Known active ingredient as new drug candidate against “monkeypox”
2023-03-22
Nitroxoline is the name of the new drug candidate that could potentially be used to treat mpox. It was identified by scientists at Goethe University and the University of Kent as part of a multi-site study. The results of their research will now allow clinical trials to begin soon.
The current mpox outbreak is the first of this size to occur outside of Africa and also the first mpox outbreak caused by human-to-human transmission. People with immunodeficiencies are particularly at risk from the disease. Although antiviral agents have already been shown to inhibit the replication ...
Why subvariants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus accelerated the pandemic
2023-03-22
The COVID-19 pandemic has killed nearly 7 million people worldwide (1.1 million in the United States) and severely harmed many millions more, though vaccines and antiviral treatments measurably reduced the potential loss of life and health.
A Commonwealth Fund report, for example, estimated COVID-19 vaccines alone prevented more than 18 million additional hospitalizations and 3.2 million additional deaths in the U.S.
The pandemic has never been simple or easy. For example, the emergence of viral variants, in particular recent versions of the Omicron, fueled new surges of infection and disease throughout 2022 and into 2023.
“There were real concerns ...
Semiconductor lattice marries electrons and magnetic moments
2023-03-22
ITHACA, N.Y. -- A model system created by stacking a pair of monolayer semiconductors is giving physicists a simpler way to study confounding quantum behavior, from heavy fermions to exotic quantum phase transitions.
The group’s paper, “Gate-Tunable Heavy Fermions in a Moiré Kondo Lattice,” published March 15 in Nature. The lead author is postdoctoral fellow Wenjin Zhao in the Kavli Institute at Cornell.
The project was led by Kin Fai Mak, professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences, and Jie Shan, professor of applied and engineering physics in Cornell Engineering ...
Nominations sought for 2024 Watanabe Prize in Translational Research
2023-03-22
Indiana University School of Medicine is accepting nominations until May 1 for the 2024 August M. Watanabe Prize in Translational Research.
The Watanabe Prize is one of the nation’s largest and most prestigious research awards recognizing senior investigators focused on shepherding scientific discoveries into new therapies for patients. Nominees should be members of the scientific or medical communities who have demonstrated outstanding accomplishments in translational research.
The winner will receive $100,000 and will spend Sept. 18-20, 2024, in Indianapolis as a vising dignitary, sharing insights and knowledge with audiences at IU School of Medicine and its partner institutions. ...
Dr. Ekta Khurana receives grant to study prostate cancer evolution
2023-03-22
Dr. Ekta Khurana, an associate professor of physiology and biophysics at Weill Cornell Medicine, has received a 3-year, $1.2 million grant from the United States Department of Defense to investigate how prostate cancer cells evolve to become resistant to hormone-blocking therapy. This work will contribute to further understanding prostate cancer and the development of effective targeted therapies for the disease.
Prostate cancer growth is dependent on androgens – male hormones such as testosterone ­– binding ...
New UBC water treatment zaps ‘forever chemicals’ for good
2023-03-22
Engineers at the University of British Columbia have developed a new water treatment that removes “forever chemicals” from drinking water safely, efficiently – and for good.
“Think Brita filter, but a thousand times better,” says UBC chemical and biological engineering professor Dr. Madjid Mohseni, who developed the technology.
Forever chemicals, formally known as PFAS (per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances) are a large group of substances that make certain products non-stick or stain-resistant. There are more than ...
Photosynthesis ‘hack’ could lead to new ways of generating renewable energy
2023-03-22
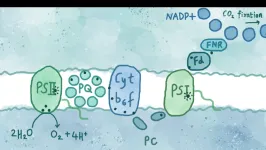
Researchers have ‘hacked’ the earliest stages of photosynthesis, the natural machine that powers the vast majority of life on Earth, and discovered new ways to extract energy from the process, a finding that could lead to new ways of generating clean fuel and renewable energy.
An international team of physicists, chemists and biologists, led by the University of Cambridge, was able to study photosynthesis – the process by which plants, algae and some bacteria convert sunlight into energy – ...
Simulated terrible drivers cut the time and cost of AV testing by a factor of one thousand
2023-03-22
Photos // Video
The push toward truly autonomous vehicles has been hindered by the cost and time associated with safety testing, but a new system developed at the University of Michigan shows that artificial intelligence can reduce the testing miles required by 99.99%.
It could kick off a paradigm shift that enables manufacturers to more quickly verify whether their autonomous vehicle technology can save lives and reduce crashes. In a simulated environment, vehicles trained by artificial intelligence perform perilous maneuvers, forcing the AV to make decisions that confront drivers only rarely on ...
