Polyamorous relationships can have as many benefits as monogamous ones, shows research
2023-04-03
Polyamorists face stigma and discrimination in their day-to-day lives, yet research shows that having a romantic relationship with more than one person at a time may offer emotional and physical benefits to all parties.
Monogamy is frequently portrayed as the ideal form of romantic love in many modern societies. From the stories we read as children, to the films and books we consume as adults – we are told that to achieve happiness we need to find our one true soulmate to share the rest of our lives with.
At the same time, states and governments offer financial, legal, and social incentives to married couples. Meanwhile men and women who deviate from these monogamous ...
Aston University establishes new independent investment company
2023-04-02
Aston University is one of eight research intensive universities in the Midlands to establish a new investment company to accelerate the commercialisation of university spinouts and early-stage IP rich businesses in the region.
Midlands Mindforge Limited has been co-founded by Aston University, University of Birmingham, Cranfield University, Keele University, University of Leicester, Loughborough University, University of Nottingham and University of Warwick, collectively Midlands Innovation.
This ambitious, patient capital ...
Outbreak of typhoid on Dutch ship traced to contaminated drinking water
2023-04-02
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Saturday 1 April
A large outbreak of typhoid on a ship in the Netherlands has been traced to contaminated water, this year's European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April) will hear.
Seventy-two cases of typhoid were confirmed in the spring 2022 outbreak on the Liberty Ann, an old cruise ship which was being ...
Extremely rare gene variants point to a potential cause of age-related macular degeneration
2023-04-01
A study from the National Eye Institute (NEI) identified rare genetic variants that could point to one of the general mechanisms driving age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a common cause of vision loss in older adults. The variants generate malformed proteins that alter the stability of the membrane attack complex (MAC), which may drive a chronic inflammatory response in the retina. The findings, published in the journal iScience, point to MAC as a potential therapeutic target to slow or prevent the development of AMD. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
There are many known genetic variants that raise or lower ...
After spinal cord injury, kinesthetic sense helps restore movement, model suggests
2023-04-01
For nearly 50 years, a jawless fish called the lamprey has interested scientists because of its remarkable ability to recover from spinal cord injuries. A new study reveals a possible technique lampreys may use to swim again, despite sparse neural regeneration.
Christina Hamlet of Bucknell University and collaborators, including Jennifer R. Morgan of the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL), used a mathematical model to demonstrate how lampreys may use body-sensing feedback to regain swimming abilities after spinal injury. The ...
Cookin' with gas: UWO professor earns patent for flameless industrial oven
2023-04-01
Pawel Olszewski, a University of Wisconsin Oshkosh associate mechanical engineering technology professor, recently was granted a U.S. patent for his flameless impingement oven, designed and built in the Teaching and Energy Research Industrial Lab (TERIL) on the Oshkosh campus.
Olszewski began the patent process back in 2019 with WiSys, the Wisconsin-based nonprofit dedicated to helping inventors protect their intellectual property, and received the news of approval in February.
Titled “flameless impingement oven,” the invention is patent number US 11,585,601 ...
This is your brain on everyday life
2023-04-01
A new study from a Washington University researcher offers fresh insights into how the brain goes to great lengths to processes and remember everyday events.
Zachariah Reagh, an assistant professor of psychological and brain sciences in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, and co-author Charan Ranganath of the University of California, Davis, used functional MRI scanners to monitor the brains of subjects watching short videos of scenes that could have come from real life. These included men and women working ...
Iguana stole my cake! and left behind a nasty surprise
2023-04-01
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Friday 31 March
**Note – the press release is available in Spanish and Portuguese, see links below**
A 3-year-old girl was infected with an unusual Mycobacterium marinum infection, that developed following an iguana bite while she was on holiday in Costa Rica, report the doctors who treated her ...
Combination therapy a promising option for advanced kidney cancer patients already treated with immunotherapy
2023-04-01
Study Title: Belzutifan plus cabozantinib for patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma previously treated with immunotherapy: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study
Publication: The Lancet Oncology, March 31, 2023, 6:30pm ET, https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(23)00097-9/fulltext
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Toni K. Choueiri, MD
Summary:
Immunotherapies, such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1, have become standard first line therapies for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer). Most patients, however, eventually experience disease progression, with no consensus on what therapy to use next. In this ...
