Aging | Parsing chronological and biological age effects on vaccine responses
2023-03-27
“Ultimately, while both chronological and biological age appear to be important determinants of vaccine-preventable outcomes in older adults, the underlying context and mechanisms of their effects remain unclear.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 27, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 5, entitled, “Parsing chronological and biological age effects on vaccine responses.”
Researchers ...
Beneficial bacteria in the infant gut uses nitrogen from breast milk to support baby’s health
2023-03-27
A University of Massachusetts Amherst nutrition scientist who has spent his career studying breast milk has demonstrated how beneficial microbes in the gut of infants use nitrogen from human milk to support pediatric nutrition and development.
“The molecules in breast milk not only feed the baby but also feed the baby’s microbiome,” says David Sela, associate professor of food science and director of the Fergus M. Clydesdale Center for Foods for Health and Wellness. “This ...
Study finds neighborhood apps increase perceptions of crime rates
2023-03-27
How often do you glance at your neighborhood app, like Nextdoor or others, and learn about some crime in your area? Surely, it was not the intention of the app developers, but every time you hear of a crime nearby you might think that crime in your area is rampant. A new study by a University of Houston psychologist indicates that is exactly how the mind works – those helpful and popular neighborhood apps are actually increasing perceptions of crime rates that may not be as high as you think.
“Neighborhood ...
Can cannabis use disorder be accurately diagnosed?
2023-03-27
Cannabis use disorder is defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders as a problematic pattern leading to clinically significant impairment or distress, with symptoms that may include increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, strong desire to use marijuana and spending large amounts of time using cannabis.
Tammy Chung, director of the Center for Population Behavioral Health at Rutgers Institute for Health, Health Care Policy and Aging Research, along with colleagues Marc Steinberg of Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School and Mary Barna Bridgeman of the Rutgers ...
SCAI and HRS release expert consensus on transcatheter left atrial appendage closure
2023-03-27
WASHINGTON (March 27, 2023) – Today, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) released an updated expert consensus statement on transcatheter left atrial appendage closure (LAAC). SCAI and HRS prioritized the development of an updated consensus statement to provide recommendations on contemporary, evidence-based best practices for transcatheter LAAC focusing on endovascular devices.
Left atrial appendage closure is a minimally invasive procedure that is used to reduce the risk of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation. ...
Beaver fossil named after Buc-ee’s
2023-03-27
A new species of ancient beaver that was rediscovered by researchers in The University of Texas at Austin’s fossil collections has been named after Buc-ee’s, a Texas-based chain of popular travel centers known for its cartoon beaver mascot.
The beaver is called Anchitheriomys buceei, or “A. buceei” for short.
Steve May, a research associate at the UT Jackson School of Geosciences, said that the beaver’s Texas connection and a chance encounter with a Buc-ee’s billboard are what inspired the name.
May is the lead author of the paper that describes A. buceei, along with another, much smaller, species of fossil beaver. Published ...
James Chappell wins NSF CAREER Award
2023-03-27
HOUSTON – (March 27, 2023) – Rice University bioscientist and synthetic biologist James Chappell has won a National Science Foundation CAREER Award to develop RNA programming methods to improve human health and the environment.
“Synthetic biology has progressed a lot in the past decade, and we’ve gotten really good at genetically programming microbes in confined laboratory environments where conditions are ideal,” said Chappell, an assistant professor both of biosciences and of bioengineering. “But, of course, most microbes on the planet don't live in pure cultures where the temperature is always 37 degrees ...
In bid to make child cancer treatments safer, scientists find possible warning signs of severe reaction
2023-03-27
Scientists seeking a way to eliminate an adverse reaction to treatments for acute lymphocytic leukemia, a common childhood cancer, have found what they believe to be an early warning indicator.
Mouse studies conducted by Rutgers researchers as part of a larger scientific team are pointing to vitamin A levels as a signal that a patient may or may not be vulnerable to a dangerous toxicity.
Summarizing their findings in Science Translational Medicine, the scientists found that, in patients being treated for acute lymphocytic leukemia with the chemotherapy drug asparaginase, there is an ...
HIV can persist for years in myeloid cells of people on antiretroviral therapy
2023-03-27
A subset of white blood cells, known as myeloid cells, can harbor HIV in people who have been virally suppressed for years on antiretroviral therapy, according to findings from a small study supported by the National Institutes of Health. In the study, researchers used a new quantitative method to show that HIV in specific myeloid cells—short-lived monocytes and longer-lived monocyte-derived macrophages—can be reactivated and infect new cells. The findings, published in Nature Microbiology, suggest that ...
