Galaxy clusters yield new evidence for standard model of cosmology
2023-04-03
Cosmologists have found new evidence for the standard model of cosmology – this time, using data on the structure of galaxy clusters.
In a recent study, a team led by physicists at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University made detailed measurements of the X-ray emission from galaxy clusters, which revealed the distribution of matter within them. In turn, the data helped the scientists test the prevailing theory of the structure and evolution of the universe, known as Lambda-CDM.
Getting there wasn’t an easy task, however.
Here's ...
New UH project combats food insecurity through AI
2023-04-03
One in eight Texans experiences food insecurity, according to the non-profit agency Feeding America. That means 1.4 million Texas households are food insecure, with limited or inconsistent access to nutritious food for an active, healthy life. The USDA's most recent survey on the issue reported that Texas is among the top nine U.S. states with a higher prevalence of food insecurity than the national average.
To address this issue, a University of Houston-led team is developing an artificial intelligence-based platform that can support the food charity ecosystem through data-driven technologies.
"The commitment of our team is to help our fellow ...
Generosity is left-wing
2023-04-03
Is the tendency to share with other people linked to political orientation? And in which way? In a new study, researchers from the IMT School for Advanced Studies Lucca, Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, and University of Milan Bicocca show that around the world left-leaning people are more inclined to be altruistic, in general and towards the international community. On the other hand, conservative and right people tend to be more altruistic towards their country. What might sound like the confirmation of a prejudice, is in reality a tendency observed worldwide through a ...
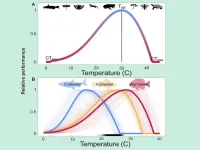
Innovative method predicts the effects of climate change on cold-blooded animals
2023-04-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In the face of a warming climate that is having a profound effect on global biodiversity and will change the distribution and abundance of many animals, a Penn State-led research team has developed a statistical model that improves estimates of habitat suitability and extinction probability for cold-blooded animals as temperatures climb.
Cold-blooded animals — a diverse group including fish, reptiles, amphibians and insects — comprise most species on Earth. The body temperature of cold-blooded animals is strongly influenced by the temperature of their environment. Because their growth, reproductive success ...
Gulf offshore oil and gas production has double the climate impact as inventories report
2023-04-03
Images
By directly measuring greenhouse gas emissions from an airplane flying over the Gulf of Mexico, a University of Michigan-led team found that the nation's largest offshore fossil fuel production basin has twice the climate warming impact as official estimates.
The work could have bearing on future energy production in the gulf, as decisions about expanding oil and gas harvesting depend on calculations of the climate impact.
While a gap between reported and measured methane emissions in the basin has been noted in the past, this study is believed ...
Squash bees flourish in response to agricultural intensification
2023-04-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — While pollinator populations of many species have plummeted worldwide, one bee species is blowing up the map with its rapid population expansion. The key to this insect’s success? Its passion for pumpkins, zucchinis, and other squashes, and the massive increase in cultivation of these crops across North America over the last 1,000 years.
A new study led by Penn State found that the squash bee (Eucera pruinosa) has evolved in response to intensifying agriculture — namely squashes in the genus ...
Strong ultralight material could aid energy storage, carbon capture
2023-04-03
HOUSTON – (April 3, 2023) – 2D materials get their strength from their atom-thin, sheetlike structure. However, stacking multiple layers of a 2D material will sap it of the qualities that make it so useful.
Rice University materials scientist Jun Lou and collaborators at the University of Maryland showed that fine-tuning interlayer interactions in a class of 2D polymers known as covalent organic frameworks (COFs) can determine the materials’ loss or retention of desirable ...
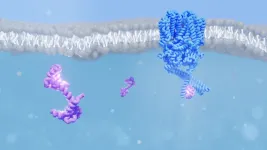
Calcium sensor helps us to see the stars
2023-04-03
Using cryo-electron microscopy and mass spectrometry, researchers from PSI have deciphered the structure of an ion channel found in the eye while it interacts with the protein calmodulin – a structure that has eluded scientists for three decades. They believe that this interaction could explain how our eyes can achieve such remarkable sensitivity to dim light. Their results are published in the journal PNAS.
As you look at the bright screen of your phone or computer, ion channels in your eyes close in response to the light. This is the final step of a biochemical ...
New research could spur broader use of 2D materials
2023-04-03
They’re considered some of the strongest materials on the planet, but tapping that strength has proved to be a challenge.
2D materials, thinner than the most delicate onionskin paper, have attracted intense interest because of their incredible mechanical properties. Those properties, however, dissipate when the materials are stacked in multiple layers, thus limiting their usefulness.
