Pregnant women show robust and variable immunity during COVID-19
2023-04-12
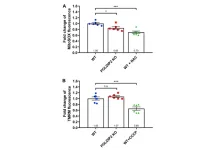
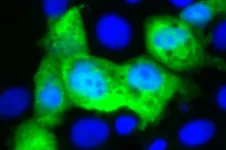
New research from the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) has found that pregnant women display a strong immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection, comparable to that of non-pregnant women.
Published in JCI Insight, the study looked at the immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in unvaccinated pregnant and non-pregnant women and found similar levels of antibodies and T and B cell responses, responsible for long-term protection.
Lead author of the paper, University of ...
Antimicrobial stewardship programs essential for preventing C. difficile in hospitals
2023-04-12
ARLINGTON, Va. (April 12, 2023) — Five medical organizations say it is essential that hospitals establish antimicrobial stewardship programs to prevent Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile) infections. These infections, linked to antibiotic use, cause difficult-to-treat diarrhea, longer hospital stays, and higher costs. C. difficile infections are fatal for more than 12,000 people in the United States each year.
Strategies to Prevent Clostridioides difficile Infections in Acute Care Hospitals: 2022 Update, gives evidence-based, ...
Mitochondria power-supply failure may cause age-related cognitive impairment
2023-04-12
LA JOLLA—(April 12, 2023) Brains are like puzzles, requiring many nested and codependent pieces to function well. The brain is divided into areas, each containing many millions of neurons connected across thousands of synapses. These synapses, which enable communication between neurons, depend on even smaller structures: message-sending boutons (swollen bulbs at the branch-like tips of neurons), message-receiving dendrites (complementary branch-like structures for receiving bouton messages), and power-generating mitochondria. To create a cohesive brain, all these pieces must be accounted for.
However, in the aging brain, these ...
Education and peer support cut binge-drinking by National Guard members in half, study shows
2023-04-12
A new study shows promise for reducing risky drinking among Army National Guard members over the long term, potentially improving their health and readiness to serve.
The number of days each month that Guard members said they had been binge-drinking dropped by up to half, according to the new findings by a University of Michigan team published in the journal Addiction.
The drop happened over the course of a year among Guard members who did multiple brief online education sessions designed for members of the military, and among those who did an initial online education session followed by supportive ...
World’s biggest cumulative logjam, newly mapped in the Arctic, stores 3.4 million tons of carbon
2023-04-11
WASHINGTON — Throughout the Arctic, fallen trees make their way from forests to the ocean by way of rivers. Those logs can stack up as the river twists and turns, resulting in long-term carbon storage. A new study has mapped the largest known woody deposit, covering 51 square kilometers (20 square miles) of the Mackenzie River Delta in Nunavut, Canada, and calculated that the logs store about 3.4 million tons (about 3.1 million metric tons) of carbon.
“To put that in perspective, that’s about two and a half million ...
Life cycle assessment can help with the transition to the circular economy
2023-04-11
According to Bening Mayanti's doctoral dissertation at the University of Vaasa, the use of life cycle assessment combined with economic models can help companies to take steps toward the circular economy.
– We often hear claims about some solutions being circular, sustainable, or green. Instead of blindly accepting those claims, we should ask justifications, ‘How so?’ says Mayanti, who publicly defended her dissertation on Wednesday, 5 April.
Before deciding on circular economy solutions and building supply chains, it is worth doing a careful analysis. ...
From waste to wonder: unlocking nature’s biochemical recycling secrets
2023-04-11
A new perspective published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology uncovers a previously unknown biochemical recycling process in animals. The authors review a flurry of recent papers demonstrating that animals extensively recycle biochemical waste to produce novel chemicals that play key roles in biology, from regulating behavior to development and aging.
These studies show that the genes previously thought to code for carboxylesterases, enzymes that hydrolyze esters, actually play a pivotal role in assembling a wide range of new metabolites from building blocks generally considered “cellular waste.” Surprisingly, the so-called carboxylesterases were found to contribute ...
Yossi Sheffi on AI and the future of the supply chain
2023-04-11
Global supply chains are immense feats of technological and organizational sophistication. They are also, as the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic showed, vulnerable to unexpected developments. Will that change as artificial intelligence becomes a bigger part of supply chains? And what will happen to workers in the process?
MIT Professor Yossi Sheffi explores these topics in a new book, “The Magic Conveyor Belt: AI, Supply Chains, and the Future of Work,” published by MIT’s CTL Media. Sheffi, the Elisha Gray II Professor of Engineering ...
Tax credit tool tracks EV savings
2023-04-11
Oak Ridge National Laboratory researchers have developed an online resource to help consumers understand the electric vehicle tax credits available through the Inflation Reduction Act.