Final Human Brain Project Summit closes with a vision for the future of digital brain research
2023-04-01
The ten-year European Flagship Human Brain Project (HBP) links brain research with computing and technology in a large-scale, interdisciplinary approach. During the HBP Summit, researchers presented the abundant scientific achievements of the project and the legacy that it will leave for the research community. With the project approaching its conclusion in September 2023, a focal point of the final HBP Summit in Marseille was the discussion of the future of digital brain research.
One of the lasting contributions of the project is the research infrastructure EBRAINS, which provides open access to advanced technologies, tools, data and services for brain research and will ...
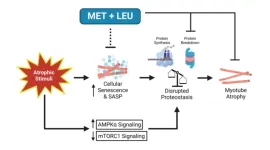
Metformin & leucine prevent cellular senescence & proteostasis disruption
2023-03-31
“Cellular senescence and disrupted proteostasis induced by myotube atrophy are prevented with low-dose metformin and leucine cocktail.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 31, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 6, entitled, “Cellular senescence and disrupted proteostasis induced by myotube atrophy are prevented with low-dose metformin and leucine cocktail.”
Aging coincides with the accumulation of senescent cells within skeletal muscle that produce inflammatory products, known as the senescence-associated secretory ...
Plastic transistor amplifies biochemical sensing signal
2023-03-31
Molecules in our body send faint biochemical signals when health issues arise
New technology boosts these signals by 1,000 times
New approach paves way for sensing signals in real-time in the body without sending blood or saliva samples to a lab
EVANSTON, Ill. — The molecules in our bodies are in constant communication. Some of these molecules provide a biochemical fingerprint that could indicate how a wound is healing, whether or not a cancer treatment is working or that a virus has invaded the body. If we could sense these signals in ...
Childhood asthma declines during COVID-19 pandemic
2023-03-31
Half as many children in the United States were diagnosed with asthma in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic compared to previous years, and Rutgers researchers think fewer colds may be part of the reason.
In a new Rutgers study, published in Respiratory Research, researchers examined the rates of new asthma diagnoses in a large commercial insurance claims database during the first year of the pandemic compared with rates of new diagnoses during the previous three years.
Using the Health Core Integrated Research ...
Study shows ketamine could be beneficial for treating brain injury in children
2023-03-31
A common anesthesia drug could be beneficial in reducing pressure inside the skull of children with traumatic brain injuries (TBI), according to a study published in Critical Care Medicine.
Ketamine, a drug that has been used for anesthesia since the 1970s, has traditionally been avoided for patients with TBI due to early studies suggesting that it could raise the pressure inside of the skull, known as intracranial pressure (ICP).
More recent studies have suggested otherwise, said lead author Michael Wolf, MD, assistant professor of Pediatrics and Neurological ...
Yak milk consumption among Mongol Empire elites
2023-03-31
Photos
For the first time, researchers have pinpointed a date when elite Mongol Empire people were drinking yak milk, according to a study co-led by a University of Michigan researcher.
By analyzing proteins found within ancient dental calculus, an international team of researchers provides direct evidence for consumption of milk from multiple ruminants, including yak. In addition, they discovered milk and blood proteins associated with both horses and ruminants. The team's results are published in Communication Biology.
The study presents novel protein findings from an elite Mongol Era cemetery ...
Hope for salamanders? Illinois study recalibrates climate change effects
2023-03-31
URBANA, Ill. – For tiny salamanders squirming skin-to-soil, big-picture weather patterns may seem as far away as outer space. But for decades, scientists have mostly relied on free-air temperature data at large spatial scales to predict future salamander distributions under climate change. The outlook was dire for the mini ecosystem engineers, suggesting near elimination of habitat in crucial areas.
Now, University of Illinois researchers are tuning into the microclimates that really matter to the imperiled amphibians and forecasting a somewhat more hopeful future.
“The ...
Engineered E. coli delivers therapeutic nanobodies to the gut
2023-03-31
BOSTON-- Humans are colonized with thousands of bacterial strains. Researchers are now focused on genetically modifying such bacteria to enhance their intrinsic therapeutic properties.
One goal is to develop smart microbes that release therapeutic payloads at sites of disease, thus maintaining therapeutic efficacy while limiting many of the side effects that can be associated with the systemic administration of conventional drugs.
Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), have engineered a strain of the probiotic Escherichia ...
