Researcher-community partnership uses collaborative process to yield novel insights
2023-03-17
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Until recently, psychologist Kalina Michalska had never used community-based participatory research, or CBPR, in her work, but now she can’t imagine not using it.
CBPR, which dates to the early 1930s, is an intensive research approach that involves partnerships between researchers and community members throughout the research process, giving communities a voice in how the research proceeds and allowing them to make use of the findings more effectually.
The study led by Michalska, an ...
Boosting survival of a beneficial bacterium in the human gut
2023-03-17
New Haven, Conn. — The microbes that inhabit the gut are critical for human health, and understanding the factors that encourage the growth of beneficial bacterial species — known as “good” bacteria — in the gut may enable medical interventions that promote gut and overall human health. In a new study, Yale researchers have uncovered a novel mechanism by which these bacteria colonize the gut.
Specifically, the Yale team discovered that one of the most abundant beneficial species found in the human gut showed an increase in colonization potential when experiencing carbon limitation — a finding that could yield novel clinical ...
International Society for Autism Research (INSAR) 22nd Annual Meeting to be held in Stockholm, Sweden May 3- 6, 2023
2023-03-17
The International Society for Autism Research (INSAR) will hold its 2023 Annual Meeting – the organization’s 22nd – from Wednesday, May 3 through Saturday, May 6, 2023, bringing together a global, multidisciplinary group of hundreds of autism researchers, clinicians, advocates, self-advocates, and students to exchange the latest scientific learnings and discoveries that are advancing the expanding understanding of autism and its complexities. This year’s meeting will be held in-person in Stockholm, Sweden at Stockholmsmässan, the largest exhibition facility in the Nordic region.
The INSAR ...
Genomic study of ancient humans sheds light on human evolution on the Tibetan Plateau
2023-03-17
The Tibetan Plateau, the highest and largest plateau above sea level, is one of the harshest environments settled by humans. It has a cold and arid environment and its elevation often surpasses 4000 meters above sea level (masl). The plateau covers a wide expanse of Asia—approximately 2.5 million square kilometers—and is home to over 7 million people, primarily belonging to the Tibetan and Sherpa ethnic groups.
However, our understanding of their origins and history on the plateau is patchy. Despite a rich archaeological context spanning the plateau, ...
Key role identified for nervous system in severe allergic shock
2023-03-17
DURHAM, N.C. – A key feature of the severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis is an abrupt drop in blood pressure and body temperature, causing people to faint and, if untreated, potentially die.
That response has long been attributed to a sudden dilation and leakage of blood vessels. But in a study using mice, Duke Health researchers have found that this response, especially body temperature drop, requires an additional mechanism – the nervous system.
Appearing online March 17 in the journal Science Immunology, the study could ...
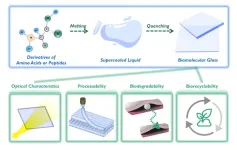
Researchers develop biodegradable, biorecyclable glass
2023-03-17
Everyone is familiar with glass—from putting on eyeglasses, pushing open the window, standing in front of a mirror, to holding a water glass. Glass is ubiquitous in nature and essential to human life.
But the widespread use of persistent, non-biodegradable glass that cannot be naturally eliminated causes long-term environmental hazards and social burdens.
To solve this problem, a research group led by Prof. YAN Xuehai from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a family of eco-friendly glass of biological origin fabricated from biologically derived amino acids or peptides. The ...
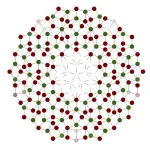
Qubits put new spin on magnetism: Boosting applications of quantum computers
2023-03-17
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 17, 2023 — Research using a quantum computer as the physical platform for quantum experiments has found a way to design and characterize tailor-made magnetic objects using quantum bits, or qubits. That opens up a new approach to develop new materials and robust quantum computing.
“With the help of a quantum annealer, we demonstrated a new way to pattern magnetic states,” said Alejandro Lopez-Bezanilla, a virtual experimentalist in the Theoretical Division at Los Alamos National Laboratory. ...
New combination of drugs works together to reduce lung tumors in mice
2023-03-17
LA JOLLA—(March 17, 2023) Cancer treatments have long been moving toward personalization—finding the right drugs that work for a patient’s unique tumor, based on specific genetic and molecular patterns. Many of these targeted therapies are highly effective, but aren’t available for all cancers, including non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) that have an LKB1 genetic mutation. A new study led by Salk Institute Professor Reuben Shaw and former postdoctoral fellow Lillian Eichner, now an assistant professor ...