Located on the Department of Energy’s fueleconomy.gov website, the tool shows eligible vehicle models along with the corresponding federal tax credit.
The new clean vehicle tax credit is for purchases of all-electric, plug-in hybrid electric and fuel cell electric vehicles in 2023 and beyond. A separate credit is available for eligible used vehicles purchased in 2023 or after. Information on credits for vehicles purchased before ...
Knockout of AMD-associated gene POLDIP2 reduces mitochondrial superoxide in retinal cells
2023-04-11
“To our knowledge, this is the first functional study of POLDIP2 in retinal cells to understand its potential role in AMD.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 11, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 6, entitled, “Knockout of AMD-associated gene POLDIP2 reduces mitochondrial superoxide in human retinal pigment epithelial cells.”
Genetic and epidemiologic studies have significantly advanced our ...
New approach targets norovirus, world’s leading cause of foodborne infection
2023-04-11
Every year, norovirus causes hundreds of millions of cases of food poisoning — and the deaths of at least 50,000 children — yet there exists no real way to control it. The virus has proven exceptionally difficult to study in the lab, and scientists have struggled to develop effective vaccines and drugs.
A new study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis describes a creative way to make a vaccine against norovirus by piggybacking on the highly effective vaccines for rotavirus, an unrelated virus that also causes diarrhea.
The ...
Electrification push will have enormous impacts on critical metals supply chain
2023-04-11
ITHACA, N.Y. – The demand for battery-grade lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese and platinum will climb steeply as vehicle electrification speeds up and nations work to reduce greenhouse gas emissions through mid-century. This surge in demand will also create a variety of economic and supply-chain problems, according to new Cornell University research published in Nature Communications.
In the new paper, senior author Fengqi You, professor in energy systems engineering, and his colleagues examined 48 countries that are committed to playing a strong role in electrifying transportation, including the U.S., China and India.
Under ...
Takeda licenses small molecule developed by Krembil Brain Institute researchers, targeting tau protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease
2023-04-11
As announced today in a press release by biotechnology company Treventis, global pharmaceutical company Takeda has agreed to exclusively license a group of small molecules that target tau – a protein in which misfolding and aggregation are believed to be a cause of Alzheimer’s disease.
The molecules were developed by the team at Treventis, building upon the Alzheimer’s & neurodegenerative research expertise of Dr. Donald Weaver’s lab at UHN.
“There are currently no effective drugs out there that target tau in the brain,” says Dr. Donald Weaver, Senior ...
Mount Sinai researchers discover novel receptors for SARS-CoV-2 and their age-dependent expression, providing new insights for public health
2023-04-11
New York, NY (April 11, 2023) – A study led by Mount Sinai researchers Dr. Bin Zhang, the Willard T.C. Johnson Research Professor of Neurogenetics, and Dr. Christian Forst, an Associate Professor in the Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences, have identified potential novel receptors for SARS-CoV-2 and unveiled their tissue-specific and age-dependent expression. The findings were published on March 23 in the Federation of European Biochemical Societies Letters.
The study's multiscale network analysis suggests that SARS-CoV-2 utilizes multiple novel receptors, such as the TYOBP receptor CD300e, to facilitate ...
Perfume component helps lure male moth pests
2023-04-11
North Carolina State University researchers have shown that adding a small amount of a chemical used in perfumes – nonanal – to a two-chemical combination of other sex pheromones helped increase the cocktail’s effectiveness in mimicking female fall armyworm “come hither” calls to males.
The findings could eventually help farmers better detect, monitor and control fall armyworm populations, which negatively affect some 350 plant species – including crops like corn and cotton as well as turfgrass and other cultivated grasses.
“Nonanal is emitted ...
Genomic surveillance identifies global strain of emerging wheat disease fungus
2023-04-11
Pests and diseases may reduce global wheat yields by over 20%. A study published April 11th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Sergio Latorre at University College London, UK and colleagues suggest that genomic surveillance may be an effective disease management tool with the ability to trace lineages of emerging crop diseases, and to identify genetic traits for breeding disease-resistant lines.
Wheat crops across the globe are threatened by wheat blast, an emerging fungal disease. However, disease-management strategies have been unsuccessful. In order to better understand ...
$9.5M to fund cross-disciplinary chronic fatigue research
2023-04-11
ITHACA, N.Y. -- A Cornell multidisciplinary research center that studies chronic fatigue syndrome has received a five-year, $9.5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease – funding that will enable experts from disparate fields to work together on the mysterious and debilitating condition.
The Cornell Center for Enervating Neuroimmune Disease, established in 2017, ultimately seeks to understand the biological ...