“Think of a graphite pencil,” says Teng Li, Keystone Professor at the University of Maryland’s (UMD) Department of Mechanical Engineering. “Its core is made of graphite, and graphite ...
April issues of American Psychiatric Association journals cover genetic underpinnings of common disorders, a digital intervention for depression and anxiety in youth, and more
2023-04-03
WASHINGTON, D.C., April 3, 2023 — The latest issues of three of the American Psychiatric Association’s journals, The American Journal of Psychiatry, Psychiatric Services, and The American Journal of Psychotherapy, are now available online.
The April issue of The American Journal of Psychiatry features genetic, neuroimaging, and behavioral neuroscience studies that focus on the underpinnings of mood disorders, psychotic disorders, autism, and stress-related disorders. Highlights from the issue:
Lower Availability of Mitochondrial Complex I in Anterior Cingulate Cortex in ...
Royal reception on Commonwealth Day 2023 for Sri Lankan PhD researcher
2023-04-03
A PhD researcher from the University of Huddersfield’s Global Disaster Resilience Centre (GDRC) was invited by His Majesty The King and The Queen Consort to attend a special reception at Buckingham Palace and more, in celebration of Commonwealth Day 2023.
Malith Senevirathne is a PhD student at the GDRC, within the University’s School of Applied Sciences and a Research Assistant for the CORE project (sCience and human factOr for Resilient sociEty), funded by the European Commission. As ...
Can investigators use household dust as a forensic tool?
2023-04-03
A North Carolina State University-led study found it is possible to retrieve forensically relevant information from human DNA in household dust. After sampling indoor dust from 13 households, the researchers were able to detect DNA from household residents over 90% of the time, and DNA from non-occupants 50% of the time. The work could be a way to help investigators find leads in difficult cases.
Specifically, the researchers were able to obtain single nucleotide polymorphisms, or SNPs, from the dust samples. SNPs are sites within the genome that vary between individuals – corresponding ...
Center for AIDS Research receives $15 million renewal grant from NIH
2023-04-03
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has awarded a five-year, $15.45 million grant to the San Diego Center for AIDS Research (SD CFAR) at UC San Diego, renewing support that extends back to an original establishing grant in 1994 at the height of the AIDS epidemic.
"The grant renewal represents NIAID's continued and enduring investment in our mission to be a critical regional resource in HIV research and education, to advance the discovery and development of ...
Moderate exercise safe for people with muscle pain from statins
2023-04-03
Statin therapy does not exacerbate muscle injury, pain or fatigue in people engaging in moderate-intensity exercise, such as walking, according to a study published today in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology. The findings are reassuring for people who experience muscle pain or fatigue from statins but need to engage in physical activity to keep their cholesterol levels low and their hearts healthy.
Statins have long been the gold standard for lowering LDL or “bad” cholesterol ...
NC State researchers assemble pathogen ‘tree of life’
2023-04-03
A new online tool – the first of its kind for plant pathogens – will help researchers across the globe identify, detect and monitor species of Phytophthora, which have been responsible for plant diseases ranging from the devastating 1840s Irish potato famine to sudden oak death that still plagues West Coast oak population.
The new pathogen “tree of life” provides a plethora of information about each of the more than 192 formally described species – including their evolutionary history and relationships within groups – as well as more than 30 other informally described taxa. It also includes ...
National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research marks 75th anniversary
2023-04-03
Alexandria, VA – A symposium to kick off the year-long celebration of the 75th Anniversary of the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) was featured at the 52nd Annual Meeting & Exhibition of the AADOCR, held in conjunction with the 47th Annual Meeting of the CADR. The AADOCR/CADR Annual Meeting & Exhibition took place at the Oregon Convention Center in Portland on March 15-18, 2023.
The symposium explored a brief history of the founding of NIDCR and its early activities, followed by reflections of the former directors, Harold C. Slavkin, Lawrence A. Tabak and Martha ...
AADOCR announces 2023 AADOCR Hatton Competition and Award Winners
2023-04-03
Alexandria, VA – The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) has announced the winners of the 2023 AADOCR Hatton Competition. The winners were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the AADOCR, which was held in conjunction with the 47th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), that took place on March 15, 2023.
The Hatton Award was first presented as the "Novice Award" in 1953 and is the oldest IADR/AADOCR ...