New type of friction discovered in ligand-protein systems
2023-03-31
An interdisciplinary research team of the Institutes of Physical Chemistry and Physics of the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt-am-Main has discovered a new, direction-dependent friction in proteins called anisotropic friction. “Until now, nobody had observed that friction in biomolecules was dependent on direction,” says physicist Dr. Steffen Wolf of the University of Freiburg. The results have been published as cover story in the scientific journal “Nano Letters.”
Experiments on model complex of protein-ligands
Proteins constitute the microscopic machinery of cells. They perform work during their functional cycles. Accordingly, ...
New UNC Chapel Hill study quantifies $562M in financial risk from Hurricane Florence using novel modeling approach that evaluates risk of mortgage default and property abandonment
2023-03-31
When Hurricane Florence made landfall on North Carolina’s coast in 2018, it brought record rainfall causing catastrophic flooding and damages to communities across the eastern portion of the state.
Estimating the financial impacts of household flooding is complex because direct damages often snowball into other financial risks, like a decrease in property value or loss of equity. Generally, post-disaster damage assessments focus on insured and uninsured losses, but these numbers do not account for the secondary impacts to households, lenders, local governments and other stakeholders who may also share in the financial consequences if a property owner defaults ...
What is foreign exchange market or simply Forex?
2023-03-31
The Forex market, also known as the foreign exchange market or simply Forex (short for "foreign exchange"), is a decentralized global market where various currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. The primary purpose of the Forex market is to facilitate international trade and investment by allowing businesses, governments, and individuals to convert one currency into another.
Can cities make room for woodpeckers?
2023-03-31
Researchers are deploying the latest mapping techniques to identify the most important suburban habitat for North America’s largest woodpecker.
University of Cincinnati doctoral student Ruijia Hu said wildlife habitat in congested places like southwest Ohio is becoming increasingly fragmented as forests give way to new construction. Eventually, this could spell trouble to an animal with specific habitat needs like Ohio’s pileated woodpecker.
Pileated woodpeckers are crow-sized birds with colorful red crests and striking white facial stripes. They are found in forests from British Columbia to Florida. They have the ...
Study: ChatGPT has potential to help cirrhosis, liver cancer patients
2023-03-31
A new study by Cedars-Sinai investigators describes how ChatGPT, an artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot, may help improve health outcomes for patients with cirrhosis and liver cancer by providing easy-to-understand information about basic knowledge, lifestyle and treatments for these conditions.
The findings, published in the peer-reviewed journal Clinical and Molecular Hepatology, highlights the AI system’s potential to play a role in clinical practice.
“Patients with cirrhosis and/or liver cancer and their caregivers often have unmet needs and insufficient knowledge about managing and preventing complications of their disease,” ...
A healthy microbiome may prevent deadly infections in critically ill people
2023-03-31
Twenty to 50 per cent of all critically ill patients contract potentially deadly infections during their stay in the intensive care unit or in hospital after being in the ICU – markedly increasing the risk of death.
“Despite the use of antibiotics, hospital-acquired infections are a major clinical problem that persists to be a huge issue for which we don’t have good solutions,” says Dr. Braedon McDonald, MD, PhD, an intensive care physician at the Foothills Medical Centre (FMC) and assistant professor at the ...
Academic institutions receive lower financial returns from biotechnology licenses than commercial firms
2023-03-31
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
The financial terms of biotechnology licenses from academic institutions are significantly less favorable than those of comparable licenses between commercial firms according to a new study from Bentley University’s Center for Integration of Science and Industry. The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, shows that the royalties and payments to academic institutions are significantly lower than those to commercial firms for similar licenses and products at the same stages of development.
The article, titled “Comparing the economic terms of biotechnology licenses from academic institutions with those ...
Harnessing nature to promote planetary sustainability
2023-03-31
As Earth’s population grows, the demands of modern lifestyles place mounting strain on the global environment. Proposed solutions to preserve and promote planetary sustainability can sometimes prove more harmful than helpful. However, technologies that harness natural processes could be more successful.
Such technologies are the focus of the latest issue of the open access journal PLOS Biology, which features a special collection publishing March 31st of papers highlighting biology-based solutions that could be applied to reduce carbon dioxide emissions, eliminate non-degradable plastics, produce food or energy ...
[1] ... [2008]
[2009]
[2010]
[2011]
[2012]
[2013]
[2014]
[2015]
2016
[2017]
[2018]
[2019]
[2020]
[2021]
[2022]
[2023]
[2024]
... [8823]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.