Multiple substance use disorders may share inherited genetic signature
2023-03-22
A new study suggests that a common genetic signature may increase a person’s risk of developing substance use disorders, regardless of whether the addiction is to alcohol, tobacco, cannabis or opioids. The research, led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, eventually could lead to universal therapies to treat multiple substance use disorders and potentially help people diagnosed with more than one.
Published March 22 in the journal Nature Mental Health, the study’s findings are drawn from an analysis of genomic data from more than 1.1 million people of mostly European ancestry and a smaller ...
How vision begins
2023-03-22
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have deciphered the molecular processes that first occur in the eye when light hits the retina. The processes – which take only a fraction of a trillionth of a second – are essential for human sight. The study has now been published in the scientific journal Nature.
It only involves a microscopic change of a protein in our retina, and this change occurs within an incredibly small time frame: it is the very first step in our light perception and ability to see. It is also the ...
New NIH study reveals shared genetic markers underlying substance use disorders
2023-03-22
By combing through genomic data of over 1 million people, scientists have identified genes commonly inherited across addiction disorders, regardless of the substance being used. This dataset – one of the largest of its kind – may help reveal new treatment targets across multiple substance use disorders, including for people diagnosed with more than one. The findings also reinforce the role of the dopamine system in addiction, by showing that the combination of genes underlying addiction disorders was also associated with regulation of dopamine signaling.
Published ...
Surprisingly simple explanation for the alien comet 'Oumuamua's weird orbit
2023-03-22
In 2017, a mysterious comet dubbed 'Oumuamua fired the imaginations of scientists and the public alike. It was the first known visitor from outside our solar system, it had no bright coma or dust tail, like most comets, and a peculiar shape — something between a cigar and a pancake — and its small size more befitted an asteroid than a comet.
But the fact that it was accelerating away from the sun in a way that astronomers could not explain perplexed scientists, leading some to suggest that it was an alien spaceship.
Now, a University of California, Berkeley, astrochemist ...
Smaller, denser, better illuminators for computational microscopy
2023-03-22
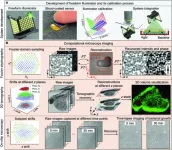
Seeking to expand the possibilities offered by programmable illumination, a group of researchers at the University of Connecticut developed a strategy for constructing and calibrating freeform illuminators offering greater flexibility for computational microscopy. Their calibration method uses a blood-coated sensor for reconstruction of light source positions. They demonstrated the use of calibrated freeform illuminators for Fourier ptychographic microscopy, 3D tomographic imaging and on-chip microscopy and used a calibrated freeform illuminator in an experiment to track bacterial growth.
The group’s research was published Feb. 20 in Intelligent Computing, a Science ...
Binghamton University reaches highest ever score for LGBTQ+ inclusion
2023-03-22
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Binghamton University, State University of New York scored a nearly perfect ranking on the latest national Campus Pride Index, which measures a university’s commitment to LGBTQ+ safety and inclusivity on campus. The University received a 4.5 out of 5, an increase from the 3.5 scores received in previous years.
Nicholas Martin, assistant director of the LGBTQ Center at Binghamton University, sees this as a reflection of the organization’s dedication and Binghamton’s real commitment to outreach.
“Our ...
Researchers make biodegradable optical components from crab shells
2023-03-22
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a process to turn crab shells into a bioplastic that can be used to make optical components known as diffraction gratings. The resulting lightweight, inexpensive gratings are biodegradable and could enable portable spectrometers that are also disposable.
“The Philippines is known for delicious seafood, but this industry is also a source of large amounts of solid waste such as discarded crab shells,” said research team leader Raphael A. Guerrero, from Ateneo de Manila University in the Philippines. “We wanted to find an alternative use for crab shell ...
Beethoven’s genome offers clues to composer’s health and family history
2023-03-22
University of Cambridge Media Release
Beethoven’s genome offers clues to composer’s health and family history
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 11:00 US ET / 15:00 UK / 16:00 CET ON WEDNESDAY 22nd MARCH 2023
International team of scientists deciphers renowned composer’s genome from locks of hair.
Study shows Beethoven was predisposed to liver disease, and infected with Hepatitis B, which – combined with his alcohol consumption – may have contributed to his death.
DNA ...
Ludwig von Beethoven’s genome sheds light on chronic health problems and cause of death
2023-03-22
In 1802, Ludwig van Beethoven asked his brothers to request that his doctor, J.A. Schmidt, describe his malady—his progressive hearing loss—to the world upon his death so that "as far as possible at least the world will be reconciled to me after my death." Now, more than two centuries later, a team of researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on March 22 have partially fulfilled his wish by analyzing DNA they lifted and pieced together from locks of his hair.