Study offers insights into how COVID variants escape immune system ‘killers’
2023-04-11
New Haven, Conn. — Omicron subvariants of SARS-CoV-2 — the virus behind COVID-19 — have shown an uncanny knack for evading antibodies produced either by vaccines or exposure to earlier versions of the virus, leading to many breakthrough infections. However, in order to sicken people, these viral variants must also avoid “killer” T cells, immune cells that are unleashed when the immune system detects foreign pathogens.
A new Yale study published April 10 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences reveals new insights into how these Omicron variants are able to avoid destruction by these T cells.
For the study, ...
Untangling the mystery of sleep
2023-04-11
At a glance
Dragana Rogulja is using fruit flies and mice to explore tantalizing questions about sleep.
Her research delves into why sleep is necessary for survival, and how the sleeping brain disconnects from the world.
Rogulja’s research has identified a critical connection between the brain and the gut.
If translated into humans, the results of her work could lead to new ways for improving sleep and reducing damage from sleep deprivation.
Sleep is one of the most essential human activities — so essential, in fact, that if we don’t get enough sleep for even one ...
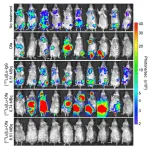
New nuclear medicine therapy cures human non-hodgkin lymphoma in preclinical model
2023-04-11
Reston, VA—A new nuclear medicine therapy can cure human non-Hodgkin lymphoma in an animal model, according to research published in the April issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine. A single dose of the radioimmunotherapy, [177Lu]Lu-ofatumumab, was found to quickly eliminate tumor cells and extend the life of mice injected with cancerous cells for more than 221 days (the trial endpoint), compared to fewer than 60 days for other treatments and just 19 days in untreated control mice.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a common blood malignancy. The ...
Preprints are the rational choice for satisfying the Nelson Memo requirements
2023-04-11
Preprints allow for free and rapid dissemination of publicly funded research results, and federal agencies should include them in their public access policies as they look to meet the requirements of the US Office of Science and Technology Policy “Nelson Memorandum.” arXiv–the e-print repository for physics, math, computer science and other disciplines–and bioRxiv and medRxiv–preprint servers for biology and the health sciences–address the unique role of preprints and the value they bring as they release their responses to the Nelson Memo.
“US ...
UTA research uses seawater to remove carbon dioxide from atmosphere
2023-04-11
A University of Texas at Arlington researcher is working to create a process that uses seawater to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Erika La Plante, assistant professor in the Materials Science and Engineering Department, received a $125,000 subgrant from the University of California–Los Angeles (UCLA) as part of a larger Department of Energy Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy grant for the work.
The UCLA team developed a continuous electrolytic pH pump that uses high-alkalinity seawater with high concentrations of carbon dioxide and cations ...
Daily statin reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease in people living with HIV, large NIH study finds
2023-04-11
A National Institutes of Health (NIH) clinical trial was stopped early because a daily statin medication was found to reduce the increased risk of cardiovascular disease among people living with HIV in the first large-scale clinical study to test a primary cardiovascular prevention strategy in this population. A planned interim analysis of data from the Randomized Trial to Prevent Vascular Events in HIV (REPRIEVE) study found that participants who took pitavastatin calcium, a daily statin, lowered their risk of major adverse cardiovascular ...
Lightning strike creates phosphorus material for the first time on Earth
2023-04-11
TAMPA, Fla. (April 11, 2023) – After lightning struck a tree in a New Port Richey neighborhood, a University of South Florida professor discovered the strike led to the formation of a new phosphorus material. It was found in a rock – the first time in solid form on Earth – and could represent a member of a new mineral group.
“We have never seen this material occur naturally on Earth – minerals similar to it can be found in meteorites and space, but we've never seen this exact material anywhere,” said geoscientist Matthew Pasek.
In a recent study published in Communications Earth & Environment, Pasek examines ...
US natural gas pipelines vulnerable to electric outages
2023-04-11
Natural gas supplies 32% of all primary energy in the United States, its share of electricity generation having nearly doubled from 2008 to 2021. The cross-country natural gas pipeline system used to be powered mainly by natural gas, but recently has switched in places to electric power. The natural gas pipeline system has generally been much more reliable than the electric power system. The new dependence on electricity has created a vulnerability during hurricanes and other events that can take out electric power, since lack of natural gas may in turn cause gas-powered electric ...
[1] ... [2001]
[2002]
[2003]
[2004]
[2005]
[2006]
[2007]
[2008]
2009
[2010]
[2011]
[2012]
[2013]
[2014]
[2015]
[2016]
[2017]
... [8836]
Press-News.org - Free Press Release Distribution service.