AADOCR announces Winners of the 2023 AADOCR/CADR Joseph Lister Award for New Investigators
2023-04-03
Alexandria, VA – The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) has announced the winners of the 2023 AADOCR/CADR Joseph Lister Award for New Investigators. The winners were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the AADOCR, which was held in conjunction with the 47th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), that took place on March 15, 2023.
First given in 2018, the AADOCR/CADR Joseph Lister Award for New Investigators is managed by AADOCR and supported by Johnson & Johnson Consumer, Inc. It was created to award young investigators ...
AADOCR announces Winners of the 2023 Student Competition for Advancing Dental Research Application (SCADA)
2023-04-03
Alexandria, VA – The American Association for Dental, Oral, and Craniofacial Research (AADOCR) has announced the winners of the 2023 Student Competition for Advancing Dental Research Application (SCADA). The winners were recognized during the Opening Ceremonies of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the AADOCR, which was held in conjunction with the 47th Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for Dental Research (CADR), that took place on March 15, 2023.
In 2017, AADOCR and Dentsply Sirona joined forces to co-sponsor SCADA, which was previously known as the Student Clinicians of ...
Smart watches could predict higher risk of heart failure
2023-04-03
Wearable devices such as smart watches could be used to detect a higher risk of developing heart failure and irregular heart rhythms in later life, suggests a new study led by UCL researchers.
The peer-reviewed study, published in The European Heart Journal – Digital Health, looked at data from 83,000 people who had undergone a 15-second electrocardiogram (ECG) comparable to the kind carried out using smart watches and phone devices.
The researchers identified ECG recordings containing extra heart beats which are usually benign but, if they occur frequently, are linked to conditions such as heart failure and arrhythmia ...
Cold is beneficial for healthy aging
2023-04-03
Cold activates a cellular cleansing mechanism that breaks down harmful protein aggregations responsible for various diseases associated with aging. In recent years, studies on different model organisms have already shown that life expectancy increases significantly when body temperature is lowered. However, precisely how this works has still been unclear in many areas. A research team at the University of Cologne’s CECAD Cluster of Excellence in Aging Research has now unlocked one responsible mechanism. The study ‘Cold ...
Tiny eye movements are under a surprising degree of cognitive control
2023-04-03
A very subtle and seemingly random type of eye movement called ocular drift can be influenced by prior knowledge of the expected visual target, suggesting a surprising level of cognitive control over the eyes, according to a study led by Weill Cornell Medicine neuroscientists.
The discovery, described Apr. 3 in Current Biology, adds to the scientific understanding of how vision—far from being a mere absorption of incoming signals from the retina—is controlled and directed by cognitive processes.
“These ...
Griffin Charitable Foundation donates $71,000 to the Masonic Medical Research Institute
2023-04-03
UTICA, NY –A $71,000 donation by the Griffin Charitable Foundation, based in Rome, New York, was awarded to the Masonic Medical Research Institute (MMRI) to purchase a new state-of-the-art microscope for imaging cells. “It came as wonderful news that the Foundation pledged this generous donation,” said Stephen F. Izzo, MMRI’s Development Director. “This gift will make a profound impact on our research capabilities.”
The Griffin Charitable Foundation supports not-for-profit entities serving Rome and select organizations ...
Patients with schizophrenia have favorable surgical risk, opening the door for ethical consideration of neurosurgical interventions like Deep Brain Stimulation
2023-04-03
AURORA, Colo. (April 3, 2023) – A study published in Frontiers in Surgery finds that people with schizophrenia (SZ) and schizoaffective disorder (SAD) have overall lower surgical risk than people with Parkinson’s disease, which is reassuring when considering potential surgical interventions such as Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for the treatment of SZ and SAD.
DBS, a procedure that implants electrodes in the deeper structures of the brain connected to generators in the chest, is rare in treating SZ and ...
A 21st-century remedy for missed meds
2023-04-03
HOUSTON – (April 3, 2023) – Missing crucial doses of medicines and vaccines could become a thing of the past thanks to Rice University bioengineers’ next-level technology for making time-released drugs.
“This is a huge problem in the treatment of chronic disease,” said Kevin McHugh, corresponding author of a study about the technology published online in Advanced Materials. “It’s estimated that 50% of people don't take their medications correctly. With this, you’d give them one shot, and they’d be all set for the next couple of months.”
When patients fail to take prescription medicine or take it incorrectly, the costs can ...
[1] ... [2018]
[2019]
[2020]
[2021]
[2022]
[2023]
[2024]
[2025]
2026
[2027]
[2028]
[2029]
[2030]
[2031]
[2032]
[2033]
[2034]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.