“Our primary goal was to shed light on Beethoven’s health problems, which famously include progressive hearing loss, beginning in his mid- to late-20s and eventually leading to him ...
Unusual Toxoplasma parasite strain killed sea otters and could threaten other marine life
2023-03-22
Scientists in California are raising the alarm about a newly reported form of toxoplasmosis that kills sea otters and could also infect other animals and people. Although toxoplasmosis is common in sea otters and can sometimes be fatal, this unusual strain appears to be capable of rapidly killing healthy adult otters. This rare strain of Toxoplasma hasn’t been detected on the California coast before, and may be a recent arrival, but scientists are concerned that if it contaminates the marine food chain it could potentially pose a public health risk.
“I have studied Toxoplasma infections in sea otters for 25 years — I have never ...
Sea otters killed by unusual parasite strain
2023-03-22
Four sea otters that stranded in California died from an unusually severe form of toxoplasmosis, according to a study from the California Department of Fish and Wildlife and the University of California, Davis. The disease is caused by the microscopic parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Scientists warn that this rare strain, never previously reported in aquatic animals, could pose a health threat to other marine wildlife and humans.
The preliminary findings, published in the journal Frontiers in Marine Science, note that toxoplasmosis is common in sea otters and can be fatal. This unusual strain appears to be especially virulent and capable of rapidly killing healthy adult otters.
The ...
Prevalence of statin use for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease by race, ethnicity, 10-year disease risk
2023-03-22
About The Study: Statin use for primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) was low among all race and ethnicity groups regardless of ASCVD risk, with the lowest use occurring among Black and Hispanic adults in this study of survey data representing 39.4 million adults. Improvements in access to care may promote equitable use of primary prevention statins in Black and Hispanic adults.
Authors: Joshua A. Jacobs, Pharm.D., of the Spencer Fox Eccles University of Utah School of Medicine in Salt Lake City, and Ambarish Pandey, M.D., of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, are the corresponding authors.
To ...
Cost-effectiveness of mailed home-based HPV self-sampling kits for cervical cancer screening
2023-03-22
About The Study: In this analysis involving 19,000 female participants, mailing human papillomavirus (HPV) self-sampling kits to women overdue for cervical cancer screening was cost-effective for increased screening uptake relative to usual care. These results support mailing HPV kits as an efficient outreach strategy for increasing screening rates among eligible women in U.S. health care systems.
Authors: Richard T. Meenan, Ph.D., M.P.H., M.B.A., of Kaiser Permanente Northwest in Portland, Oregon, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link ...
Sweets change our brain
2023-03-22
Chocolate bars, crisps and fries - why can't we just ignore them in the supermarket? Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Metabolism Research in Cologne, in collaboration with Yale University, have now shown that foods with a high fat and sugar content change our brain: If we regularly eat even small amounts of them, the brain learns to consume precisely these foods in the future.
Why do we like unhealthy and fattening foods so much? How does this preference develop in the brain? "Our tendency to eat high-fat and high-sugar foods, the so-called Western diet, could be innate or develop as a result of being overweight. But we think that the brain learns this preference," ...
Study determines most effective ways for hospitals to reduce medication errors
2023-03-22
A new study from researchers from Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, has shed new light on the best strategies hospitals can use for medication reconciliation, the critical and difficult task of updating and verifying a patient’s medication lists and orders, regardless of where they are in the health care system. The study, published in BMJ Quality and Safety, is a new analysis of data from the second Multi-center Medication Reconciliation ...
New invention: The oxygen-ion battery
2023-03-22
Lithium-ion batteries are ubiquitous today - from electric cars to smartphones. But that does not mean that they are the best solution for all areas of application. TU Wien has now succeeded in developing an oxygen-ion battery that has some important advantages. Although it does not allow for quite as high energy densities as the lithium-ion battery, its storage capacity does not decrease irrevocably over time: it can be regenerated and thus may enable an extremely long service life.
In addition, oxygen-ion batteries can be ...
Europe’s most powerful 7-tesla MRI machine in operation
2023-03-22
On Wednesday, 22 March 2023, at Otto von Guericke University Magdeburg, Europe’s most powerful 7-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine was formally inaugurated. The symbolic push of the button to start the high-performance MRI machine for future research work took place in the presence of the Minister of Science for Saxony-Anhalt, Prof. Dr. Armin Willingmann.
Henceforth, the MAGNETOM Terra.X Impulse Edition will enable brain functions and structures to be mapped and measured on site with a previously unachievable level of precision. “With ...
[1] ... [2030]
[2031]
[2032]
[2033]
[2034]
[2035]
[2036]
[2037]
2038
[2039]
[2040]
[2041]
[2042]
[2043]
[2044]
[2045]
[2046]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.