The Greenland Ice Sheet is close to a melting point of no return
2023-03-27
American Geophysical Union
Press Release 23-11
27 March 2023
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/the-greenland-ice-sheet-is-close-to-a-melting-point-of-no-return/
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, +1 (202) 777-7492, news@agu.org (UTC-4 hours)
Contact information for the researchers:
Dennis Höning, Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, dennis.hoening@pik-potsdam.de (UTC+1 hour)
WASHINGTON — The Greenland Ice Sheet covers 1.7 million ...
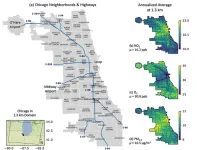
Chicago pollution varies by neighborhood
2023-03-27
New simulation combines emissions with weather and chemistry in an air-quality model
First neighborhood-scale simulation of its kind focused on Chicago tracks air quality hour by hour across areas as small as 1.3 kilometers-sized blocks
Simulation can show how pollutants move across space and time throughout the city and surrounding areas
Air pollution along highways is consistently worse than other areas, regardless of season or time of day
EVANSTON, Ill. — If you live along one of the major interstate highways running through Chicago or directly next to Lake Michigan, you are regularly exposed to more air pollution than ...
Moffitt researchers discover two-pronged approach to stimulate STING antitumor activity
2023-03-27
TAMPA, Fla. – Immunotherapies have greatly improved the outcomes of many patients with melanoma. But there is still a need for new approaches for the subset of patients who do not respond well to this type of therapy. Moffitt Cancer Center researchers are looking at new targets to help inhibit tumor development and promote antitumor immunity, one being the STING signaling pathway. In a new article published in Nature Communications, a team of Moffitt and University of Miami Miller School of Medicine investigators demonstrate that targeting the STING pathway with a combination strategy ...
Making immunizations more effective
2023-03-27
In addition to an antigen, many vaccines also contain substances, called adjuvants, which stimulate the immune system. By using computer-aided molecular design and machine learning, a Chinese research team has now developed two novel broad-spectrum adjuvants that can significantly amplify the immune response to vaccines. As reported in the journal Angewandte Chemie, they were able to enhance the effectiveness of immunization against certain forms of cancer in animal models.
Adjuvants amplify and prolong the effect of vaccine immunizations. Aluminum salts have been successfully used ...
JWST confirms giant planet atmospheres vary widely
2023-03-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – An international team of astronomers has found the atmospheric compositions of giant planets out in the galaxy do not fit our own solar system trend.
Using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the researchers discovered that the atmosphere of exoplanet HD149026b, a ‘hot Jupiter’ orbiting a star comparable to our sun, is super-abundant in the heavier elements carbon and oxygen – far above what scientists would expect for a planet of its mass.
These findings, published in “High atmospheric metal enrichment for a Saturn-mass ...
Breakthrough Brain Imaging: Experts use new microscope, AI algorithm, and voltage indicators to image electrical activity deep in the brain
2023-03-27
When studying the brain, researchers are just beginning to use a method known as voltage imaging to track neural activity in the living animal. While this approach is a promising way to better understand neuron firing, behavior, and cognition, there are limitations and risk factors. The practice requires putting a lot of light into the brain (which can lead to overheating) and only has the capacity to image ten neurons at a time.
New research from Jerry Chen, a Boston University College of Arts & Sciences assistant professor of biology, and collaborators aims to address these challenges. Published today in Nature Methods, ...
RIT researcher receives funding to improve infrastructure safety for nuclear waste disposal
2023-03-27
Researchers at Rochester Institute of Technology are investigating the combined physical effects of heat, chemical reactions, and seismic activity on concrete lining structures used to dispose of nuclear waste. Results from the work could improve nuclear waste infrastructure designs, better long-term safety management, and refine strategies to meet climate change targets.
Lu Sun, a professor in RIT’s College of Engineering Technology (CET), received a grant of nearly $500,000 from the Nuclear Regulatory Commission for “High temperature and seismic response of concrete lining structures and clay in nuclear waste disposal.” ...
NASA’s Webb measures the temperature of a rocky exoplanet
2023-03-27
An international team of researchers has used NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope to measure the temperature of the rocky exoplanet TRAPPIST-1 b. The measurement is based on the planet’s thermal emission: heat energy given off in the form of infrared light detected by Webb’s Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI). The result indicates that the planet’s dayside has a temperature of about 500 kelvins (roughly 450 degrees Fahrenheit) and suggests that it has no significant atmosphere.
This is the first detection of any form of light emitted by an exoplanet as small and as cool as the rocky planets in our own solar system. The result ...
