appears to have volcanic activity, according to a new research paper that offers strong evidence to answer the lingering question about whether Earth’s sister planet currently has eruptions and lava flows.
Venus, although similar to Earth in size and mass, differs markedly in that it does not have plate tectonics. The boundaries of Earth’s moving surface plates are the primary locations of volcanic activity.
New research by University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute research professor Robert Herrick revealed ...
A nonnative tree species reclaims its prominence after extreme weather
2023-03-15
The long-term effects on forests of more extreme climate events, plus other drivers of forest change, are highly uncertain. A new study of the tropical forests across Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands (USVI), spanning 19 years, found that after Hurricane Maria in 2017, the total biomass of a fast-growing nonnative species, the African tulip Tree (Spathodea campanulata), may again be overtaking that of the most common group of native tree species, even though, at least for young and small trees, nonnatives ...
Antidepressant medication may be key to help people stop use of cocaine while in treatment for opioid use disorder
2023-03-15
For some people receiving methadone for treatment of opioid use disorder (OUD), the co-use of opioids and stimulants such as cocaine is an issue. Now, a new study led by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers found that bupropion, an antidepressant medication also used for smoking cessation, may help people stop using cocaine while in treatment for OUD.
The results of the study were published March 15 in JAMA Network Open.
For this double-blind randomized study, the researchers used an adaptive treatment design, meaning that it allowed ...
Zook joins The Gerontological Society of America’s Board of Directors
2023-03-15
The Gerontological Society of America (GSA) — the nation’s largest interdisciplinary organization devoted to the field of aging — has named David Zook of Faegre Drinker LLP as an at-large member of its Board of Directors.
GSA’s Board of Directors provides governance oversight, establishes Society policy, sets the organization’s strategic plan, and oversees implementation thereof. It comprises 12 members representing the broad diversity of the Society’s membership. Zook’s three-year term became effective January 1.
“GSA is very effective in applying knowledge to policymaking as the role of older individuals in our society continues to evolve,” ...
Breakthrough drug combination remains safe and effective in patients with cystic fibrosis after four years
2023-03-15
Patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) face difficulty breathing and a decline in lung function and are at risk of early death. CF is an inherited condition that results in thick mucus build-up, persistent infection and inflammation in the lungs.
Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) researcher Patrick Flume, M.D., was lead author of a recent Journal of Cystic Fibrosis article reporting the findings of a trial of a two-drug combination for treating CF. The study demonstrated long-term safety and clinical benefit of the combination therapy. Flume is director of the ...
[1] ... [2044]
[2045]
[2046]
[2047]
[2048]
[2049]
[2050]
[2051]
2052
[2053]
[2054]
[2055]
[2056]
[2057]
[2058]
[2059]
[2060]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.