Biomarkers show promise for identifying early risk of pancreatic cancer
2023-03-17
DURHAM, N.C. – A research team at Duke Health has identified a set of biomarkers that could help distinguish whether cysts on the pancreas are likely to develop into cancer or remain benign.
Appearing online March 17 in the journal Science Advances, the finding marks an important first step toward a clinical approach for classifying lesions on the pancreas that are at highest risk of becoming cancerous, potentially enabling their removal before they begin to spread.
If successful, the biomarker-based approach could address the biggest impediment to decreasing the ...
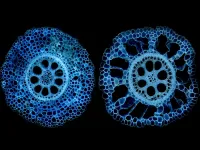
Discovery of root anatomy gene may lead to breeding more resilient corn crops
2023-03-17
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — A new discovery, reported in a global study that encompassed more than a decade of research, could lead to the breeding of corn crops that can withstand drought and low-nitrogen soil conditions and ultimately ease global food insecurity, according to a Penn State-led team of international researchers.
In findings published March 16 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, the researchers identified a gene encoding a transcription factor – a protein useful for converting DNA into RNA – that triggers a genetic sequence responsible for the development of an important trait enabling corn roots ...
New study shows social media content opens new frontiers for sustainability science researchers
2023-03-17
With more than half of the world’s population active on social media networks, user-generated data has proved to be fertile ground for social scientists who study attitudes about the environment and sustainability.
But several challenges threaten the success of what's known as social media data science. The primary concern, according to a new study from an international research team, is limited access to data resulting from restrictive terms of service, shutdown of platforms, data manipulation, censorship and regulations.
The study, published online March ...
East and West Germans show preference for different government systems 30 years on
2023-03-17
Even after 27 years of reunification, East Germans are still more likely to be pro-state support than their Western counterparts, a new study published in the De Gruyter journal German Economic Review finds. Of the sample studied, 48% of respondents from the East said it was the government’s duty to support the family compared to 35% from the West.
The study led by Prof. Nicola Fuchs-Schündeln of Goethe University Frankfurt, Germany builds on her earlier work which evaluated results from the German Socio-Economic Panel, a regular survey of around 15,000 households. The survey has been running in the federal ...
NASA announces future launch for USU-led space weather mission
2023-03-17
NORTH LOGAN, UTAH - NASA has announced that the launch of the Utah State University Space Dynamics Laboratory and College of Science-led Atmospheric Waves Experiment, or AWE, is scheduled for December 2023. The NASA-funded instrument will launch from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station to the International Space Station.
AWE Principal Investigator Michael Taylor from USU’s College of Science leads a team of scientists that will provide new details about how the weather on Earth interacts with, and affects, space weather. To do that, the AWE instrument, measuring about 54 centimeters by 1 meter and weighing less than 57 kilograms, will peer into Earth’s ...
Quantum sensing in outer space: New NASA-funded research will build next-gen tech to better measure climate
2023-03-17
Texas Engineers are leading a multi-university research team that will build technology and tools to improve measurement of important climate factors by observing atoms in outer space.
They will focus on the concept of quantum sensing, which use quantum physics principles to potentially collect more precise data and enable unprecedented science measurements. These sensors could help satellites in orbit collect data about how atoms react to small changes in their environment, and using that to infer the ...
Scientists identify the mechanisms leading to resistance to lung cancer treatment with Sotorasib, the first KRAS inhibitor
2023-03-17
A collaborative study carried out by the groups of Matthias Drosten, principal investigator at the Cancer Research Center (CSIC- University of Salamanca), and Mariano Barbacid, head of the Experimental Oncology group at the CNIO, reveals the mechanisms responsible for the development of tumor resistance to Sotorasib, the first approved inhibitor against the KRAS oncogene.
The study, recently published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, shows that lung tumor cells can rapidly adapt to this drug by increasing the number of copies of the mutated KRAS gene targeted by the treatment and by increased expression of xenobiotic pathways that limit ...
Fossil site is ‘Rosetta Stone’ for understanding early life
2023-03-17
Fossil site is ‘Rosetta Stone’ for understanding early life
Leading edge technology has uncovered secrets about a world-renowned fossil hoard that could offer vital clues about early life on earth.
Researchers who analysed the 400 million-year-old-cache, found in rural north-east Scotland, say their findings reveal better preservation of the fossils at a molecular level than was previously anticipated.
Fresh scrutiny of the exquisitely preserved treasure trove from Aberdeenshire has enabled scientists to identify the chemical fingerprints of the various organisms within ...
3D-printed revolving devices can sense how they are moving
2023-03-17
Integrating sensors into rotational mechanisms could make it possible for engineers to build smart hinges that know when a door has been opened, or gears inside a motor that tell a mechanic how fast they are rotating. MIT engineers have now developed a way to easily integrate sensors into these types of mechanisms, with 3D printing.