Benefiting from orphan drug and rare pediatric disease designations for gene therapy
2023-03-27
Providing an overview of the submissions process and examples of U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) applications for Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) and Rare Pediatric Disease Designation (RPDD), a new article can help developers of gene therapies for rare genetic diseases. The article is published in the peer-reviewed journal Human Gene Therapy. Click here to read the article now.
Anne Pariser and Elizabeth Ottinger, from the National Center for Advances in Translational Sciences (NCATS), National Institutes of Health, and coauthors, describe the ODD and RPDD programs, which provide financial incentives for the development of ...
Study paves way to more efficient production of 2G ethanol using specially modified yeast strain
2023-03-27
A Brazilian study paves the way to increased efficiency of second-generation (2G) ethanol production based on the discovery of novel targets for metabolic engineering in a more robust strain of industrial yeast. An article on the study is published in the journal Scientific Reports.
The databases compiled by the authors are at the disposal of the scientific community in the repository of the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), which is a member of the Dataverse Project, an international collaborative initiative supported by FAPESP.
First-generation (1G) ethanol is produced from sources rich in carbohydrates ...
UC Davis Health collaborates with Propeller Health to improve clinical outcomes of COPD patients
2023-03-27
UC Davis Health and Propeller Health have announced a new collaboration that will offer personalized treatment for high-risk patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) aiming to improve their health outcomes.
As part of the collaboration, UC Davis Health will provide the Propeller program – including sensors, mobile app, web portal, and personalized support – to eligible patients, with eventual expansion to patients in other UC locations and UC affiliates. The sensors attach to a patient’s inhaler to capture unique signals that record events, such as ...
Largest study to date of minipuberty identifies two new patterns of the reproductive hormone, AMH, in infant girls
2023-03-27
Minipuberty is a stage of reproductive development during infancy in both sexes when reproductive hormones change and reproductive organs develop. The importance of minipuberty is not well understood but could represent an opportunity for the early identification of future reproductive conditions and enable prompt treatment. Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) is one of the hormones that changes during minipuberty, and it plays a key role in the development of reproductive organs in boys. However, the role of AMH in infant girls is less clear.
In ...
Bomb-sniffing rodents undergo ‘unusual’ reproductive transformations
2023-03-27
ITHACA, N.Y. – Female giant African pouched rats, used for sniffing out landmines and detecting tuberculosis, can undergo astounding reproductive organ transformations, according to a new study.
The paper, “Extreme plasticity of reproductive state in a female rodent,” which published March 27 in Current Biology, explores how traits once considered “fixed” in adult animals may become variable under specific pressures.
Though these rodents could have important military, biodetection and humanitarian uses, breeding them at high rates has been a challenge. ...
ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial results: The new standard of care in advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer
2023-03-27
EMBARGO DATE: Monday, March 27, 2023, 12:30 pm ET
PRESS RELEASE
ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial results:
The new standard of care in advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer
ENGOT, NSGO-CTU & GOG-Foundation proudly announce the ground-breaking results of ENGOT-EN6-NSGO/GOG-3031/RUBY trial.
The results reveal improvement in overall survival at 24 months in whole study population from 56% (CP+placebo) to 71.3% (CP+dostarlimab). “although these are interim data, we believe they are robust and will be confirmed with longer follow-up.”, said Mansoor R Mirza.
The trial is presented on 27th of March 2023 through ESMO’s ...
Human body a breeding ground for antimicrobial resistance genes
2023-03-27
The community of microbes living in and on our bodies may be acting as a reservoir for antibiotic resistance, according to new research from the Earlham Institute and Quadram Institute in Norwich.
The use of antibiotics leads to ‘collateral damage’ to the microbiome, ramping0 up the number of resistance genes being passed back and forth between strains in the microbiome.
The findings also suggest these genes spread so easily through a population that, regardless of your own health and habits, the number of resistance genes in your gut is heavily influenced by national trends in antibiotic consumption.
The rise of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) among human pathogens is widely seen ...
U of I study gives a thumbs up to carefully formulated vegan diets for dogs
2023-03-27
URBANA, Ill. – In today’s pet food market, there are products to match nearly every lifestyle, value system, and price point pet owners demand, including vegan formulations. New University of Illinois research shows at least two human-grade, lightly cooked vegan diets provide adequate nutrition for dogs.
“The trends of vegan foods and human grade foods are increasing for dogs. Because people are feeding these diets to their pets, it’s important they be tested like all other foods to make sure they're safe and ‘complete and balanced,’” ...
[1] ... [2033]
[2034]
[2035]
[2036]
[2037]
[2038]
[2039]
[2040]
2041
[2042]
[2043]
[2044]
[2045]
[2046]
[2047]
[2048]
[2049]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.