Even though advances in 3D printing enable rapid fabrication of rotational mechanisms, integrating sensors into the designs is still notoriously difficult. Due to the complexity of the rotating parts, sensors are typically embedded manually, after the device has already ...
Tackling gambling harm among Armed Forces veterans
2023-03-17
Swansea University News Release
17 March 2023
£1 million for projects involving Swansea experts to tackle gambling harm among Armed Forces veterans
Research to tackle gambling harm among Armed Forces veterans has received a major boost with three awards, totalling £1 million, for new projects in the field that involve Swansea University experts.
The projects include evaluating a smartphone app for veterans with gambling disorder and PTSD, which is aimed at reducing symptoms,
The three projects ...
Rivers and streams in the Andean Cordillera are hot spots for greenhouse gases emissions
2023-03-17
A new scientific study by researchers from the University of Liège (Belgium) shows that rivers in the Andean mountains contribute 35% and 72% of riverine emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2 ) and methane (CH4 ) in the Amazon basin, the world's largest river. This study is published in the journal Communications Earth & Environment.
Rivers contribute substantially to global emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4). The Amazon River, the World's largest river, plays an important role in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. It is the largest river on the planet in terms of freshwater flow," explains Alberto Borges, ...
Dual-task walking performance may be an early indicator of accelerated brain aging
2023-03-17
Boston, MA -- Walking is a complex task that is most commonly performed while completing other tasks like talking, reading signs, or making decisions. For most, after the age of 65, such “dual tasking” worsens walking performance and may even cause unsteadiness. Intriguingly, older adults that are more affected by dual tasking are at higher risk of suffering adverse health outcomes, including both falls and dementia.
A new research study published in Lancet Healthy Longevity has reported that the ability to dual task when walking starts to decline by the age of 55, up to a decade before ‘old ...
New study counts the environmental cost of managing Japanese knotweed
2023-03-17
New Swansea University research has looked at the long-term environmental impact of different methods to control Japanese knotweed.
The invasive species has been calculated to cost more than £165 million to manage every year in the UK alone. Its presence can blight property purchases for households across the country.
This has led to the development of different ways of trying to control it but with sustainability becoming increasingly important, understanding the effect of these management methods is vital.
A new study, led by biosciences lecturer Dr Sophie Hocking and looking ...
Discovery of an unexpected function of blood immune cells : Their ability to proliferate !
2023-03-17
The ability of a cell to divide, to proliferate, is essential for life and gives rise to the formation of complex organisms from a single cell. It also allows the replacement of used cells from a limited number of “stem” cells, which then proliferate and specialize. In cancer, however, cell proliferation is no longer controlled and becomes chaotic. Researchers from the GIGA Institute at the University of Liège have discovered that, in a healthy individual, certain blood immune cells, the monocytes, ...
Women working rotating shifts especially likely to be frail, York study finds
2023-03-17
March 17, 2023, TORONTO — A new study led by researchers at York University has found a link between shift work and frailty among middle-aged and older workers in Canada, especially for women on rotating shifts.
While there is a large body of research suggesting the disruptions to circadian rhythms that shift workers experience are linked to various illnesses, this study was the first to take a comprehensive or “holistic” look at the connection between shift work and frailty.
“We cannot ignore the negative health outcomes related to shift work, including cardiovascular diseases, ...
Argonne hosts conference for undergraduate women in physics
2023-03-17
The U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory hosted an American Physical Society (APS) Conference for Undergraduate Women in Physics (CUWiP) on Jan. 20-22. The conference series, sponsored by DOE and the National Science Foundation, is designed to support undergraduate women and gender minorities in physics by connecting them with resources, community, information on graduate school and professionals in their field. It also provides students with access to other women in physics with whom they can share experiences, advice and ideas.
The January 2023 event is one of 14 APS CUWiP events hosted across the country and ...
How can we tackle the biggest challenges? Ask a plant
2023-03-17
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., March 16, 2023 — Without plants, we’d have no air to breathe or food to eat, yet plant science lingers in the shadowy wings while other fields take center stage. With the goal of shining the spotlight on plants, a new study presents the field’s top 100 most pressing questions for research to address the greatest challenges facing humanity.
“The study highlights the importance of plant science for society by laying out myriad questions and technical challenges ...
[1] ... [2039]
[2040]
[2041]
[2042]
[2043]
[2044]
[2045]
[2046]
2047
[2048]
[2049]
[2050]
[2051]
[2052]
[2053]
[2054]
[2055]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.